DLX精确覆盖与重复覆盖模板题
hihoCoder #1317 : 搜索四·跳舞链
原题地址:http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1317
时间限制:10000ms
单点时限:1000ms
内存限制:256MB
描述
小Ho最近遇到一个难题,他需要破解一个棋局。
棋局分成了n行,m列,每行有若干个棋子。小Ho需要从中选择若干行使得每一列有且恰好只有一个棋子。
比如下面这样局面:
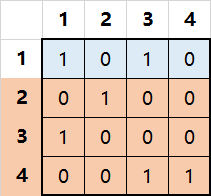
其中1表示放置有棋子的格子,0表示没有放置棋子。
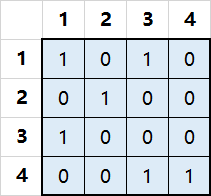
对于上面这个问题,小Ho经过多次尝试以后得到了解为选择2、3、4行就可以做到。
但是小Ho觉得自己的方法不是太好,于是他求助于小Hi。
小Hi:小Ho你是怎么做的呢?
小Ho:我想每一行都只有两种状态,选中和未被选中。那么我将选中视为1,未选中视为0。则每一种组合恰好对应了一个4位的01串,也就是一个4位的二进制数。
小Hi:恩,没错。
小Ho:然后我所做的就是去枚举每一个二进制数然后再来判定是否满足条件。
小Hi:小Ho你这个做法本身没什么问题,但是对于棋盘行数再多一点的情况就不行了。
小Ho:恩,我也这么觉得,那你有什么好方法么?
小Hi:我当然有了,你听我慢慢道来。
输入
第1行:1个正整数t,表示数据组数,1≤t≤10。
接下来t组数据,每组的格式为:
第1行:2个正整数n,m,表示输入数据的行数和列数。2≤n,m≤100。
第2..n+1行:每行m个数,只会出现0或1。
输出
第1..t行:第i行表示第i组数据是否存在解,若存在输出"Yes",否则输出"No"。
样例输入
2
4 4
1 1 0 1
0 1 1 0
1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1
4 4
1 0 1 0
0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0
0 0 1 1
样例输出
No
Yes
DLX精确覆盖
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath> #define LL long long using namespace std; const int maxnode = ; //最多多少个‘1’
const int MaxM = ;
const int MaxN = ; struct DLX
{
int n,m,SIZE;
int U[maxnode],D[maxnode],R[maxnode],L[maxnode],Row[maxnode],Col[maxnode];//L,R,D,U四个数组记录某节点上下左右邻居
int H[MaxN], S[MaxM];//H记录排头,S记录某列有多少个节点
int ansd, ans[MaxN];
void init(int _n,int _m)
{
n = _n;
m = _m;
for(int i = ;i <= m;i++)
{
S[i] = ;
U[i] = D[i] = i;
L[i] = i-;
R[i] = i+;
}
R[m] = ; L[] = m;
SIZE = m;
for(int i = ;i <= n;i++)
H[i] = -;
}
void Link(int r,int c)
{
++S[Col[++SIZE]=c];
Row[SIZE] = r;
D[SIZE] = D[c];
U[D[c]] = SIZE;
U[SIZE] = c;
D[c] = SIZE;
if(H[r] < )H[r] = L[SIZE] = R[SIZE] = SIZE;
else
{
R[SIZE] = R[H[r]];
L[R[H[r]]] = SIZE;
L[SIZE] = H[r];
R[H[r]] = SIZE;
}
}
void exact_Remove(int c)
{
L[R[c]] = L[c]; R[L[c]] = R[c];
for(int i = D[c];i != c;i = D[i])
for(int j = R[i];j != i;j = R[j])
{
U[D[j]] = U[j];
D[U[j]] = D[j];
--S[Col[j]];
}
}
void repeat_remove(int c) {
for(int i = D[c]; i != c; i = D[i])
L[R[i]] = L[i], R[L[i]] = R[i];
}
void repeat_resume(int c) {
for(int i = U[c]; i != c; i = U[i])
L[R[i]] = R[L[i]] = i;
} int f() { //估价函数。
bool vv[MaxM];
int ret = , c, i, j;
for(c = R[]; c != ; c = R[c]) vv[c] = ;
for(c = R[]; c != ; c = R[c])
if(vv[c]) {
++ret, vv[c] = ;
for(i = D[c]; i != c; i = D[i])
for(j = R[i]; j != i; j = R[j])
vv[Col[j]] = ;
}
return ret;
} void repeat_dance(int d) {
if(d + f() >= ansd) return; //估价函数剪枝,A*搜索
