2、Spring Boot配置
1.配置文件
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名是固定的;
•application.properties
•application.yml
配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值;SpringBoot在底层都给我们自动配置好;
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language):以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;以前的配置文件;大多都使用的是xxxx.xml文件;
范例:YAML配置例子
|
server: port: 8081 |
范例:XML配置
|
<server> <port>8081</port> </server> |
2.YAML语法
[1].基本语法
语法: K: V:表示一对键值对(: v之间有个空格)
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
|
server: port: 8081 path: /hello |
属性和值也是大小写敏感;
[2].值的写法
(1).普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k: v:字面直接来写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
"":双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi
'':单引号;会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’:输出;zhangsan \n lisi
(2).对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对)
k: v:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进
对象还是k: v的方式
|
friends: lastName: zhangsan age: 20 |
行内写法:
|
friends: {lastName: zhangsan,age: 18} |
(3).数组(List、Set)
用- 值表示数组中的一个元素
|
pets: - cat - dog - pig |
行内写法
|
pets: [cat,dog,pig] |
[3].配置文件值注入
application.yml
|
server: port: 8081 person: lastname: zhangsan age: 18 boss: false birth: 2020/1/1 maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12} lists: - lisi - zhaoliu - zhangsan dog: name: 狗狗 age: 2 |
javaBean:
|
