c语言实现--带头结点单链表操作
可能是顺序表研究的细致了一点,单链表操作一下子就实现了。这里先实现带头结点的单链表操作。
大概有以下知识点.
1;结点:结点就是单链表中研究的数据元素,结点中存储数据的部分称为数据域,存储直接后继地址的部分称为指针域。
2;结点示意图:
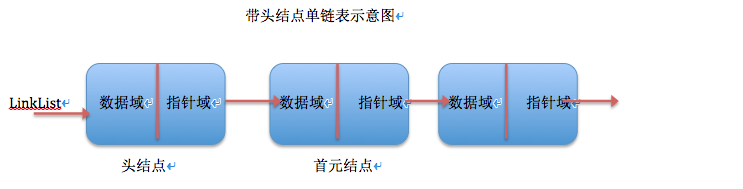
3;头指针:头指针始终指向链表第一个元素,当有头结点时头结点就是链表第一个元素。头指针具有标识左右,故头指针命名为链表的名字,这里为linklist。头指针是一定存在的。
4;头结点:引入头结点的目的是,将链表首元结点的插入和删除操作与其他结点的插入和删除操作统一起来。(即头指针地址不在发生变化)
5;单链表结点结构体表示:
1 struct LNode
2 {
3 int data; //姑且认为其数据为整型
4 struct LNode * next;
5 };
6
7 typedef struct LNode * linklist
6;单链表的操作集合,头文件 defs.h
1 #ifndef _DEFS_H_
2 #define _DEFS_H_
3
4 #include<stdio.h>
5 #include<stdlib.h>
6 #include<malloc.h>
7
8 struct LNode //单链表结点的定义
9 {
10 int data;
11 struct LNode * next;
12 }
13 typedef struct LNode * linklist
14
15 //操作集合
16 void InitList(linklist *L); //申请头结点,头指针地址改变
17 void DestroyList(linklist *L); //须释放头结点,头指针地址改变
18 void ClearList(linklist L); //保留头结点,头指针地址不变
19 void ListEmpty(linklist L);
20 int ListLength(linklist L);
21 int GetElem(linklist L, int i, int *e);
22 int LocateElem(linklist L, int e);
23 int PriorElem(linklist L, int cur_e, int *pri_e);
24 int NextElem(linklist L, int cur_e, int *nex_e);
25 int ListInsert(linklist L, int i, int e); //插入不改变头指针的值
26 int ListDelete(linklist L, int i, int *e); //删除操作也不改变头指针的值
27 void TravelList(linklist L);
28 #endif
7;InitList操作实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 void InitList(linklist *L) //接受头指针的地址值
4 {
5 *L = (linklist)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode)); //*L表示头指针
6
7 if (*L == NULL)
8 {
9 printf("分配结点失败。\n");
10 exit(-1);
11 }
12 (*L)->next = NULL; //置头结点的next域为空
13 }
InitList.c
8;DestroyList操作的实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 void DestroyList(linklist *L) //接受的参数为头指针的地址值
4 {
5 linklist p ;
6 while (*L)
7 {
8 p = (*L)->next; //释放结点之前先保存结点的下一个地址,防止线索被断
9 free(*L);
10 *L = p; //将下一个结点,作为释放结点
11 }
12 }
DestroyList.c
9;ClearList操作的实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 void ClearList(linklist L) //保留头结点
4 {
5 linklist p = L->next; //p将头指针的next值保存起来,p指向首元结点
6 L->next = NULL;
7
8 DestroyList(&p); //调用撤销函数,释放后面的结点
9
10 }
ClearList.c
10;ListEmpty操作的实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 void ListEmpty(linklist L)
4 {
5 if (L->next == NULL) //判断头结点指针域是否为空
6 printf("链表为空.\n");
7 else
8 printf("链表不为空.\n");
9 }
ListEmpty.c
11;ListLength操作实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 int ListLength(linklist L)
4 {
5 int j=0; //作为计数器
6 linklist p = L->next; //p指向首元结点,作为移动指针
7
8 while (p) //从首元结点开始
9 {
10 ++j;
11 p = p->next;
12 }
13 return j;
14 }
ListLength.c
12;GetElem操作实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 int GetElem(linklist L, int i, int *e) // 1<= i <=ListLength(L)
4 {
5 int j = 0; //j作为计数器
6 linklist p = L;
7
8 while (p && j<i) //找到第i个结点
9 {
10 ++j;
11 p = p->next;
12 }
13 if (!p || i<1) //取值位置不合理
14 exit(0);
15
16 *e = p->data;
17 return 0;
18 }
GetElem.c