if(R[] == ) {
if(d < ansd) ansd = d;
return;
}
int c = R[], i, j;
for(i = R[]; i; i = R[i])
if(S[i] < S[c]) c = i;
for(i = D[c]; i != c; i = D[i]) {
repeat_remove(i);
for(j = R[i]; j != i; j = R[j]) repeat_remove(j);
repeat_dance(d + );
for(j = L[i]; j != i; j = L[j]) repeat_resume(j);
repeat_resume(i);
}
}
void exact_resume(int c)
{
for(int i = U[c];i != c;i = U[i])
for(int j = L[i];j != i;j = L[j])
++S[Col[U[D[j]]=D[U[j]]=j]];
L[R[c]] = R[L[c]] = c;
}
//d为递归深度
bool exact_Dance(int d)
{
if(R[] == )
{
ansd = d;
return true;
}
int c = R[];
for(int i = R[];i != ;i = R[i])
if(S[i] < S[c])
c = i;
exact_Remove(c);
for(int i = D[c];i != c;i = D[i])
{
ans[d] = Row[i];
for(int j = R[i]; j != i;j = R[j]) exact_Remove(Col[j]);
if(exact_Dance(d+))return true;
for(int j = L[i]; j != i;j = L[j]) exact_resume(Col[j]);
}
exact_resume(c);
return false;
}
}; DLX g;
int main()
{
int n,m;
int t;
cin>>t; while( t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
g.init(n,m);
for(int i = ;i <= n;i++)
{
int num;
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&num);
if(num==) g.Link(i,j);
}
}
if(!g.exact_Dance())printf("No\n");
else
printf("Yes\n");
}
return ;
}
HDU 3498 whosyourdaddy
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3498
whosyourdaddyTime Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others) Problem sevenzero Input There Output One Sample 5 4 1 2 1 3 2 4 4 5 6 4 1 2 1 3 1 4 4 5 Sample Output 2 3 Author sevenzero Source 2010 ACM-ICPC Multi-University Training Contest(7)——Host by HIT |
DLX重复覆盖
n个敌对单元,m对单元互相相邻,建图的邻接矩阵,DLX。
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath> #define LL long long using namespace std; const int maxnode = ; //最多多少个1
const int MaxM = ;
const int MaxN = ; struct DLX
{
int n,m,SIZE;
int U[maxnode],D[maxnode],R[maxnode],L[maxnode],Row[maxnode],Col[maxnode];//L,R,D,U四个数组记录某节点上下左右邻居
int H[MaxN], S[MaxM];//H记录行头,S记录某列有多少个节点
int ansd, ans[MaxN];
void init(int _n,int _m)
{
n = _n;
m = _m;
for(int i = ;i <= m;i++)
{
S[i] = ;
U[i] = D[i] = i;
L[i] = i-;
R[i] = i+;
}
R[m] = ; L[] = m;
SIZE = m;
for(int i = ;i <= n;i++)
H[i] = -;
}
void Link(int r,int c)
{
++S[Col[++SIZE]=c];
Row[SIZE] = r;
D[SIZE] = D[c];
U[D[c]] = SIZE;
U[SIZE] = c;
D[c] = SIZE;
if(H[r] < )H[r] = L[SIZE] = R[SIZE] = SIZE;
else
{
R[SIZE] = R[H[r]];
L[R[H[r]]] = SIZE;
L[SIZE] = H[r];
R[H[r]] = SIZE;
}
}
void exact_Remove(int c)
{
L[R[c]] = L[c]; R[L[c]] = R[c];