/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties: 告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定 默认从全局配置文件中获取值 * prefix="person":配置文件中将下面的所有属性进行一一映射 */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; |
可以导入配置文件处理器,以后编写配置就有提示
|
<!-- 可以导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行白丁会有提示 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> |
(1).properties配置文件在idea中默认utf-8可能会乱码
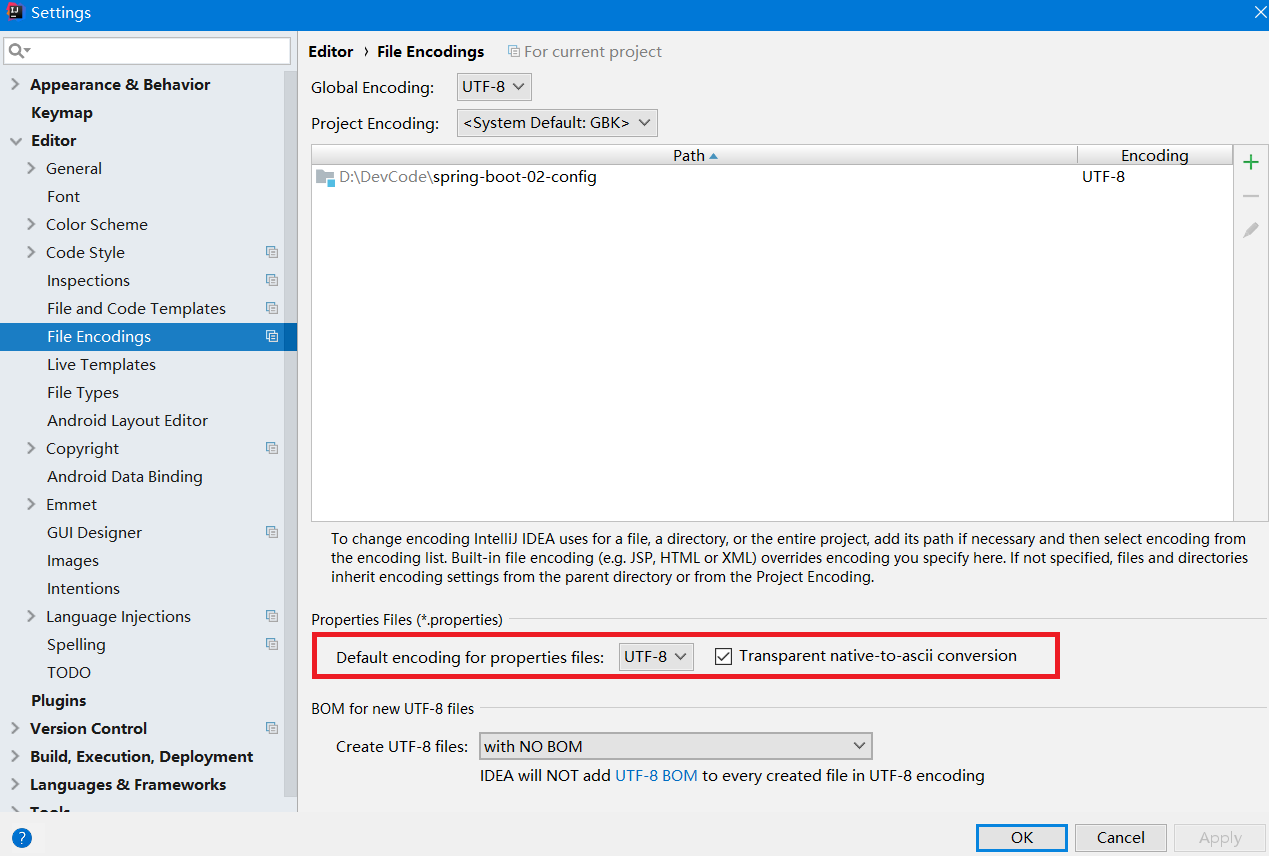
(2).@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
配置文件yml还是properties以上方式都能获取到值;
如何选择以上方式:
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
(3).配置文件注入值数据校验
|
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") @Validated public class Person { /** * <bean class="Person"> * <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property> * <bean/> */ //lastName必须是邮箱格式 //@Value("${person.last-name}") private String lastName; //@Value("#{11*2}") private Integer age; //@Value("true") private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; |
(4).@PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件;
|
/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties: 告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定 默认从全局配置文件中获取值 * prefix="person":配置文件中将下面的所有属性进行一一映射 */ @PropertySource(value={"classpath:person.properties"}) @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") //@Validated public class Person { /** * <bean class="Person"> * <properties name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></properties> * </bean> */ // @Value("${person.last-name}") private String lastName; // @Value("#{11*2}") private Integer age; // @Value("true") private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog; |
