线性回归(regression)
- 简介
回归分析只涉及到两个变量的,称一元回归分析。一元回归的主要任务是从两个相关变量中的一个变量去估计另一个变量,被估计的变量,称因变量,可设为Y;估计出的变量,称自变量,设为X。
回归分析就是要找出一个数学模型Y=f(X),使得从X估计Y可以用一个函数式去计算。
当Y=f(X)的形式是一个直线方程时,称为一元线性回归。这个方程一般可表示为Y=A+BX。根据最小平方法或其他方法,可以从样本数据确定常数项A与回归系数B的值。
- 线性回归方程
Target:尝试预测的变量,即目标变量
Input:输入
Slope:斜率
Intercept:截距
举例,有一个公司,每月的广告费用和销售额,如下表所示:
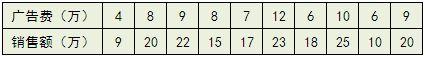
如果把广告费和销售额画在二维坐标内,就能够得到一个散点图,如果想探索广告费和销售额的关系,就可以利用一元线性回归做出一条拟合直线:
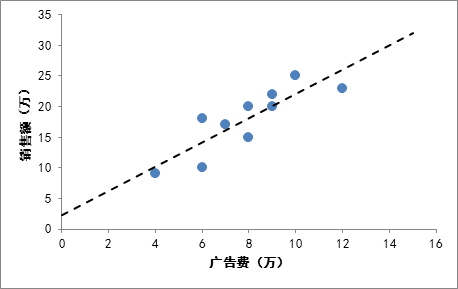
有了这条拟合线,就可以根据这条线大致的估算出投入任意广告费获得的销售额是多少。
- 评价回归线拟合程度的好坏
我们画出的拟合直线只是一个近似,因为肯定很多的点都没有落在直线上,那么我们的直线拟合的程度如何,换句话说,是否能准确的代表离散的点?在统计学中有一个术语叫做R^2(coefficient ofdetermination,中文叫判定系数、拟合优度,决定系数),用来判断回归方程的拟合程度。
要计算R^2首先需要了解这些:
总偏差平方和(又称总平方和,SST,Sum of Squaresfor Total):是每个因变量的实际值(给定点的所有Y)与因变量平均值(给定点的所有Y的平均)的差的平方和,即,反映了因变量取值的总体波动情况。如下:
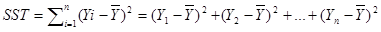
回归平方和(SSR,Sum of Squares forRegression):因变量的回归值(直线上的Y值)与其均值(给定点的Y值平均)的差的平方和,即,它是由于自变量x的变化引起的y的变化,反映了y的总偏差中由于x与y之间的线性关系引起的y的变化部分,是可以由回归直线来解释的。
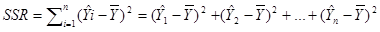
残差平方和(又称误差平方和,SSE,Sum of Squaresfor Error):因变量的各实际观测值(给定点的Y值)与回归值(回归直线上的Y值)的差的平方和,它是除了x对y的线性影响之外的其他因素对y变化的作用,是不能由回归直线来解释的。
SST(总偏差)=SSR(回归线可以解释的偏差)+SSE(回归线不能解释的偏差)
所画回归直线的拟合程度的好坏,其实就是看看这条直线(及X和Y的这个线性关系)能够多大程度上反映(或者说解释)Y值的变化,定义
R^2=SSR/SST 或 R^2=1-SSE/SST
R^2的取值在0,1之间,越接近1说明拟合程度越好
- 代码实现
环境:MacOS mojave 10.14.3
Python 3.7.0
使用库:scikit-learn 0.19.2
sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression官方库:https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html
>>> from sklearn import linear_model
>>> reg = linear_model.LinearRegression()
>>> reg.fit([[0, 0], [1, 1], [2, 2]], [0, 1, 2])#以(x,y)形式训练
...
LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=None,
normalize=False)
>>> reg.coef_
array([0.5, 0.5]) #第一个是斜率,第二个是截距
举例,以年龄与资产净值为例

图中蓝点是训练数据,用于计算得出拟合曲线;红点是测试数据,用于计算拟合曲线的拟合程度
均属于样本,仅仅是随机分离出来。
Main.py 主程序以及画图
import numpy
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg') import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from studentRegression import studentReg
from class_vis import prettyPicture from ages_net_worths import ageNetWorthData ages_train, ages_test, net_worths_train, net_worths_test = ageNetWorthData() reg = studentReg(ages_train, net_worths_train) plt.clf()
plt.scatter(ages_train, net_worths_train, color="b", label="train data")
plt.scatter(ages_test, net_worths_test, color="r", label="test data")
plt.plot(ages_test, reg.predict(ages_test), color="black")
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.xlabel("ages")
plt.ylabel("net worths") print ("katie's net worth prediction: ", reg.predict(27)) #预测结果
print ("r-squared score:",reg.score(ages_test,net_worths_test))
print ("slope:", reg.coef_) #获取斜率
print ("intercept:" ,reg.intercept_) #获取截距 plt.savefig("test.png") print ("\n ######## stats on test dataset ########\n")
print ("r-squared score: ",reg.score(ages_test,net_worths_test)) #通过使用测试集,可以察觉到过拟合等情况 print ("\n ######## stats on training dataset ########\n")
print ("r-squared score: ",reg.score(ages_train,net_worths_train)) plt.scatter(ages_train,net_worths_train)
plt.plot(ages_train,reg.predict(ages_train),color='blue',linewidth=3)
plt.xlabel('ages_train')
plt.ylabel('net_worths_train')
plt.show()
class_vis.py 绘图与保存图像
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pylab as pl def prettyPicture(clf, X_test, y_test):
x_min = 0.0; x_max = 1.0
y_min = 0.0; y_max = 1.0 # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
h = .01 # step size in the mesh
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max()) plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=pl.cm.seismic) # Plot also the test points
grade_sig = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
bumpy_sig = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
grade_bkg = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1]
bumpy_bkg = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1] plt.scatter(grade_sig, bumpy_sig, color = "b", )
plt.scatter(grade_bkg, bumpy_bkg, color = "r",)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("bumpiness")
plt.ylabel("grade") plt.savefig("test.png")
ages_net_worths.py 样本点数据
import numpy
import random def ageNetWorthData(): random.seed(42)
numpy.random.seed(42) ages = []
for ii in range(100):
ages.append( random.randint(20,65) )
net_worths = [ii * 6.25 + numpy.random.normal(scale=40.) for ii in ages]
### need massage list into a 2d numpy array to get it to work in LinearRegression
ages = numpy.reshape( numpy.array(ages), (len(ages), 1))
net_worths = numpy.reshape( numpy.array(net_worths), (len(net_worths), 1)) from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
ages_train, ages_test, net_worths_train, net_worths_test = train_test_split(ages, net_worths) return ages_train, ages_test, net_worths_train, net_worths_test
studentRegression.py 线性回归
def studentReg(ages_train, net_worths_train):
from sklearn import linear_model
reg = linear_model.LinearRegression()
reg.fit(ages_train, net_worths_train)
return reg
得到结果:
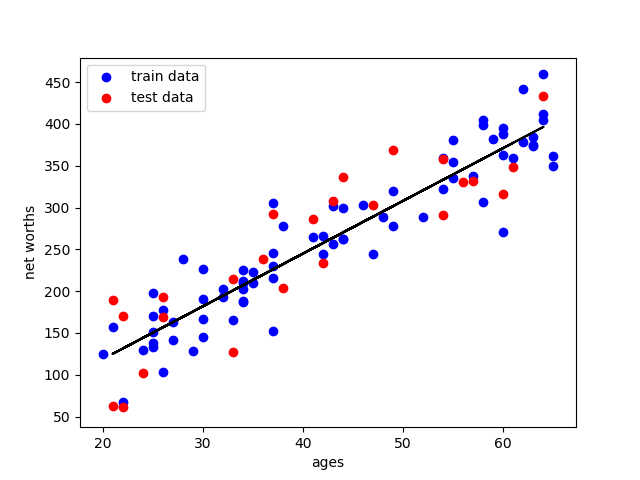
同时得到:
R^2: 0.7889037259170789
slope: [[6.30945055]]
intercept: [-7.44716216]
拟合程度约为0.79,还算可以
线性回归(regression)的更多相关文章
- ### 线性回归(Regression)
linear regression logistic regression softmax regression #@author: gr #@date: 2014-01-21 #@email: fo ...
- 线性回归 Linear Regression
成本函数(cost function)也叫损失函数(loss function),用来定义模型与观测值的误差.模型预测的价格与训练集数据的差异称为残差(residuals)或训练误差(test err ...
