Java 计算两点间的全部路径(二)
一、有向线段,存储开始点与结束点
/**
* 有方向的线段
*
* @author Gm
*
*/
public class DirectionLine implements Cloneable {
private String beginNode;
private String endNode;
public DirectionLine(String beginNode, String endNode) {
this.beginNode = beginNode;
this.endNode = endNode;
}
public String toString() {
return beginNode + "->" + endNode;
}
public String getBeginNode() {
return beginNode;
}
public void setBeginNode(String beginNode) {
this.beginNode = beginNode;
}
public String getEndNode() {
return endNode;
}
public void setEndNode(String endNode) {
this.endNode = endNode;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
DirectionLine dl = (DirectionLine) obj;
if (this.getBeginNode().equals(dl.getBeginNode()) && this.getEndNode().equals(dl.getEndNode())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
三、过滤无效节点
public class Graph {
List<DirectionLine> directionLines = null; // 已知的路径(有向线,包含:开始点、结束点)
List<String> visitedList = new ArrayList<String>(); // 存放已经访问过点的节点
Set<String> resultSet = new HashSet<String>(); // 目的访问路径(点的集合)
Set<DirectionLine> loopList = new HashSet<DirectionLine>(); // 已知的回路(有向线,包含:开始点、结束点)
public Graph(List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
this.directionLines = directionLines;
}
public List<DirectionLine> getDirectionLines() {
return directionLines;
}
public void setDirectionLines(List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
this.directionLines = directionLines;
}
public List<String> getVisitedList() {
return visitedList;
}
public void setVisitedList(List<String> visitedList) {
this.visitedList = visitedList;
}
public Set<String> getResultSet() {
return resultSet;
}
public void setResultSet(Set<String> resultSet) {
this.resultSet = resultSet;
}
public Set<DirectionLine> getLoopList() {
return loopList;
}
public void setLoopList(Set<DirectionLine> loopList) {
this.loopList = loopList;
}
/**
* 路径遍历的核心算法
*
* @param startNode
* @param endNode
*/
public void getAllPaths(String startNode, String endNode) {
visitedList.add(startNode);
// System.out.println("访问的起点->终点:" + startNode + "->" + endNode);
for (int z = 0; z < directionLines.size(); z++) {
// System.out.println("遍历次数:" + z + ",路径:" + directionLines.get(z).toString());
if (directionLines.get(z).getBeginNode().equals(startNode)) { // 寻找找以startNode开始的路径
if (directionLines.get(z).getEndNode().equals(endNode)) { // 如果以endNode结尾,则为一条有效路径
resultSet.add(visitedList.toString().substring(0, visitedList.toString().lastIndexOf("]")) + "," + endNode + "]");
continue;
}
// System.out.println("已访问过的节点:" + visitedList.toString());
if (!visitedList.contains(directionLines.get(z).getEndNode())) {// 此节点仍未遍历,则继续迭代
getAllPaths(directionLines.get(z).getEndNode(), endNode);
} else {// 证明存在回路
loopList.add(directionLines.get(z));
}
}
}
visitedList.remove(startNode);
}
}
public class MapVisit {
/**
* 构造初始化路径--已知
*
*/
public List<DirectionLine> init() {
List<DirectionLine> directionLines = new ArrayList<DirectionLine>();
String str = CommonUtil.readToString("room_layout2.json");
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(str);
for (Entry<String, Object> entry : jsonObject.entrySet()) {
String startNode = "node" + entry.getKey();
JSONObject child_nodes = JSONObject.parseObject(entry.getValue().toString());
for (Entry<String, Object> child_entry : child_nodes.entrySet()) {
String endNode = "node" + child_entry.getKey();
// System.out.println(startNode + ":" + endNode);
directionLines.add(new DirectionLine(startNode, endNode));
}
}
return directionLines;
}
/**
* 判断所有路径中是否有以beginNode节点为起点的基本路径
*
* @param beginNode
* @param directionLines
* @return
*/
public boolean existBeginNode(String beginNode, List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
boolean result = false;
for (DirectionLine dl : directionLines) {