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
|
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"}) 导入Spring的配置文件让其生效 |
不编写Spring的配置文件
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="helloService" class="com.pluto.springboot.service.HelloService"></bean> </beans> |
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1)、配置类@Configuration------>Spring配置文件
2)、使用@Bean给容器中添加组件
|
/** * @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件 * * 在配置文件中用<bean><bean/>标签添加组件 * */ @Configuration public class MyAppConfig { //将方法的返回值添加到容器中;容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名 @Bean public HelloService helloService02(){ System.out.println("配置类@Bean给容器中添加组件了..."); return new HelloService(); } } |
[4].配置文件占位符

|
# idea配置文件默认为utf-8 #����Person��ֵ person.last-name=张三${random.uuid} person.age=${random.int} person.birth=2020/1/1 person.boss=false person.maps.k1=v1 person.maps.k2=14 person.lists=a,b,c person.dog.name=${person.last-name}_dog person.dog.age=15 |
[5].Profile
在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
默认使用application.properties的配置;
(1).在配置文件中指定开发环境
|
application.properties server.port=8081 spring.profiles.active=dev |
|
application-dev.properties server.port=8083 |
(2).yml文档快
yml支持多文档块方式
|
server: port: 8081 spring: profiles: active: prod --- server: port: 8083 spring: profiles: dev --- server: port: 8088 spring: profiles: prod |
(3).激活指定profile
