3D集合图元:最小边界框/包围盒(boundingbox)
对于2D边界框的应用时比较广泛地,它为一个简单匹配建立了很小的计算规则,3D模型的boundingbox则比较困难,计算代价较大。对于PCL库的使用则降低了计算难度,三维数值化降低了建模过程,可以使用简单的边界框规则。
对于 如何获取最大最小值过程:在载入时去 进行一个 简单 一次交换排序,选取最小最大值... 计算边界框.
引自天行健,君子以自强不息的 文章;
原文链接:http://www.cppblog.com/lovedday/archive/2008/02/23/43122.html
矩形边界框 / 包围盒
另一种常见的用来界定物体的几何图元是矩形边界框,矩形边界框可以是与轴对齐的或是任意方向的。轴对齐矩形边界框有一个限制,就是它的边必须垂直于坐标轴。缩写AABB常用来表示axially aligned bounding box(轴对齐矩形边界框),OBB用来表示oriented bounding
box(方向矩形边界框)。轴对齐矩形边界框不仅容易创建,而且易于使用。
一个3D的AABB就是一个简单的六面体,每一边都平行于一个坐标平面。矩形边界框不一定是立方体,它的长、宽、高可以彼此不同。在图12.10中,画出了一些简单的3D物体和它们的AABB。
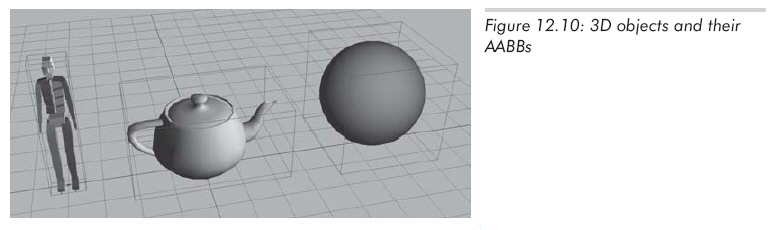
AABB的表达方法
先介绍AABB的一些重要性质和引用这些值时所用到的记法。AABB内的点满足下列等式:
xmin≤ x ≤ xmax
ymin≤ y ≤ ymax
zmin≤ z ≤ zmax
特别重要的两个点为:
pmin = [xmin ymin zmin]
pmax = [xmax ymax zmax]
中心点c为:
c = (pmin + pmax) /2
"尺寸向量"s是从pmin指向pmax的向量,包含了矩形边界的长、宽、高:
s = pmax - pmin
还可以求出矩形边界框的"半径向量"r,它是从中心指向pmax的向量:
r = pmax - c =
s/2
明确地定义一个AABB只需要pmin、pmax、c、s、r这5个向量中的两个(除s和r不能配对外,它们中的任意两个都可配对)。在一些情况下,某些配对形式比其他的会更有用。我们建议用pmin和pmax表示一个边界框,因为实际应用中,使用它们的频率远高于c、s、r。当然,由pmin和pmax计算其余三个中的任意一个都是很容易的。
在我们的C++代码中,使用下面的类表示AABB,这是一个缩略的代码清单。
#ifndef AABB3_H
#define AABB3_H
#include "vector3.h"
class cMatrix4x3; //---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implement a 3D axially aligned bounding box
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class cAABB3
{
public:
cVector3 min, max; public:
// query for dimentions
cVector3 size() const { return max - min; }
float x_size() { return max.x - min.x; }
float y_size() { return max.y - min.y; }
float z_size() { return max.z - min.z; }
cVector3 center() const { return (min + max) * 0.5f; } // fetch one of the eight corner points
cVector3 corner(int i) const; // "Empty" the box, by setting the values to really large/small numbers.
void empty(); // add a point to the box
void add(const cVector3& p); // add an AABB to the box
void add(const cAABB3& box); // return true if the box is empty
bool is_empty() const; // return true if the box contains a point
bool contains(const cVector3& p) const; // transform the box and compute the new AABB
void set_to_transformed_box(const cAABB3& box, const cMatrix4x3& m); // return the clostet point on this box to another point
cVector3 clostet_point_to(const cVector3& p) const;
}; #endif
计算AABB
计算一个顶点集合的AABB是非常简单的,先将最小值和最大值设为"正负无穷大"或任何比实际中用到的数都大或小得多的数。接着,遍历全部点,并扩展边界框直到它包含所有点为止。
我们在cAABB类中引入了两个辅助函数,第一个函数负责"清空"AABB
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// "Empty" the box, by setting the values to really large/small numbers.
