mysql内存管理
1 内存管理结构
mysql有自己的内存申请和释放机制
mysql层有mem_root
innodb层有mem_heap,mem_pool,buf_pool
它们的结构图如下
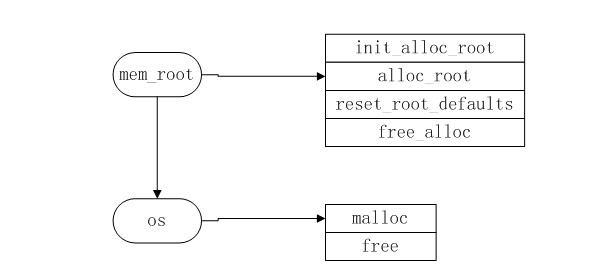

2 mem_root
mem_root是mysql层的动态内存管理
typedef struct st_used_mem
{ /* struct for once_alloc (block) */
struct st_used_mem *next; /* Next block in use */
unsigned int left; /* memory left in block */
unsigned int size; /* size of block */
} USED_MEM; typedef struct st_mem_root
{
USED_MEM *free; /* blocks with free memory in it */
USED_MEM *used; /* blocks almost without free memory */
USED_MEM *pre_alloc; /* preallocated block */
/* if block have less memory it will be put in 'used' list */
size_t min_malloc;
size_t block_size; /* initial block size */
unsigned int block_num; /* allocated blocks counter */
/*
first free block in queue test counter (if it exceed
MAX_BLOCK_USAGE_BEFORE_DROP block will be dropped in 'used' list)
*/
unsigned int first_block_usage; void (*error_handler)(void);
} MEM_ROOT;
mem_root主要由两个链表组成free和used。
free:存放有空闲的block,其中的block可能部分被使用。
used:存放已使用的block,其中block可能有少量空闲.
block_size:初始块大小,后面分配的块可能比block_size大。
pre_alloc:一直指向初始化时分配的block,改block开始在free链表中,随着内存的不断申请,改block可能会存在于used链表中
2.1 init_alloc_root
初始化一个block放入free链表,pre_alloc指向这个链表
2.2 alloc_root
首先从free链表中查找,如果有空间合适的block,则直接使用,若该block剩余空间小于min_malloc,则会放入used链表头部。如果没有空间合适的block,则新分配block放入free链表尾部。
2.3 reset_root_defaults
1没有初始化的mem_root不需要reset
满足if (!mem_root->pre_alloc || mem_root->pre_alloc->size != size)才reset
2 只释放完全没有使用的空闲块。
2.4 free_root
MY_MARK_BLOCKS_FREE:释放所有块
MY_KEEP_PREALLOC:只保留pre_alloc块
3 mem_pool
内存池。innodb早期自己实现的一套伙伴算法内存管理系统,由参数innodb_use_sys_malloc 控制开启和关闭,默认关闭,即直接从操作系统申请和释放内存.参见http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E17952_01/refman-5.5-en/innodb-performance-use_sys_malloc.html
mem_pool_t
/** Data structure for a memory pool. The space is allocated using the buddy
algorithm, where free list i contains areas of size 2 to power i. */
struct mem_pool_t{
byte* buf; /*!< memory pool */
ulint size; /*!< memory common pool size */
ulint reserved; /*!< amount of currently allocated
memory */
ib_mutex_t mutex; /*!< mutex protecting this struct */
UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(mem_area_t)
free_list[]; /*!< lists of free memory areas: an
area is put to the list whose number
is the 2-logarithm of the area size */
};
/** Memory area header */
struct mem_area_t{