1).在配置文件中指定spring.profiles.active=dev
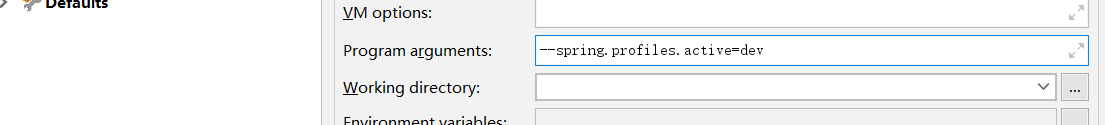
2).命令行
(1.Program arguments
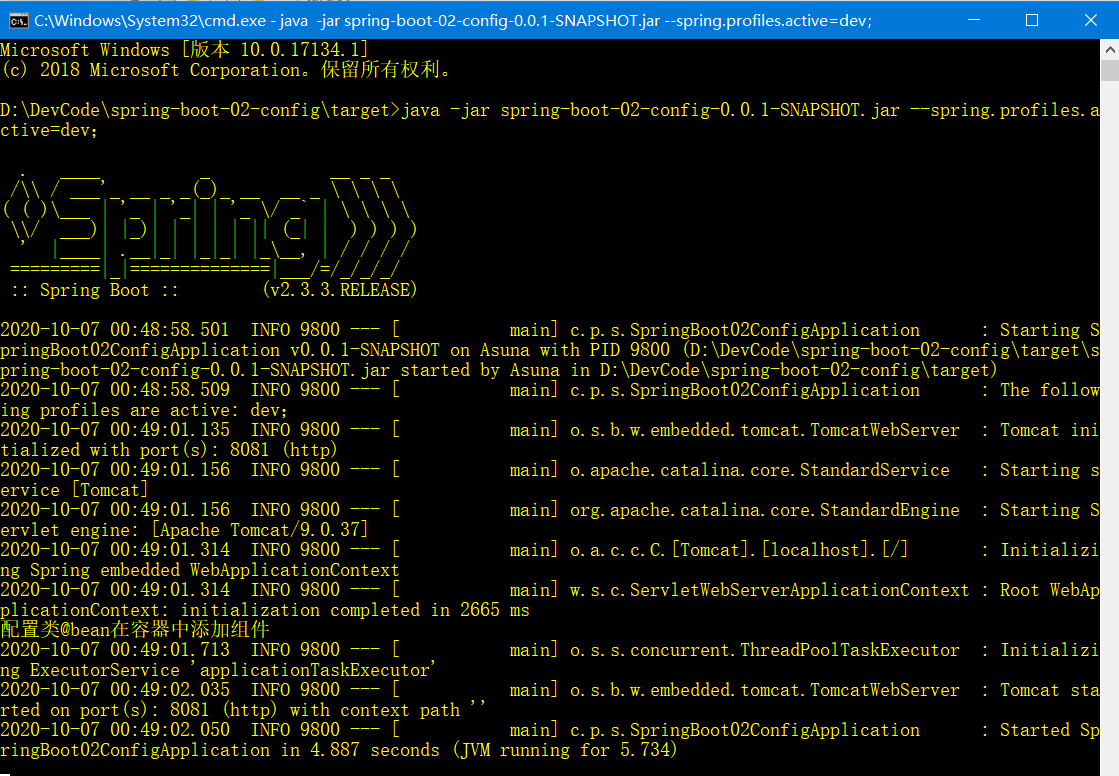
(2.CMD
|
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev; |
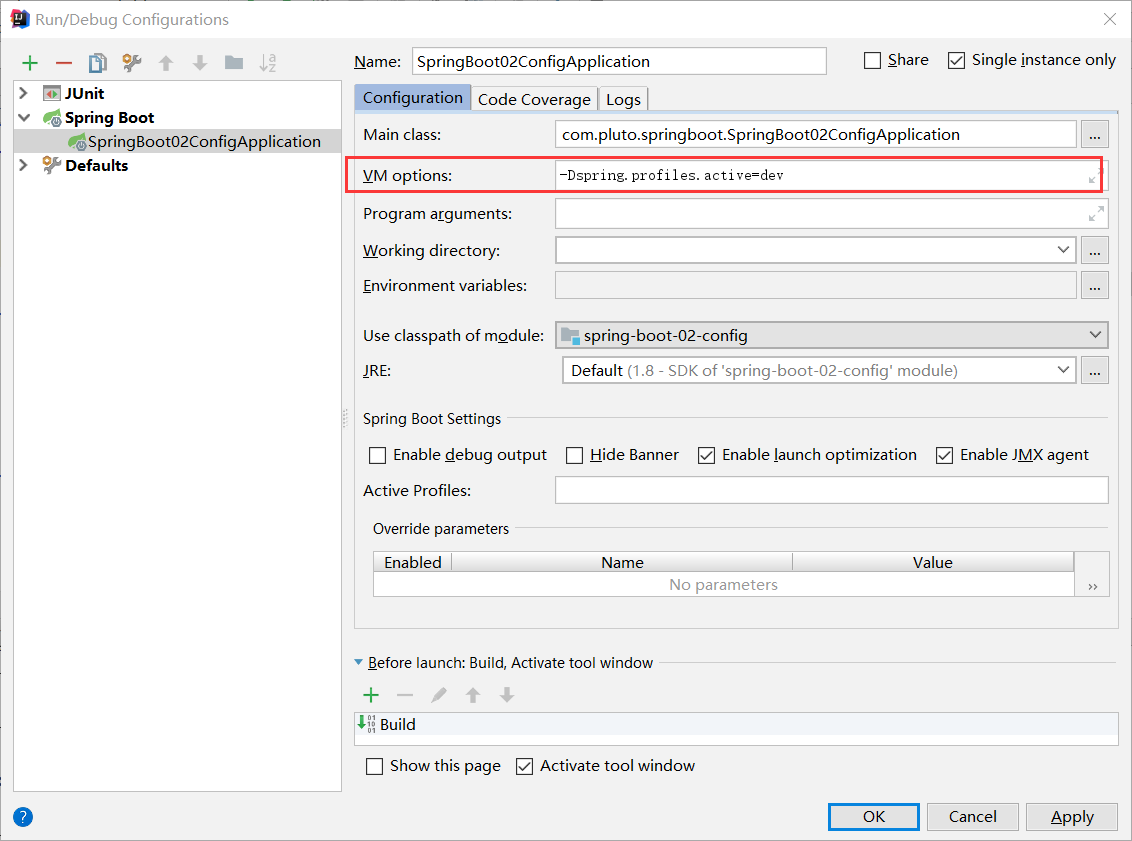
(3.虚拟机参数
|
-Dspring.profiles.active=dev |
[6].配置文件加载位置
springboot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件
–file:./config/
–file:./
–classpath:/config/
–classpath:/
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件;它们成互补配置;

我们还可以通过spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件位置
项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;指定配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置;
通过packet生成jar包


|
D:\DevCode\spring-boot-02-config-02\target>java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.config.location=G:/application.properties |
[7].外部配置加载顺序
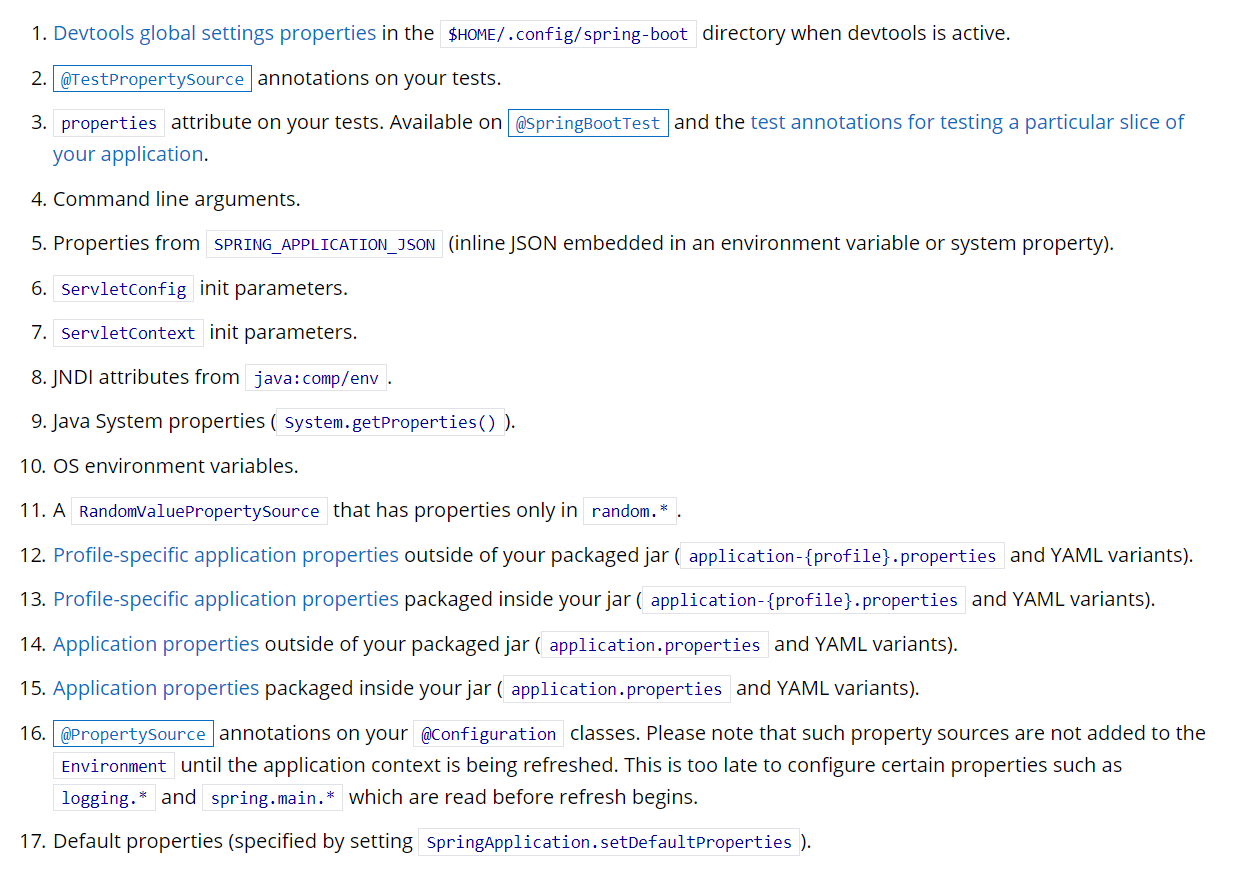
SpringBoot也可以从以下位置加载配置; 优先级从高到低;高优先级的配置覆盖低优先级的配置,所有的配置会形成互补配置
(1).命令行
多个配置用空格分开; --配置项=值
|
java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8086 --server.context-path=/hello |
(2)..来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
(3),Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
(4).操作系统环境变量
(5).RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找
优先加载带profile
(6).jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
(7).jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
加载不带profile
(8).jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
(9).jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