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void cAABB3::empty()
{
const float big_number = 1e37f; min.x = min.y = min.z = big_number;
max.x = max.y = max.z = -big_number;
}
第二个函数将单个点"加"到AABB中,并在必要的时候扩展AABB以包含每个点:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Add a point to the box
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void cAABB3::add(const cVector3& p)
{
// expand the box as necessary to contain the point
if(p.x < min.x) min.x = p.x;
if(p.x > max.x) max.x = p.x;
if(p.y < min.y) min.y = p.y;
if(p.y > max.y) max.y = p.y;
if(p.z < min.z) min.z = p.z;
if(p.z > max.z) max.z = p.z;
}
现在,从一个点集创建矩形边界框,可以使用下面的代码:
Listing 12.1: Computing the AABB for a set of points
// Our list of points
const int n;
Vector3 list[n];
// First, empty the box
AABB3 box;
box.empty();
// Add each point into the box
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; ++i)
box.add(list[i]);
取得AABB的顶点:
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Return one of the 8 corner points. The points are numbered as follows:
//
// 6 7
// ------------------------------
// /| /|
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// 2 / | 3 / |
// /----------------------------/ |
// | | | |
// | | | | +Y
// | 4 | | |
// | |-----------------|----------| |
// | / | / 5 |
// | / | / | +Z
// | / | / |
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / |/
// |/ |/ ----------------- +X
// ------------------------------
// 0 1
//
// Bit 0 selects min.x vs. max.x
// Bit 1 selects min.y vs. max.y
// Bit 2 selects min.z vs. max.z
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
cVector3 cAABB3::corner(int i) const
{
assert(i >= 0 && i <= 7); // make sure index is in range
return cVector3((i & 1) ? max.x : min.x,
(i & 2) ? max.y : min.y,
(i & 4) ? max.z : min.z);
}
其他的相关函数,具体功能详见注释:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Add an AABB to the box
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void cAABB3::add(const cAABB3& box)
{
// expand the box as necessary
if(box.min.x < min.x) min.x = box.min.x;
if(box.min.x > max.x) max.x = box.min.x;
if(box.min.y < min.y) min.y = box.min.y;
if(box.min.y > max.y) max.y = box.min.y;
if(box.min.z < min.z) min.z = box.min.z;
if(box.min.z > max.z) max.z = box.min.z;
} //---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Return true if the box is empty
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool cAABB3::is_empty() const
{
// check if we're inverted on any axis
return (min.x > max.x) || (min.y > max.y) || (min.z > max.z);