- 线性回归、梯度下降(Linear Regression、Gradient Descent)
转载请注明出自BYRans博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/ 实例 首先举个例子,假设我们有一个二手房交易记录的数据集,已知房屋面积.卧室数量和房屋的交易价格,如下表: ...
- Matlab实现线性回归和逻辑回归: Linear Regression & Logistic Regression
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7732417 本文为Maching Learning 栏目补充内容,为上几章中所提到单参数线性 ...
- Stanford机器学习---第二讲. 多变量线性回归 Linear Regression with multiple variable
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7700772 本栏目(Machine learning)包括单参数的线性回归.多参数的线性回归 ...
- Sklearn库例子2:分类——线性回归分类(Line Regression )例子
线性回归:通过拟合线性模型的回归系数W =(w_1,…,w_p)来减少数据中观察到的结果和实际结果之间的残差平方和,并通过线性逼近进行预测. 从数学上讲,它解决了下面这个形式的问题: Lin ...
- 机器学习之多变量线性回归(Linear Regression with multiple variables)
1. Multiple features(多维特征) 在机器学习之单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable)我们提到过的线性回归中,我们只有一个单一特征量 ...
- 多元线性回归(Linear Regression with multiple variables)与最小二乘(least squat)
1.线性回归介绍 X指训练数据的feature,beta指待估计得参数. 详细见http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E4%B8%80%E8%88%AC%E7%BA%BF%E6% ...
- Locally weighted linear regression(局部加权线性回归)
(整理自AndrewNG的课件,转载请注明.整理者:华科小涛@http://www.cnblogs.com/hust-ghtao/) 前面几篇博客主要介绍了线性回归的学习算法,那么它有什么不足的地方么 ...
- Linear Regression(线性回归)(一)—LMS algorithm
(整理自AndrewNG的课件,转载请注明.整理者:华科小涛@http://www.cnblogs.com/hust-ghtao/) 1.问题的引出 先从一个简单的例子说起吧,房地产公司有一些关于Po ...
随机推荐
- xunsearch实战经验总结
一.定义好配置文件(非常关键) a):如果需要做精确搜索建议对字段设定index=self,tokenizer = full,不然xunsearch会对字段做分词处理: b):数字区间搜索需设定 ty ...
- PHP学习总结(6)——PHP入门篇之PHP语句结束符
PHP语句结束符 有的小伙伴们是不是已经注意在每一条PHP代码行结尾处都会有一个分号:.对的,这点注意,在PHP编程中需要在每条语句的末尾加入分号:.但要注意,分号:一定在半角状态下输入噢.
- FreeMarker 语法 null 的处理
一.java 代码 @Test public void testFreeMarker() throws Exception { //1.创建一个模板文件 //2.创建一个Configuration对象 ...
- SimpleDateFormat 格式化 解析
package chengbaoDemo; import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text ...
- Using index, using temporary, using filesort - how to fix this?
解释一: These are the following conditions under which temporary tables are created. UNION queries use ...
- 具体解释Redis源代码中的部分高速排序算法(pqsort.c)
看标题.你可能会疑惑:咦?你这家伙.怎么不解说完整的快排,仅仅讲一部分快排---.- 哎,冤枉. "部分快排"是算法的名字.实际上本文相当具体呢.本文差点儿与普通快排无异.看懂了本 ...
- 小米2S电池电量用尽充电无法开机解决方法
背景: 昨晚睡觉前关机,记得电量还有百分之七八十,但早上起床后,指示灯一直红灯闪烁.按开机键和其它键都没反应! ! 解决方法: 扣下电池,用万能充冲电,略微多冲一会,由于 ...
- 普通androidproject转换为C/C++project之后,再还原成androidproject的解决方式
我们在调试android程序时,可能会把androidproject转换成C/C++project,或者Add Native Support.可是,我们怎么把C/C++project还原成普通的and ...
- Linux下安装intellij idea
1.下载 http://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download/#section=linux 我下载的是不带jdk的版本 2.放入opt目录中 3.解压到usr下面的intel ...
- 英语发音规则---G字母
英语发音规则---G字母 一.总结 一句话总结: 1.G发[g]音? bag [bæg] n. 袋:猎获物 go [gəʊ] vi. 走:达到 garden ['gɑːd(ə)n] n. 花园 gla ...