13;LocateElem操作实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 int LocateElem(linklist L, int e)
4 {
5 linklist p = L->next; //p作为移动指针,p指向第一个元素
6 int j = 0; //j作为计数器
7
8 while (p)
9 {
10 ++j;
11 if (p->data == e)
12 return j;
13 p = p->next;
14 }
15 return 0;
16 }
LocateElem.c
14;PriorElem操作实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 int PriorElem(linklist L, int cur_e, int *pri_e) //第一个元素无前驱
4 {
5 linklist p = L->next; //p指向首元结点
6 linklist q;
7
8 while (p)
9 {
10 q = p->next; //q为p的后继
11
12 if (q && q->data == cur_e) //则p就是q的前驱
13 *pri_e = p->data;
14 p = q; //循环
15 }
16 return 0;
17 }
PriorElem.c
15;NextElem操作的实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 int NextElem(linklist L, int cur_e, int *nex_e) //最后一个元素无后继
4 {
5 linklist p = L->next; //p指向首元结点
6 linklist q;
7
8 while (p)
9 {
10 q = p->next; //q为p的后继
11
12 if (q && p->data == cur_e) //p有后继,且p的数据域与当前值相等
13 *nex_e = q->data;
14 p = q; //更新p
15 }
16 return 0;
17 }
NextElem.c
16;ListInsert操作的实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 int ListInsert(linklist L, int i, int e) //1<= i <= ListLength(L)
4 {
5 int j=0; //j为基数器
6 linklist p = L; //p为移动指针,p指向头结点
7 linklist q, s;
8
9 while (p && j<i-1) //找到第i-1个结点
10 {
11 ++j;
12 p = p->next;
13 }
14
15 if (!p || i<1) //插入位置不合理
16 return 0;
17
18 q = p->next; //q指向第i个结点
19
20 s = (linklist)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
21 if (!s) //分配失败
22 exit(-1);
23
24 s->data = e; //置s的数据域为e
25 s->next = q; //插入操作,是指针连起来
26 p->next = s;
27 return 0;
28 }
ListInsert.c
17;ListDelete操作的实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 int ListDelete(linklist L, int i, int *e) // 1<= i <=ListLength(L)
4 {
5 int j = 0; //j为计数器
6 linklist p = L;
7 linklist q;
8
9 while (p && j<i-1) //找到第i-1个结点
10 {
11 ++j;
12 p = p->next;
13 }
14
15 if (!p || i<1) //删除位置不合理
16 exit(0);
17 q = p->next; //q指向第i个结点
18
19 *e = q->data; //先将第i个结点的数据域带出
20 p->next = q->next; //连起指针
21 free(q); //释放第i个结点
22
23 return 0;
24 }
ListDelete.c
18;TravelList操作实现
1 #include"defs.h"
2
3 void TravelList(linklist L)
4 {
5 linklist p = L->next; //p指向首元结点
6 int j = 0; //j为计数器
7
8 while (p)
9 {
10 ++j;
11 printf("第%d个结点的数据域的值为:%d\n", j, p->data);
12 p = p->next; //更新p
13 }
14 }
TravelList.c
19;makefile的实现,其代码与顺序表的一样,这里换成另一种写法
1 object = main.o InitList.o DestroyList.o ClearList.o ListEmpty.o \
2 ListLength.o GetElem.o LocateElem.o PriorElem.o NextElem.o \
3 ListInsert.o ListDelete.o TravelList.o
4
5 test : $(object)
6 gcc -g -Wall -o test $(object)
7
8 $(object) : defs.h
9
10 .PHONY : clean
11 clean :
12 rm -f *.o
20;顺序表与单链表的比较
顺序表是用一段地址连续的存储单元来存放数据元素,适合查找,不适合频繁插入和删除(没一次操作都是O(n));
单链表是用不连续的存储单元,其数据元素之间是用指针来连接,每一次的查找都必须通过头指针来遍历,因此其不适合频繁的查找。但是对于插入和删除操作,它不需要移动其它元素,算法时间复杂度为O(1),因此特别适合频繁的插入和删除操作。
c语言实现--带头结点单链表操作的更多相关文章
- 数据结构之 线性表---单链表操作A (删除链表中的指定元素)
数据结构上机测试2-1:单链表操作A Time Limit: 1000MS Memory limit: 4096K 题目描述 输入n个整数,先按照数据输入的顺序建立一个带头结点的单链表,再输入一个数据 ...