} //---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Return true if the box contains a point
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool cAABB3::contains(const cVector3& p) const
{
// check for overlap on each axis
return (p.x >= min.x) && (p.x <= max.x) &&
(p.y >= min.y) && (p.y <= max.y) &&
(p.z >= min.z) && (p.z <= max.z);
} //---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// return the closest point on this box to another point
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
cVector3 cAABB3::clostet_point_to(const cVector3& p) const
{
// "push" p into the box, on each dimension. cVector3 r; if(p.x < min.x)
r.x = min.x;
else if(p.x > max.x)
r.x = max.x;
else
r.x = p.x; if(p.y < min.y)
r.y = min.y;
else if(p.y > max.y)
r.y = max.y;
else
r.y = p.y; if(p.z < min.z)
r.z = min.z;
else if(p.z > max.z)
r.z = max.z;
else
r.z = p.z; return r;
}
AABB与边界球
很多情况下,AABB比边界球更适合于做定界球:
(1)计算一个点集的AABB,在编程上更容易实现,并能在较短的时间内完成。计算边界球则困难得多。
(2)对实际世界里的许多物体,AABB提供了一种"更紧凑"的边界。当然,对于某些物体,边界球更好(设想一个本身就是球形的物体)。在极端情况下,AABB的体积可能仅相当于边界球体积的1/2,大部分时候边界球的体积会比矩形框的体积大得多,比较一下电线杆的边界球和AABB就知道了。图12.11所示为不同物体的AABB与边界球的比较。
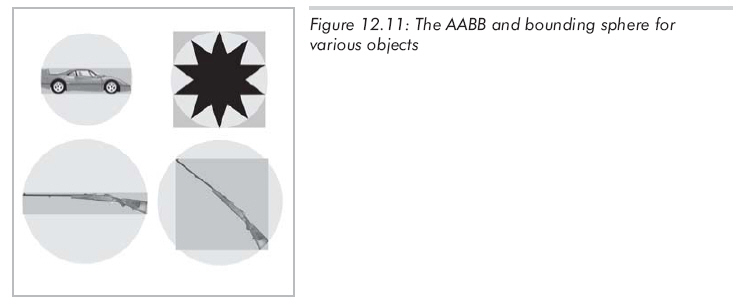
边界球的根本问题是它的形状只有一个自由度----半径,而AABB却有三个自由度----长、宽、高。因此,它可以调节这些自由度以适应不同物体。对图12.11中的大部分物体,除了右上角的星形体外,AABB都比边界球小。对这颗星,边界球也仅比AABB略小一些。通过图12.11,我们可以注意到AABB对物体的方向很敏感。比较下面两支枪的AABB,图中枪的大小都是相同的,只是方向不同而已;还应注意到在这一情况下边界球大小相同,因为边界球对物体方向不敏感。
变换AABB
当物体在虚拟世界中移动时,它的AABB也需要随之移动。此时我们有两个选择----用变换后的物体来重新计算AABB,或者对AABB做和物体同样的变换。所得到的结果不一定是轴对齐的(如果物体旋转),也不一定是盒状的(如果物体发生了扭曲)。不过,通过"变换后的AABB"进行计算要比通过"经过变换后的物体"计算AABB快得多,因为AABB只有8个顶点。
通过"变换后的AABB"计算不能只是简单地变换8个顶点,也不能通过转换原pmin和pmax来得到新的pmin和pmax
----这样可能会导致xmin > xmax。为了计算新的AABB,必须先变换8个顶点,再从这8个顶点中计算一个新的AABB。
根据变换的不同,这种方法可能使新边界框比原边界框大许多。例如,在2D中,45度的旋转会大大增加边界框的尺寸,如图12.12所示:
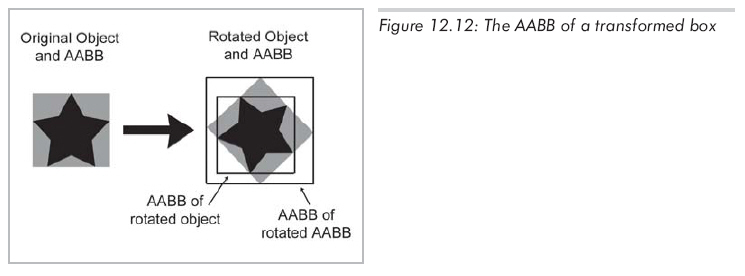
比较图12.12中原AABB(灰色框)和新AABB(右边较大的方框),它是通过旋转后的AABB计算的,新AABB几乎是原来的两倍。注意,如果从旋转后的物体而不是通过旋转后的AABB来计算新AABB,它的大小将和原来的AABB相同。
可以利用AABB的结构来加快新的AABB的计算速度,而不必先变换8个顶点,再从这8个顶点中计算新AABB。
让我们简单回顾一下3x3矩阵变换一个3D点的过程:
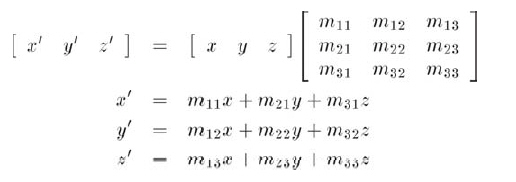
设原边界框为xmin,xmax,ymin...,新边界框计算将得到x'min,x'max,y'min...。现在我们的任务就是想办法加快计算x'min的速度,换句话说,我们希望找到m11x+m21y+m31z的最小值,其中[x,
y, z]是原8个顶点中的任意一个,我们所要做的就是找出这些点经过变换后谁的x坐标最小。看第一个乘积:m11x,为了最小化乘积,必须决定是用xmin还是xmax来代换其中的x。显然,如果m11>0,用xmin能得到最小化乘积;如果m11<0,则用xmax能得到最小化乘积。比较方便的是,不管xmin和xmax中哪个被用来计算xmin,都可以用另外一个来计算xmax。可以对矩阵9个元素中的每个都应用这个计算过程,
如下列代码所示:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Transform the box and compute the new AABB. Remember, this always
// results in an AABB that is at least as big as the origin, and may be
// considerably bigger.