for(int i = D[c];i != c;i = D[i])
for(int j = R[i];j != i;j = R[j])
{
U[D[j]] = U[j];
D[U[j]] = D[j];
--S[Col[j]];
}
}
void repeat_remove(int c) {
for(int i = D[c]; i != c; i = D[i])
L[R[i]] = L[i], R[L[i]] = R[i];
}
void repeat_resume(int c) {
for(int i = U[c]; i != c; i = U[i])
L[R[i]] = R[L[i]] = i;
} int f() { //估价函数。
bool vv[MaxM];
int ret = , c, i, j;
for(c = R[]; c != ; c = R[c]) vv[c] = ;
for(c = R[]; c != ; c = R[c])
if(vv[c]) {
++ret, vv[c] = ;
for(i = D[c]; i != c; i = D[i])
for(j = R[i]; j != i; j = R[j])
vv[Col[j]] = ;
}
return ret;
} void repeat_dance(int d) {
if(d + f() >= ansd) return; //估价函数剪枝,A*搜索
if(R[] == ) {
if(d < ansd) ansd = d;
return;
}
int c = R[], i, j;
for(i = R[]; i; i = R[i])
if(S[i] < S[c]) c = i;
for(i = D[c]; i != c; i = D[i]) {
repeat_remove(i);
for(j = R[i]; j != i; j = R[j]) repeat_remove(j);
repeat_dance(d + );
for(j = L[i]; j != i; j = L[j]) repeat_resume(j);
repeat_resume(i);
}
}
void exact_resume(int c)
{
for(int i = U[c];i != c;i = U[i])
for(int j = L[i];j != i;j = L[j])
++S[Col[U[D[j]]=D[U[j]]=j]];
L[R[c]] = R[L[c]] = c;
}
//d为递归深度
bool exact_Dance(int d)
{
if(R[] == )
{
ansd = d;
return true;
}
int c = R[];
for(int i = R[];i != ;i = R[i])
if(S[i] < S[c])
c = i;
exact_Remove(c);
for(int i = D[c];i != c;i = D[i])
{
ans[d] = Row[i];
for(int j = R[i]; j != i;j = R[j]) exact_Remove(Col[j]);
if(exact_Dance(d+))return true;
for(int j = L[i]; j != i;j = L[j]) exact_resume(Col[j]);
}
exact_resume(c);
return false;
}
}; DLX dlx;
int main()
{
int n,m;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
dlx.init(n,n);
while(m--)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
dlx.Link(a,b);
dlx.Link(b,a);
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)dlx.Link(i,i);
dlx.ansd=0x3f3f3f;
dlx.repeat_dance();
printf("%d\n",dlx.ansd);
}
return ;
}
DLX精确覆盖与重复覆盖模板题的更多相关文章
- SPOJ 1771&&DLX精确覆盖,重复覆盖
DLX的题,做过这题才算是会吧. 这道题转化成了精确覆盖模型来做,一开始,只是单纯的要覆盖完行列和斜线,WA. 后来醒悟了,不能这样,只要覆盖全部行或列即可.虽然如此,但某些细节地方很关键不能考虑到. ...
- DLX 舞蹈链 精确覆盖 与 重复覆盖
精确覆盖问题:给定一个由0-1组成的矩阵,是否能找到一个行的集合,使得集合中每一列都恰好包含一个1 还有重复覆盖问题 dancing links 是 一种数据结构,用来优化搜索,不算是一种算法.(双向 ...
- HDU 3957 Street Fighter (最小支配集 DLX 重复覆盖+精确覆盖 )
DLX经典题型,被虐惨了…… 建一个2*N行3*N列的矩阵,行代表选择,列代表约束.前2*N列代表每个人的哪种状态,后N列保证每个人至多选一次. 显然对手可以被战胜多次(重复覆盖),每个角色至多选择一 ...
- HDU 2295 Radar dancing links 重复覆盖
就是dancing links 求最小支配集,重复覆盖 精确覆盖时:每次缓存数据的时候,既删除行又删除列(这里的删除列,只是删除表头) 重复覆盖的时候:只删除列,因为可以重复覆盖 然后重复覆盖有一个估 ...