ulint size_and_free; /*!< memory area size is obtained by
anding with ~MEM_AREA_FREE; area in
a free list if ANDing with
MEM_AREA_FREE results in nonzero */
UT_LIST_NODE_T(mem_area_t)
free_list; /*!< free list node */
};
buf:一片连续的内存区域
mem_area_t:内存块, size_and_free标记内存块的大小和是否已使用。
free_list[64]: 64个桶,每个桶编号为0,1,2,3,…,i;每个桶依次存放2i大小的内存块。
3.1初始化
mem_pool_create
在服务启动时调用一次
如初始化一个19字节的内存池
19=100011=24+21+20
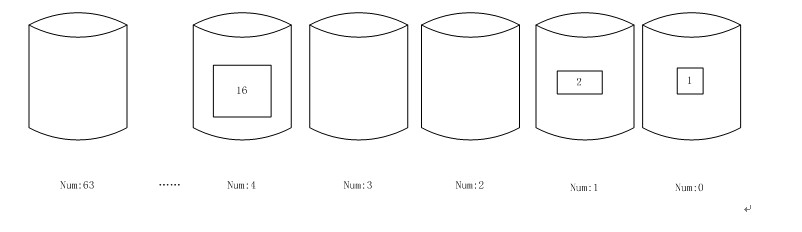
3.2 mem_area_alloc
void*
mem_area_alloc(
/*===========*/
ulint* psize, /*!< in: requested size in bytes; for optimum
space usage, the size should be a power of 2
minus MEM_AREA_EXTRA_SIZE;
out: allocated size in bytes (greater than
or equal to the requested size) */
mem_pool_t* pool)
从pool中申请内存块,psize<=2i,i为满足此条件的最小值。当第i个中存在空闲时,直接取出。当第i个中不存在空闲块时,从i+1个桶中切割一半到第i个桶中,这是一个递归的过程。具体实现在mem_pool_fill_free_list;
以申请大小为3的内存为例,(为了说明方便,这里不考虑块中MEM_AREA_EXTRA_SIZE的空间)
申请的得到大小为4的块,这是内存池中的结构如下
3.3 mem_pool_free
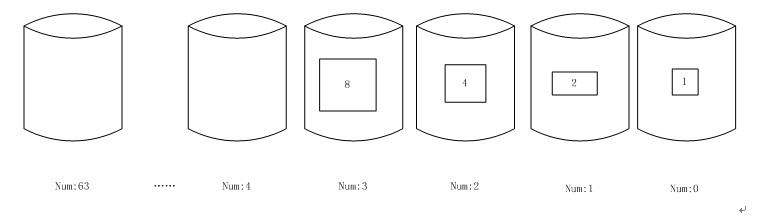
释放一个块到pool中,将块放入对应大小的桶i中,如果桶i中存在自己的伙伴(和自己相邻的内存块,可能在左边也可能在右边),则合并放入i+1的桶中,此过程递归,直到没有可以合并的伙伴。
找自己伙伴的函数如下
mem_area_t*
mem_area_get_buddy(
/*===============*/
mem_area_t* area, /*!< in: memory area */
ulint size, /*!< in: memory area size */
mem_pool_t* pool) /*!< in: memory pool */
{
mem_area_t* buddy;
ut_ad(size != );
if (((((byte*) area) - pool->buf) % ( * size)) == ) {
/* The buddy is in a higher address */
buddy = (mem_area_t*)(((byte*) area) + size);
if ((((byte*) buddy) - pool->buf) + size > pool->size) {
/* The buddy is not wholly contained in the pool:
there is no buddy */
buddy = NULL;
}
} else {
/* The buddy is in a lower address; NOTE that area cannot
be at the pool lower end, because then we would end up to
the upper branch in this if-clause: the remainder would be
0 */
buddy = (mem_area_t*)(((byte*) area) - size);
}
return(buddy);
}

找x的伙伴:
1 首先确定x的伙伴在高位还是在低位,x左边的块大小都>=x的大小,且x左边的块大小=2i*sizeof(x) (i>0);。
如果x的伙伴是y,则(c-a)%(2*sizeof(x))=sizeof(x) != 0
如果x的伙伴是z,则(c-a)%(2*sizeof(x))= 0
需要说明的是:在桶中的块都是空闲块。
以释放刚申请得的大小为4的块为例,释放后,内存结构如下,回到了初始状态。

3.4 mem_pool_free
在服务关闭时调用一次
释放buf和mem_pool结构即可
mem_pool_free(
/*==========*/
mem_pool_t* pool) /*!< in, own: memory pool */
{
ut_free(pool->buf);
ut_free(pool);
}
4 buf_pool
块/页缓存池。
4.1buf_pool_init
Innodb_buffer_pool_instances指定了bp的个数,innodb_buffer_pool_size指定所有bp的总大小。
buf_pool_init在服务启动时调用一次
bp初始化主要是申请内存,并初始化free链表。每个buf_page_t的大小为innodb_page_size.
UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(buf_page_t) free;
4.2 buf_block_alloc
从free链表头部摘出
不放入LRU链表
4.3 buf_block_free
放回free链表头部
4.4 buffer_pool_free
在服务关闭时调用一次
5 mem_heap
/** The info structure stored at the beginning of a heap block */
struct mem_block_info_t {
ulint magic_n;/* magic number for debugging */
char file_name[];/* file name where the mem heap was created */
ulint line; /*!< line number where the mem heap was created */
UT_LIST_BASE_NODE_T(mem_block_t) base; /* In the first block in the
the list this is the base node of the list of blocks;
in subsequent blocks this is undefined */
UT_LIST_NODE_T(mem_block_t) list; /* This contains pointers to next
and prev in the list. The first block allocated
to the heap is also the first block in this list,
though it also contains the base node of the list. */
ulint len; /*!< physical length of this block in bytes */
ulint total_size; /*!< physical length in bytes of all blocks
in the heap. This is defined only in the base
node and is set to ULINT_UNDEFINED in others. */
ulint type; /*!< type of heap: MEM_HEAP_DYNAMIC, or
MEM_HEAP_BUF possibly ORed to MEM_HEAP_BTR_SEARCH */
ulint free; /*!< offset in bytes of the first free position for
user data in the block */
ulint start; /*!< the value of the struct field 'free' at the
creation of the block */
#ifndef UNIV_HOTBACKUP
void* free_block;
/* if the MEM_HEAP_BTR_SEARCH bit is set in type,
and this is the heap root, this can contain an
allocated buffer frame, which can be appended as a
free block to the heap, if we need more space;
otherwise, this is NULL */
void* buf_block;
/* if this block has been allocated from the buffer
pool, this contains the buf_block_t handle;
otherwise, this is NULL */
#endif /* !UNIV_HOTBACKUP */
#ifdef MEM_PERIODIC_CHECK
UT_LIST_NODE_T(mem_block_t) mem_block_list;
/* List of all mem blocks allocated; protected
by the mem_comm_pool mutex */
#endif
};
innodb绝大多数内存申请和释放都是在mem_heap上进行的
mem_heap实际上是一个内存块链表,内存块大小依次增长,至少是两倍的增长。
5.1 mem_heap_create
初始内存块链表,根据参数初始化内存块,此时base链表只有一个内存块
if (heap && heap->magic_n != MEM_BLOCK_MAGIC_N) {
mem_analyze_corruption(heap);
}
/* In dynamic allocation, calculate the size: block header + data. */
len = MEM_BLOCK_HEADER_SIZE + MEM_SPACE_NEEDED(n);
#ifndef UNIV_HOTBACKUP
if (type == MEM_HEAP_DYNAMIC || len < UNIV_PAGE_SIZE / ) {
ut_ad(type == MEM_HEAP_DYNAMIC || n <= MEM_MAX_ALLOC_IN_BUF);
block = static_cast<mem_block_t*>(
mem_area_alloc(&len, mem_comm_pool));
} else {
len = UNIV_PAGE_SIZE;
if ((type & MEM_HEAP_BTR_SEARCH) && heap) {
/* We cannot allocate the block from the
buffer pool, but must get the free block from
the heap header free block field */
buf_block = static_cast<buf_block_t*>(heap->free_block);
heap->free_block = NULL;
if (UNIV_UNLIKELY(!buf_block)) {
return(NULL);
}
} else {
buf_block = buf_block_alloc(NULL);
}
block = (mem_block_t*) buf_block->frame;
}
ut_ad(block);
block->buf_block = buf_block;
block->free_block = NULL;
#else /* !UNIV_HOTBACKUP */
len = MEM_BLOCK_HEADER_SIZE + MEM_SPACE_NEEDED(n);
block = ut_malloc(len);
ut_ad(block);
#endif /* !UNIV_HOTBACKUP */
以上代码可以看出
Mem_heap的内存来源可以有三种
1 mem_pool 的mem_area_alloc
2 buffer_pool的buf_block_alloc
3 ut_malloc ->malloc
5.2 mem_heap_alloc
从base链表最后一个内存块分配内存,不够则新分配一个较大内存块,放入base链表的最后。
5.3 mem_heap_free_heap_top
void
mem_heap_free_heap_top(
/*===================*/
mem_heap_t* heap, /*!< in: heap from which to free */
byte* old_top)/*!< in: pointer to old top of heap */
释放base链表从old_top到最后的内存块,old_top不释放
5.4 mem_heap_free_heap_top
释放base链表最后一个内存块
5.5 mem_heap_free
释放base链表所有内存块
mysql内存管理的更多相关文章
- MySQL内存管理机制浅析
GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源. GreatSQL是MySQL的国产分支版本,使用上与MySQL一致. 目录 一.placement new的定义 二.pl ...