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void cAABB3::set_to_transformed_box(const cAABB3& box, const cMatrix4x3& m)
{
// if we're empty, then bail.
if(box.is_empty())
{
empty();
return;
}
// start with the translation portion
min = max = get_translation(m);
// examine each of the 9 matrix elements and compute the new AABB
if(m.m11 > 0.0f)
{
min.x += m.m11 * box.min.x;
max.x += m.m11 * box.max.x;
}
else
{
min.x += m.m11 * box.max.x;
max.x += m.m11 * box.min.x;
} if(m.m21 > 0.0f)
{
min.x += m.m21 * box.min.y;
max.x += m.m21 * box.max.y;
}
else
{
min.x += m.m21 * box.max.y;
max.x += m.m21 * box.min.y;
} if(m.m31 > 0.0f)
{
min.x += m.m31 * box.min.z;
max.x += m.m31 * box.max.z;
}
else
{
min.x += m.m31 * box.max.z;
max.x += m.m31 * box.min.z;
} if(m.m12 > 0.0f)
{
min.y += m.m12 * box.min.x;
max.y += m.m12 * box.max.x;
}
else
{
min.y += m.m12 * box.max.x;
max.y += m.m12 * box.min.x;
} if(m.m22 > 0.0f)
{
min.y += m.m22 * box.min.y;
max.y += m.m22 * box.max.y;
}
else
{
min.y += m.m22 * box.max.y;
max.y += m.m22 * box.min.y;
} if(m.m32 > 0.0f)
{
min.y += m.m32 * box.min.z;
max.y += m.m32 * box.max.z;
}
else
{
min.y += m.m32 * box.max.z;
max.y += m.m32 * box.min.z;
} if(m.m13 > 0.0f)
{
min.z += m.m13 * box.min.x;
max.z += m.m13 * box.max.x;
}
else
{
min.z += m.m13 * box.max.x;
max.z += m.m13 * box.min.x;
} if(m.m23 > 0.0f)
{
min.z += m.m23 * box.min.y;
max.z += m.m23 * box.max.y;
}
else
{
min.z += m.m23 * box.max.y;
max.z += m.m23 * box.min.y;
} if(m.m33 > 0.0f)
{
min.z += m.m33 * box.min.z;
max.z += m.m33 * box.max.z;
}
else
{
min.z += m.m33 * box.max.z;
max.z += m.m33 * box.min.z;
}
}
后记:
包围盒作为一种约束,和坐标系有关系,世界坐标系标定了包围盒的精度。
3D集合图元:最小边界框/包围盒(boundingbox)的更多相关文章
- OpenCV 学习笔记03 边界框、最小矩形区域和最小闭圆的轮廓
本节代码使用的opencv-python 4.0.1,numpy 1.15.4 + mkl 使用图片为 Mjolnir_Round_Car_Magnet_300x300.jpg 代码如下: impor ...
- 输出预测边界框,NMS非极大值抑制
我们预测阶段时: 生成多个锚框 每个锚框预测类别和偏移量 但是,当同一个目标上可能输出较多的相似的预测边界框.我们可以移除相似的预测边界框.——NMS(非极大值抑制). 对于一个预测边界框B,模型会计 ...