- HDU 3957 Street Fighter(搜索、DLX、重复覆盖+精确覆盖)
很久以前就看到的一个经典题,一直没做,今天拿来练手.街霸 给n<=25个角色,每个角色有 1 or 2 个版本(可以理解为普通版以及爆发版),每个角色版本可以KO掉若干人. 问最少选多少个角色( ...
- 【转】DLX 精确覆盖 重复覆盖
问题描述: 给定一个n*m的矩阵,有些位置为1,有些位置为0.如果G[i][j]==1则说明i行可以覆盖j列. Problem: 1)选定最少的行,使得每列有且仅有一个1. 2)选定最少的行,使得每列 ...
- dancing link 精确覆盖 重复覆盖 (DLX)
申明:因为转载的没有给出转载链接,我就把他的链接附上,请尊重原创: http://www.cnblogs.com/-sunshine/p/3358922.html 如果谁知道原创链接 给一下,请尊重原 ...
- HDU 5046 Airport【DLX重复覆盖】
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5046 题意: 给定n个城市的坐标,要在城市中建k个飞机场,使城市距离最近的飞机场的最长距离最小,求这 ...
- (中等) HDU 3335 , DLX+重复覆盖。
Description As we know,the fzu AekdyCoin is famous of math,especially in the field of number theory. ...
随机推荐
- Visual Studio 行末回车时运算符两侧自动加空格是怎么设置的
在工具—>选项->文本编辑器->c#->格式设置->间距后有三个选项 如果已经选中"二元运算符前后插入空格" 而VS又抽风没有这个功能时,可以选中其余 ...
- 线性判别分析(Linear Discriminant Analysis, LDA)算法初识
LDA算法入门 一. LDA算法概述: 线性判别式分析(Linear Discriminant Analysis, LDA),也叫做Fisher线性判别(Fisher Linear Discrimin ...
- java gc log
java full gc 经常带来延迟, 导致性能问题 如下命令使java虚拟机记录gc的log到文件, 帮助分析定位问题. java -Xloggc:./a.log -jar a.jar // ...
- java GC optimization, G1GC
引用 http://www.avricot.com/blog/?post/2010/05/03/Get-started-with-java-JVM-memory-(heap%2C-stack%2 ...
- Linux增加挂载盘
命令:fdisk /dev/sdb, m 命令:m,n,e,1,p,w 命令:mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb,y 挂载命令:mount -t ext4 /dev/sdb /data 获取U ...
- asp.net原理笔记----页面控件类型,页面状况和asp.net编译过程
通过查看asp.net的整个生命周期之后 了解到在aspx的页面生命周期中 调用了BuildControlTree()方法生成页面控件树 之后再调用Rend()方法根据控件树生成html返回 aspx ...
- Java List序列化的实现
概述 java中的序列化与反序列化都要求对象实现Serializable接口(其实就是声明一下),而对于List这种动态改变的集合默认是不实现这个接口的,也就是不能直接序列化.但是数组是可以序列化的, ...
- Jenkins 安装卡住不动的解决方案
如果在安装jenkins时卡在getting startted的界面,如下所示 jenkins在安装插件前总是尝试连接www.google.com,来判断网络是否连通.谷歌的网站在大陆是连不上的,所以 ...
- iOS OC08,09_内存管理
//管理内存有三种方式, //1.是垃圾回收,java常见的管理内存的方法,系统来检測对象是否被使用,是否被释放 //2.MRC手动管理引用计数,iOS管理内存的方式,程序猿通过手动的方式来管理对象是 ...
- Tomcat、Weblogic、JBoss、GlassFish、Resin、Websphere弱口令及拿webshell方法总结 [复制链接]
1.java应用服务器 Java应用服务器主要为应用程序提供运行环境,为组件提供服务.Java 的应用服务器很多,从功能上分为两类:JSP 服务器和 Java EE 服务器.1.1 常见的Se ...