- 利用 gperftools 对nginx mysql 内存管理 性能优化
利用 gperftools 对nginx 与 mysql 进行 内存管理 性能优化 降低负载. Gperftools 是由谷歌开发.官方对gperftools 的介绍为: These tools ...
- RDS MySQL内存管理
官方文档地址:https://help.aliyun.com/product/26090.html?spm=5176.7920929.1290474.7.2c6f4f7bACaToi 官方文档地址:h ...
- 使用jemalloc优化nginx和mysql内存管理
预先安装autoconf 和 make yum -y install autoconf make jemalloc的安装jiemalloc 开源项目网站 http://www.canonware.co ...
- innodb源码解析 - mem0_.c - 基本内存管理
The basic element of the memory management is called a memoryheap. A memory heap is conceptually ast ...
- jemalloc优化MySQL、Nginx内存管理
上一篇文章<TCMalloc优化MySQL.Nginx.Redis内存管理>,下面来看下jemalloc jemalloc源于Jason Evans 2006年在BSDcan confer ...
- TCMalloc优化MySQL、Nginx、Redis内存管理
TCMalloc(Thread-Caching Malloc)与标准glibc库的malloc实现一样的功能,但是TCMalloc在效率和速度效率都比标准malloc高很多.TCMalloc是 goo ...
- MySQL系列:innodb源代码分析之内存管理
在innodb中实现了自己的内存池系统和内存堆分配系统,在innodb的内存管理系统中,大致分为三个部分:基础的内存块分配管理.内存伙伴分配器和内存堆分配器.innodb定义和实现内存池的主要目的是提 ...
- MySQL InnoDB技术内幕:内存管理、事务和锁
前面有多篇文章介绍过MySQL InnoDB的相关知识,今天我们要更深入一些,看看它们的内部原理和机制是如何实现的. 一.内存管理 我们知道,MySQl是一个存储系统,数据最后都写在磁盘上.我们以前也 ...
随机推荐
- C#基础篇三流程控制1
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace P01R ...
- PHP MYSQL登陆和模糊查询
PHP MYSQL登陆和模糊查询 PHP版本 5.5.12 MYSQL版本 5.6.17 Apache 2.4.9 用的wampserver 一.PHPMYSQL实现登陆: 一共含有两个 ...
- Mysql - 增量脚本中修改字段属性
在增量部署系统的时候, 经常需要提供增量修改的脚本, 如果是修改存储过程或者自定义函数, 那还是很好改的, 不用担心表功能收到影响. 如果是改字段呢? 首先不知道字段是不是已经在系统里面, 没有的话, ...
- 如何替代即将淘汰的Flash方案?
欢迎大家前往腾讯云+社区,获取更多腾讯海量技术实践干货哦~ 本文由MarsBoy发表于云+社区专栏 | 导语 Web技术飞速发展的如今,我们在感受新技术带来的便捷和喜悦的同时,也时常在考虑着一个问题: ...
- ABP 数据库 -- ABP&EF中的多表、关联查询
本文介绍一下ABP中的多表查询. 1.创建实体 多表查询,在ABP或者EF中都很简单,这里我们创建一个Demo,一个学生实体.一个学校实体. 学校里面可以有很多学生,学生有一个学校. 实体如下: 学校 ...
- 查询Sql Server数据库对象结构
查询Sql Server数据库对象结构 查询数据库 查询架构 查询表 查询列 查询存储过程 查询视图 1.查询某一服务器下所有数据库 select t.[name] as 数据库 from sys.d ...
- 【Java基础】5、java中的匿名内部类
匿名内部类也就是没有名字的内部类 正因为没有名字,所以匿名内部类只能使用一次,它通常用来简化代码编写 但使用匿名内部类还有个前提条件:必须继承一个父类或实现一个接口 实例1:使用匿名内部类来实现抽象方 ...
- 创建Cordova项目 报错Error: Unhandled "error" event
cordova版本7.0以上版本 创建cordova项目错误信息 Error: Unhandled "error" event. ( Error from Cordova Fet ...
- ES6——TDZ(暂时性死区)
暂时性的死区(Temporal Dead Zone),简写为 TDZ: 只要块级作用域里存在let命令,它所声明的变量就绑定这个区域,不在受外部的影响 let 和 const 声明的变量不会被提升到作 ...
- JS 显示隐藏DIV
JS关闭DIV HTML <div id="bar1"> <p onclick="removeElement('bar1')">关闭&l ...