- NX二次开发-UFUN求对象的最大边界框UF_MODL_ask_bounding_box
NX9+VS2012 #include <uf.h> #include <uf_obj.h> #include <uf_modl.h> #include <u ...
- Android 手势识别类 ( 二 ) GestureDetector 源码浅析
前言:Android 关于手势的操作提供两种形式:一种是针对用户手指在屏幕上划出的动作而进行移动的检测,这些手势的检测通过android提供的监听器来实现:另一种是用 户手指在屏幕上滑动而形成一定的不 ...
- [转]TrueType字体结构
TrueType字体通常包含在单个TrueType字体文件中,其文件后缀为.TTF. OpenType字体是以类似于TrueType字体的格式编码的POSTSCRIPT字体.OPENTYPE字体使用. ...
- cocos2dx基础篇(3) 常用重要类
---------------------------------------- 入口类main.cpp 主要控制类AppDelegate.cpp -------------------------- ...
- 深度学习论文翻译解析(十二):Fast R-CNN
论文标题:Fast R-CNN 论文作者:Ross Girshick 论文地址:https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_iccv_2015/p ...
- Data Lake Analytics的Geospatial分析函数
0. 简介 为满足部分客户在云上做Geometry数据的分析需求,阿里云Data Lake Analytics(以下简称:DLA)支持多种格式的地理空间数据处理函数,符合Open Geospatial ...
- 论文翻译——Fast-R-CNN(端到端开篇, End to end)
快速的区域卷积网络方法(Fast R-CNN) 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.08083 摘要: 本文提出一种基于快速的区域卷积网络方法(Fast R-CNN) ...
随机推荐
- 洛谷P1478 陶陶摘苹果(升级版)【水题】
又是一年秋季时,陶陶家的苹果树结了n个果子.陶陶又跑去摘苹果,这次她有一个a公分的椅子.当他手够不着时,他会站到椅子上再试试. 这次与NOIp2005普及组第一题不同的是:陶陶之前搬凳子,力气只剩下s ...
- svn版本库更新后自动同步到www
注意:www目录一定要用SVN服务器 checkout出Repositories的代码 步骤: (1)新建www根目录 mkdir -p /data/www/lehuo (2)在www根目录下检出(c ...
- Linux目录与相关配置文件讲解
linux目录介绍及配置文件详细介绍 重要目录简介 目录名 作用 boot 与电脑启动相关,推荐单独分区. etc 存放配置文件 mnt 一般用来设置挂载点 src.sys.proc 与系统内核相关, ...
- luogu P4725 多项式对数函数 (模板题、FFT、多项式求逆、求导和积分)
手动博客搬家: 本文发表于20181125 13:25:03, 原地址https://blog.csdn.net/suncongbo/article/details/84487306 题目链接: ht ...
- QT中tableview不能更新数据,why?
model->select(); //model->removeColumn(0);++++++++++++++++++++ //model->setHeaderData(model ...
- 【ACM】bailian_2705_跳绳游戏_201307302003
2705:跳绳游戏总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 小朋友玩跳绳比赛,要计算在一分钟内跳了多少下.假设每秒钟跳一下,如果中途失败了,则要花三秒钟后才能开始重跳.一般小朋友跳 ...
- rabbit-入门
#启用rabbit的web管理 rabbitmq-plugins.bat enable rabbitmq_management 发布的窗口用TOPIC模式 rabbitmq没有确认消息接收的返回值,M ...
- js 清空对象\删除对象的属性
在项目中,有些对象用完后需要重置,下面简单介绍下JS中清除对象的方法.方法如下: 方法一:字面量定义对象 第一步,定义一个空对象并打印出来,代码和效果: 代码: var student = {};co ...
- iOS_网络请求_代理方式
#pragma mark - 网络请求代理方式(异步) - (IBAction)DelegateButtonDidClicked:(UIButton *)sender { // 1.拼接 urlStr ...
- HDU 1912
坑,直接把公路看成X轴来做,然后,排序扫描一下,你懂的. #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdi ...