- Java带头节点单链表的增删合并以及是否有环
带头节点单链表 1.优势: 1)当链表为空时,指针指向头结点,不会发生null指针异常 2)方便特殊操作(删除第一个有效节点或者插入一个节点在表头) 3)单链表加上头结点之后,无论单链表是否为空,头指 ...
- 单链表操作B 分类: 链表 2015-06-07 12:42 15人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
数据结构上机测试2-2:单链表操作B TimeLimit: 1000ms Memory limit: 65536K 题目描述 按照数据输入的相反顺序(逆位序)建立一个单链表,并将单链表中重复的元素删除 ...
- c语言实现--不带头结点的单链表操作
1,不带头结点的单链表操作中,除了InitList(),GetElem(),ListInsert(),ListDelete()操作与带头结点的单链表有差别外,其它的操作基本上一样. 2,不带头结点单链 ...
- C语言,单链表操作(增删改查)(version 0.1)
这天要面试,提前把链表操作重新写了一遍.备份一下,以备不时之需. 希望有人能看到这篇代码,并指正. // File Name : list.h #include "stdafx.h" ...
- C单链表操作
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define ElemType int #define Status int #define O ...
- C++学习(三十五)(C语言部分)之 单链表
单链表 就好比火车 火车头-->链表头部火车尾-->链表尾部火车厢-->链表的节点火车厢连接的部分-->指针火车中的内容-->链表节点的的数据链表节点包含数据域和指针域数 ...
- C语言版本:循环单链表的实现
SClist.h #ifndef __SCLIST_H__ #define __SCLIST_H__ #include<cstdio> #include<malloc.h> # ...
- C++ 单链表操作总结
第一.单链表的定义和操作 #include <iostream> using namespace std; template <typename T> struct Node ...
随机推荐
- MySQL学习Day01
1.MySQL的层级关系 2.xampp的安装使用 如果之前安装过mysql那么就需要将原来的mysql完全卸载干净 1.卸载之前安装的MySQL 安装xampp需要先卸载之前的mysql,以及更改m ...
- 没搞清楚网络I/O模型?那怎么入门Netty
微信搜索[阿丸笔记],关注Java/MySQL/中间件各系列原创实战笔记,干货满满. 本文是Netty系列笔记第二篇 Netty是网络应用框架,所以从最本质的角度来看,是对网络I/O模型的封装使用. ...
- Windows Server 2012 R2远程桌面默认端口修改
修改3389默认端口可使服务器安全性进一步提升,可以避免阻断大部分的恶意暴力密码爆破. 在开始--运行菜单里,输入regedit 或者: 远程登陆服务器选择系统桌面中的"Windows Po ...
- 前端基础功能,原生js实现轮播图实例教程
轮播图是前端最基本.最常见的功能,不论web端还是移动端,大平台还是小网站,大多在首页都会放一个轮播图效果.本教程讲解怎么实现一个简单的轮播图效果.学习本教程之前,读者需要具备html和css技能,同 ...
- commons-lang3相关类实例
一.ArrayUtils //1.判断两个数组长度是否相等 ArrayUtils.isSameLength(new int[] {1,2,3,4}, new int[] {1,2,3,4});//tr ...
- JVM(八)执行引擎相关内容
一:两种解释器 JAVA字节码解释器: java字节码===>c++代码==>硬编码. 首先.java文件编译成字节码,遍历每行的字节码指令,因为每个字节码指令的含义都是固定的所以可以根据 ...
- JavaScript中创建数组的方式!
JavaScript中创建数组的方式! 利用数组字面量 // 1 直接量 console.log(Array.prototype); var arr = [1, 2, 4, 87432]; // 注意 ...
- windows 系统 MySQL_5.6.21安装教程
1.双击安装文件 mysql_installer_community_V5.6.21.1_setup.1418020972.msi,等待安装界面出现,见下图: 2.勾选:I accept thel ...
- Swagger2配置与使用
Swagger2配置与使用 Swagger2介绍 前后端分离开发模式中,api文档是最好的沟通方式. Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成.描述.调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 We ...
- charles安装使用乱码连手机等问题解决方案
捣鼓半天终于安装好了,给大家分享下我的过程 1.安装, 正常网上安装即可,我安装了个有汉化包的,,推荐链接 安装方法下载破解版,安装即可 安装包地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1 ...
