codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution
D. Mike and distribution
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mike has always been thinking about the harshness of social inequality. He's so obsessed with it that sometimes it even affects him while solving problems. At the moment, Mike has two sequences of positive integers A = [a1, a2, ..., an] andB = [b1, b2, ..., bn] of length n each which he uses to ask people some quite peculiar questions.
To test you on how good are you at spotting inequality in life, he wants you to find an "unfair" subset of the original sequence. To be more precise, he wants you to select k numbers P = [p1, p2, ..., pk] such that 1 ≤ pi ≤ n for 1 ≤ i ≤ k and elements in Pare distinct. Sequence P will represent indices of elements that you'll select from both sequences. He calls such a subset P"unfair" if and only if the following conditions are satisfied: 2·(ap1 + ... + apk) is greater than the sum of all elements from sequence A, and 2·(bp1 + ... + bpk) is greater than the sum of all elements from the sequence B. Also, k should be smaller or equal to 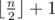 because it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
because it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
Mike guarantees you that a solution will always exist given the conditions described above, so please help him satisfy his curiosity!
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mike has always been thinking about the harshness of social inequality. He's so obsessed with it that sometimes it even affects him while solving problems. At the moment, Mike has two sequences of positive integers A = [a1, a2, ..., an] andB = [b1, b2, ..., bn] of length n each which he uses to ask people some quite peculiar questions.
To test you on how good are you at spotting inequality in life, he wants you to find an "unfair" subset of the original sequence. To be more precise, he wants you to select k numbers P = [p1, p2, ..., pk] such that 1 ≤ pi ≤ n for 1 ≤ i ≤ k and elements in Pare distinct. Sequence P will represent indices of elements that you'll select from both sequences. He calls such a subset P"unfair" if and only if the following conditions are satisfied: 2·(ap1 + ... + apk) is greater than the sum of all elements from sequence A, and 2·(bp1 + ... + bpk) is greater than the sum of all elements from the sequence B. Also, k should be smaller or equal to 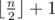 because it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
because it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
Mike guarantees you that a solution will always exist given the conditions described above, so please help him satisfy his curiosity!
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of elements in the sequences.
On the second line there are n space-separated integers a1, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — elements of sequence A.
On the third line there are also n space-separated integers b1, ..., bn (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — elements of sequence B.
On the first line output an integer k which represents the size of the found subset. k should be less or equal to 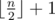 .
.
On the next line print k integers p1, p2, ..., pk (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — the elements of sequence P. You can print the numbers in any order you want. Elements in sequence P should be distinct.
5
8 7 4 8 3
4 2 5 3 7
3
1 4 5
解题思路:
这道题题意有点难描述,而且不难看懂就不多说了。
这道题难点就在于有两个数组,难以判断。 所以我们这里先讨论只有一个数组时的情况,如何使取得的数字大于剩下的?其实只要两两之间相互比较,取最大的,当序列长度为奇数时,我们可以先提出
其中一个,然后将剩余的两两比较,依旧必大于剩余的。
单个数组的问题讨论完了,然后分析两个数组,这里我们可以将其中一个数组排序用另一个数组记录排序结果(下标)id[],对下一个数组进行排序,这么说有点抽象,我把具体实现情况写一下
a[0] = 8 ,a[1] = 7,a[2] = 4, a[3] = 8,a[4] = 3;
b[0] = 4,a[1] = 2,a[2] = 5, a[3] = 3,a[4] = 7;
id[0] = 0,id[1] = 1,id[2] = 2,id[3] = 3,id[4] = 4;
先将a数组排序从大到小并用id数组记录结果(下标)
a数组排序结果 : a0 a3 a1 a2 a4
用id数组记录:id[0] = 0,id[1] = 3,id[2] = 1,id[3] = 2,id[4] = 4;
这里可以用id对b数组进行排序,因为现在id储存的是a从大到小的顺序,按这个顺序排序a必大于剩余的,
排序过程: 因为是奇数,先取出第一个 b[0] 然后取 max(b[3],b[1]),max(b[2],b[4]),这样就可以得出满足两个数组的下标序列
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int Max = +;
int m,id[Max];
long long a[Max],b[Max];
inline bool cmp(const int &x,const int &y)
{
return a[x] > a[y];
}
int main()
{
int i;
cin>>m;
for(i=;i<m;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(i=;i<m;i++) cin>>b[i];
for(i=;i<m;i++) id[i] = i;
sort(id,id+m,cmp);
int n = m/ + ;
cout<<n<<endl;
cout<<id[]+;
for(i=;i<m-;i+=){
if(b[id[i]]>b[id[i+]])
cout<<" "<<id[i]+;
else
cout<<" "<<id[i+]+;
}
if(m%==)
cout<<" "<<id[m-]+;
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution的更多相关文章
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution(贪心+思维)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/798/problem/D 题意:给出两串长度为n的数组a,b,然后要求长度小于等于n/2+1的p数组是的以p为下表a1-ap的和 ...