(10).@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
(11).通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
所有支持的配置加载来源:参考官方文档
[8].Spring自动配置原理
配置文件到底能写什么?怎么写?自动配置原理;
(1).自动配置原理
1).Spring启动的时候会自动加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能@SpringBootApplication
2).@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用

利用AutoConfigurationImportSelector给容器中导入一些组件
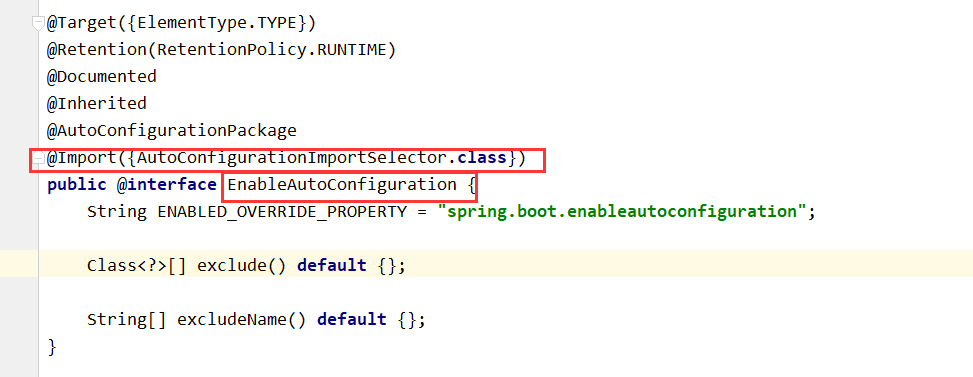
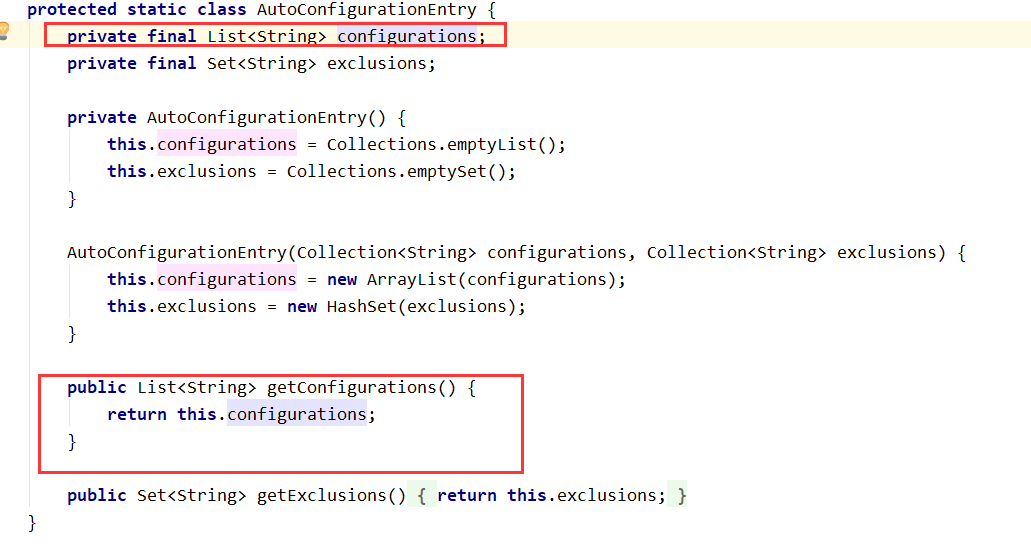
查看selectImports()方法的内容

获取候选的配置
|
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); |

|
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() |
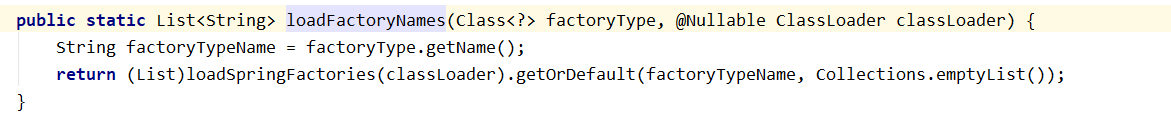
|
扫描所有jar包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象 |
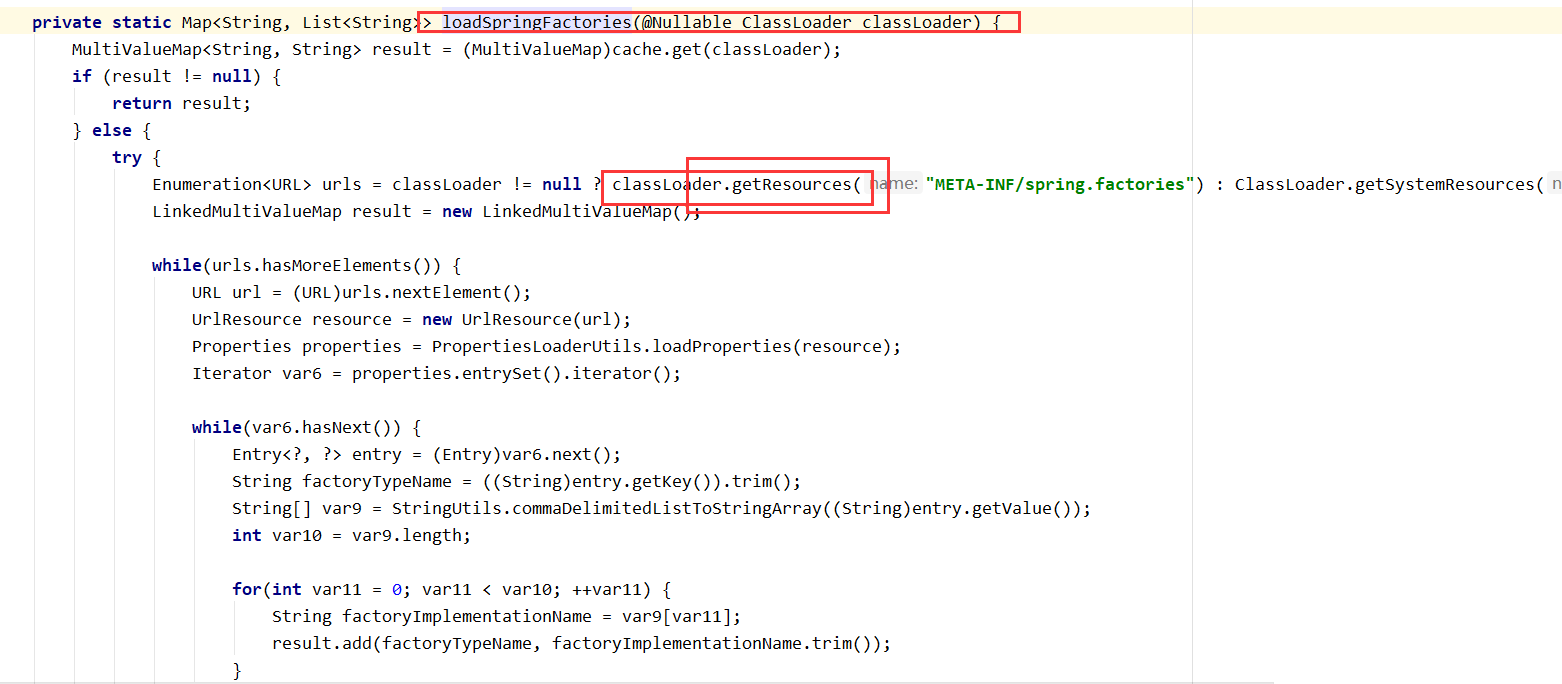
|
从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中 |
将类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;

|
# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration |
每个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
3).每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能
4).以HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(Http编码自动配置)为例解释自动配置原理
|
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件 @EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;并把HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中 @ConditionalOnWebApplication //Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效 @ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器; @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的 //即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的; public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了 private final HttpEncodingProperties properties; //只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件? public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; } |
根据当前不同的条件判断,决定这个配置类是否生效?
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
5).所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者‘;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个功能对应的这个属性类
|
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http.encoding") //从配置文件中获取指定的值和bean的属性进行绑定 public class HttpEncodingProperties { public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); |
springboot精髓:
1)、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2)、我们看我们需要的功能有没有SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类;
3)、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件有,我们就不需要再来配置了)
4)、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们就可以在配置文件中指定这些属性的值;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;
给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
(2).细节
1).@Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;
|
@Conditional扩展注解 |
作用(判断是否满足当前指定条件) |
|
@ConditionalOnJava |
系统的java版本是否符合要求 |
|
@ConditionalOnBean |
容器中存在指定Bean; |
|
@ConditionalOnMissingBean |
容器中不存在指定Bean; |
|
@ConditionalOnExpression |
满足SpEL表达式指定 |
|
@ConditionalOnClass |
系统中有指定的类 |
|
@ConditionalOnMissingClass |
系统中没有指定的类 |
|
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate |
容器中只有一个指定的Bean,或者这个Bean是首选Bean |
|
@ConditionalOnProperty |
系统中指定的属性是否有指定的值 |
|
@ConditionalOnResource |
类路径下是否存在指定资源文件 |
|
@ConditionalOnWebApplication |
当前是web环境 |
|
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication |
当前不是web环境 |
|
@ConditionalOnJndi |
JNDI存在指定项 |
自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效;
我们可以通过启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告,这样我们就可以很方便的知道哪些自动配置类生效;
|
============================ CONDITIONS EVALUATION REPORT ============================ Positive matches: 启用的自动配置类 ----------------- AopAutoConfiguration matched: - @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.auto=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition) AopAutoConfiguration.ClassProxyingConfiguration matched: - @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class 'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice' (OnClassCondition) - @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition) Negative matches: 没启用的自动配置类 ----------------- ActiveMQAutoConfiguration: Did not match: - @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition) |
参考文档:https://bitbucket.org/asomov/snakeyaml/wiki/Documentation#markdown-header-yaml-syntax
2、Spring Boot配置的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot -- 配置切换指南
一般在一个项目中,总是会有好多个环境.比如: 开发环境 -> 测试环境 -> 预发布环境 -> 生产环境 每个环境上的配置文件总是不一样的,甚至开发环境中每个开发者的环境可能也会有一 ...
- Spring Boot 配置优先级顺序
一般在一个项目中,总是会有好多个环境.比如: 开发环境 -> 测试环境 -> 预发布环境 -> 生产环境 每个环境上的配置文件总是不一样的,甚至开发环境中每个开发者的环境可能也会有一 ...