if (dl.getBeginNode().equals(beginNode)) {
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 判断所有路径中是否有以end节点为终点的基本路径
*
* @param endNode
* @param directionLines
* @return
*/
public boolean existEndNode(String endNode, List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
boolean result = false;
for (DirectionLine dl : directionLines) {
if (dl.getEndNode().equals(endNode)) {
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 根据路径获取到所有的节点
*
* @param directionLines
* @return
*/
public Set<String> getAllNodes(List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
Set<String> nodes = new HashSet<String>();
for (DirectionLine r : directionLines) {
nodes.add(r.getBeginNode());
nodes.add(r.getEndNode());
}
return nodes;
}
/**
* 获取到需要删除的路径
*
* @param beginNodes
* 无效起始节点
* @param endNodes
* 无效终结点
* @param directionLines
*/
public Set<DirectionLine> deleteDirectionLines(Set<String> beginNodes, Set<String> endNodes, List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
Set<DirectionLine> set = new HashSet<DirectionLine>();
for (String str : beginNodes) {
for (DirectionLine dl : directionLines) {
if (dl.getBeginNode().equals(str)) {
set.add(dl);
}
if (dl.getBeginNode().equals(str)) {
set.add(dl);
}
}
}
return set;
}
/**
* 过滤掉无用的节点 获取到无效开始节点和无效结束点
*
* @param all
* @param directionLines
* @param beginNodes
* @param endNodes
* @return
*/
public Set<String> filterInvalidNode(Set<String> allNodes, List<DirectionLine> directionLines, Set<String> beginNodes, Set<String> endNodes) {
Set<String> result = new HashSet<String>();
boolean isBegin = true;
boolean isEnd = true;
for (String node : allNodes) {
if (!existEndNode(node, directionLines)) { // 没有以此节点结尾的路径,则证明此节点为无用节点
isBegin = false;
beginNodes.add(node);
} else if (!existBeginNode(node, directionLines)) {// 没有以此节点开头的路径,则证明此节点为无用节点
isEnd = false;
endNodes.add(node);
} else {
result.add(node); // 有用的节点
}
}
if (isBegin == true && isEnd == true) {
return result;
} else {
return filterInvalidNode(result, directionLines, beginNodes, endNodes);
}
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
MapVisit visit = new MapVisit();
List<DirectionLine> directionLines = visit.init();
// 构造基本路径--为已知条件
Set<String> invalidBeginNodes = new HashSet<String>(); // 无效的起始节点
Set<String> invalidEndNodes = new HashSet<String>(); // 无效的结束节点
Set<String> allNodes = visit.getAllNodes(directionLines);
visit.filterInvalidNode(allNodes, directionLines, invalidBeginNodes, invalidEndNodes); // 获取到无效开始节点和无效结束点
Set<DirectionLine> invalidRoads = visit.deleteDirectionLines(invalidBeginNodes, invalidEndNodes, directionLines); // 获取需要删除的路径
directionLines.removeAll(invalidRoads); // 删除无效的路径
// System.out.println(directionLines.toString());
Graph pra = new Graph(directionLines);
String begin = "node12"; // 起始点
String end = "node1"; // 终结点
// 获取所有有效路径
pra.getAllPaths(begin, end);
Iterator<String> it = pra.getResultSet().iterator();
System.out.println("-----------------从" + begin + "至" + end + "的有效路径如下-----------------");
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
四、数据集
{"1":{"2":1},"2":{"1":1,"3":1,"19":1},"3":{"2":1,"4":1,"9":1},"4":{"3":1,"5":1},"5":{"4":1},"6":{"9":1},"7":{"10":1},"8":{"11":1},"9":{"3":1,"6":1,"10":1},"10":{"7":1,"9":1,"11":1,"12":1},"11":{"8":1,"10":1},"12":{"10":1,"13":1,"17":1},"13":{"12":1,"14":1,"15":1},"14":{"13":1,"16":1},"15":{"13":1},"16":{"14":1},"17":{"12":1,"18":1},"18":{"17":1,"19":1,"20":1},"19":{"2":1,"18":1},"20":{"18":1}}
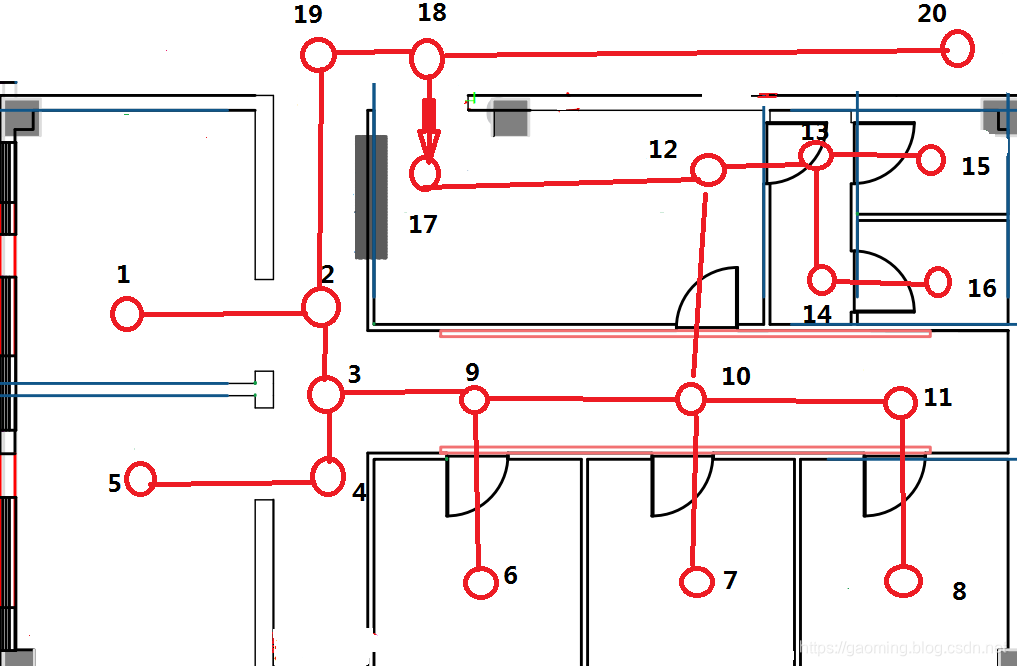
五、效果展示
-----------------从node12至node1的有效路径如下-----------------
[node12, node17, node18, node19, node2,node1]
[node12, node10, node9, node3, node2,node1]
Java 计算两点间的全部路径(二)的更多相关文章
- Java 计算两点间的全部路径(一)
算法要求: 在一个无向连通图中求出两个给定点之间的所有路径: 在所得路径上不能含有环路或重复的点: 算法思想描述: 整理节点间的关系,为每个节点建立一个集合,该集合中保存所有与该节点直接相连的节点(不 ...