- codeforces 798 C. Mike and gcd problem(贪心+思维+数论)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/798/problem/C 题意:给出一串数字,问如果这串数字的gcd大于1,如果不是那么有这样的操作,删除ai, ai + 1 ...
- 【codeforces 798D】Mike and distribution
[题目链接]:http://codeforces.com/contest/798/problem/D [题意] 让你选一个下标集合 p1,p2,p3..pk 使得2*(a[p1]+a[p2]+..+a ...
- Codeforces 798 B. Mike and strings-String的find()函数
好久好久好久之前的一个题,今天翻cf,发现这个题没过,补一下. B. Mike and strings time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per t ...
- Codeforces 798D Mike and distribution(贪心或随机化)
题目链接 Mike and distribution 题目意思很简单,给出$a_{i}$和$b_{i}$,我们需要在这$n$个数中挑选最多$n/2+1$个,使得挑选出来的 $p_{1}$,$p_{2} ...
- D. Mike and distribution 首先学习了一个玄学的东西
http://codeforces.com/contest/798/problem/D D. Mike and distribution time limit per test 2 seconds m ...
- CF410div2 D. Mike and distribution
/* CF410div2 D. Mike and distribution http://codeforces.com/contest/798/problem/D 构造 题意:给出两个数列a,b,求选 ...
- #410div2D. Mike and distribution
D. Mike and distribution time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
- Codeforces 547C/548E - Mike and Foam 题解
目录 Codeforces 547C/548E - Mike and Foam 题解 前置芝士 - 容斥原理 题意 想法(口胡) 做法 程序 感谢 Codeforces 547C/548E - Mik ...
随机推荐
- TCP/IP协议---ARP协议
ARP协议 以下就默认在以太网类型的网络. 这个协议的作用是通过ip地址(32bit)找到硬件地址(48bit).顺便提一下:在一个局域网里,大家常见的设备交换机,交换机上的主机在互相通信时,实际用的 ...
- CF1039E Summer Oenothera Exhibition 贪心、根号分治、倍增、ST表
传送门 感谢这一篇博客的指导(Orzwxh) $PS$:默认数组下标为$1$到$N$ 首先很明显的贪心:每一次都选择尽可能长的区间 不妨设$d_i$表示在取当前$K$的情况下,左端点为$i$的所有满足 ...
- 基于HTML5 Canvas 实现地铁站监控
伴随国内经济的高速发展,人们对安全的要求越来越高.为了防止下列情况的发生,您需要考虑安装安防系统: 提供证据与线索:很多工厂银行发生偷盗或者事故相关机关可以根据录像信息侦破案件,这个是非常重要的一个线 ...
- 牛客OI赛制测试赛-序列-模拟
哇这道题好坑啊,可能是我太菜了 题意就是叫把一个连续序列分成K组,使得每个组的和都相等 我最开始的想法是由于要分成K组,那我们知道,每组一定有sum(a[i])/k这样我们只需要每次当num==sum ...
- linux下配置squid 服务器,最简单使用方式
https://blog.csdn.net/unixtech/article/details/53185297 squid 查看命中率 https://blog.csdn.net/cnbird2008 ...
- git使用(2)
1.远程仓库 a SSHKEY 第1步:创建SSH Key.在用户主目录下,看看有没有.ssh目录,如果有,再看看这个目录下有没有id_rsa和id_rsa.pub这两个文件,如果已经有了,可直接跳到 ...
- 代码规范与复审2——个人博客作业week
一.关于编程规范的重要性论证 1.不支持. 1)编程规范有利于自己提高编程效率和编程质量.编码是程序员的职责,一个好的信息技术产品必然有高质量的代码,高质量的代码首先 一点它必须遵守某种编程规范.如果 ...
- 软件工程启程篇章:结对编程和进阶四则运算(197 & 199)
0x01 :序言:无关的事 I wrote a sign called "Dead End" in front of myself, but love crossed it wit ...
- 【SE】Week17 : 软件工程课程总结
软工课程总结 总算结束了一个学期大部分的事情,可以静下心来写篇软工的总结了. 在本学期的软工课程中,我担任的角色是Chronos团队的PM兼开发人员.在课程之前,我认为PM的角色应该还蛮轻松的,无非 ...
- 读书笔记(chapter7)
第七章 链接 链接是将各种代码和数据部分收集起来并且组合成为一个单一文件的过程.1.这个文件可被加载到存储器并执行:2.也可以执行于加载时,也就是在程序被加载器加载到存储器并执行:3.甚至可以执行于运 ...