- HDOJ2001计算两点间的距离
计算两点间的距离 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- hdu2001 计算两点间的距离【C++】
计算两点间的距离 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- 计算两点间的距离,hdu-2001
计算两点间的距离 Problem Description 输入两点坐标(X1,Y1),(X2,Y2),计算并输出两点间的距离. Input 输入数据有多组,每组占一行,由4个实数组成,分别表示x1 ...
- TSQL 根据经纬度计算两点间的距离;返回米(m)
-- ============================================= -- Author:Forrest -- Create date: 2013-07-16 -- Des ...
- 转:Math: Math.atan() 与 Math.atan2() 计算两点间连线的夹角
我们可以使用正切操作将角度转变为斜率,那么怎样利用斜率来转换为角度呢?可以利用斜率的反正切函数将他转换为相应的角度.as中有两个函数可以计算反正切,我们来看一下. 1.Math.atan() Math ...
- 经纬度计算两点间的距离,根据距离排序SQL
#java的Utilspublic class DistanceUtil { // 地球平均半径 private static final double EARTH_RADIUS = 6378137; ...
- J - 计算两点间的距离
Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Description 输入两 ...
- 计算两点间的距离-hdu2001
Problem Description 输入两点坐标(X1,Y1),(X2,Y2),计算并输出两点间的距离. Input 输入数据有多组,每组占一行,由4个实数组成,分别表示x1,y1,x2,y2 ...
随机推荐
- GitHub:Microsoft
ylbtech-GitHub:Microsoft 1.返回顶部 2.返回顶部 3.返回顶部 4.返回顶部 5.返回顶部 1. https://github.com/microsoft ...
- c# 动态编译CodeDomProvider.CompileAssemblyFromSource(CompilerParameters cp,string code)
1.使用c#动态编译,可参考如下: //生成c#代码 string code = GenerateCode(); CodeDomProvider cdp = CodeDomProvider.Creat ...
- 动态初始化swiper时,轮播图划不动得各种bug解决方法
var mybanner = new Swiper('.i-gd-banner', { speed: 500, loop: true, observer:true,//修改swiper自己或子元素时, ...
- 使用gimp画线、矩形、圆等
使用gimp画线.矩形.圆等 https://blog.csdn.net/tody_guo/article/details/7628508 2012年06月03日 19:08:47 Tody Guo ...
- ansible加速不管用
ansible加速 试过不管用,反而更慢 cat > /root/.ssh/config <<EOF Host * Compression yes ServerAliveInterv ...
- 关于ckeditor在IE下出现不兼容的问题
今天在用ckeditor时在ie下测试出现了不兼容问题,样式,字体等属性设置不了. 后来在html标签上方添加了: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD ...
- Java并发编程之程序运行堆栈分析
Java程序运行的堆栈分析 1.JVM运行时数据区 JVM通过加载class文件的数据来执行程序.JVM在运行时会划分不同的区域以存放数据.如下图所示: 线程共享部分:所有线程都能访问这块内存的数据, ...
- Win10无线网络配置VMware的nat网络
1.在windows上用运行cmd,用ipconfig /all查看可用网络的dns服务器 2.配置VMnet8,其dns与本地的dns服务器相同 3.打开VMware Workstation 的编辑 ...
- celery 调用scrapy
我的环境: celery 3.1.25 python 3.6.9 window10 celery tasks 代码如下,其中 QuotesSpider 是我的scrapy项目爬虫类名称 from ce ...
- JS中正则表达式应用
判断字符串是否含有中文字符: var pattern = /.*[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+.*$/; var str = "asd按时"; console.log(patte ...