- spring boot 配置注入
spring boot配置注入有变量方式和类方式(参见:<spring boot 自定义配置属性的各种方式>),变量中又要注意静态变量的注入(参见:spring boot 给静态变量注入值 ...
- Spring boot配置多个Redis数据源操作实例
原文:https://www.jianshu.com/p/c79b65b253fa Spring boot配置多个Redis数据源操作实例 在SpringBoot是项目中整合了两个Redis的操作实例 ...
- spring boot配置springMVC拦截器
spring boot通过配置springMVC拦截器 配置拦截器比较简单, spring boot配置拦截器, 重写preHandle方法. 1.配置拦截器: 2重写方法 这样就实现了拦截器. 其中 ...
- spring boot配置mybatis和事务管理
spring boot配置mybatis和事务管理 一.spring boot与mybatis的配置 1.首先,spring boot 配置mybatis需要的全部依赖如下: <!-- Spri ...
- [转] Spring Boot配置多个DataSource
[From] https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/article/001484212576147b1f07dc0ab9147a1a97662a0bd270c20000 Sprin ...
- Spring boot 配置异步处理执行器
示例如下: 1. 新建Maven 项目 async-executor 2.pom.xml <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0 ...
- Spring boot配置404、500页面
Spring boot 配置404页面很简单,如果你访问的url没有找到就会出现spring boot 提示的页面,很明显Spring boot不用配置就可以显示404页面了. 在template下创 ...
- Spring Boot 配置元数据指南
1. 概览 在编写 Spring Boot 应用程序时,将配置属性映射到 Java bean 上是非常有用的.但是,记录这些属性的最好方法是什么呢? 在本教程中,我们将探讨 Spring Boot C ...
随机推荐
- MySQL备份和恢复[3]-mysqldump备份工具
mysqldump 概述 逻辑备份工具: mysqldump, mydumper, phpMyAdmin Schema和数据存储在一起.巨大的SQL语句.单个巨大的备份文件 mysqldump:是My ...
- 在电脑上操作手机屏幕scrcpy工具就搞定了
手机安卓版本:10 电脑:win64 使用步骤 电脑步骤 下载scrcpy scrcpy 是免费开源的投屏软件,支持将安卓手机屏幕投放在 Windows.macOS.GNU/Linux 上,并可直接借 ...
- 在java的多态调用中,new的是哪一个类就是调用的哪个类的方法。
在java的多态调用中,new的是哪一个类就是调用的哪个类的方法.(x) 原因: ava多态有两种情况:重载和覆写 在覆写中,运用的是动态单分配,是根据new的类型确定对象,从而确定调用的方法: 在重 ...
- 阿里云MNS官方PHP版SDK缺少message tag问题处理
最近在使用阿里云MNS官方PHP版SDK的过程中,发现发送到topic的消息,不能设置tag(其它语言版本SDK支持tag,如java,python),但在阿里云控制台页面发送是可以设置tag的. 因 ...
- day04 Selenium请求库
1.什么是Selenium? Selenium是一个自动测试工具,它可以帮我通过代码去实现驱动浏览器自动执行相应的操作. 所以我们也可以用它来做爬虫. 2.为什么要适用s ...
- 基于flask的python注册到eureka
Eureka架构中的三个核心角色: 服务注册中心 Eureka的服务端应用,提供服务注册和发现功能,就是刚刚我们建立的eureka-demo 服务提供者 提供服务的应用,可以是SpringBoot应用 ...
- 学会这些CSS,再也不用切图!!!
三角形 利用border-color支持transparent这一特性,隐藏三条边框,实现三角形. <style> .triangle { width: 0; height: 0; bor ...
- 4G DTU模块和串口设备连接的方式
首先说下解决思路: 由于考虑到串口开发很麻烦,所以后来买了一个4g模块的dtu. 所以最后的解决方案是,plc串口设备与dtu相连,由于dtu是透传模式,使用java与4g模块进行通信就完事了. 虽然 ...
- mq_open失败,Invalid argument
经四处查找,终于发现原因: (1)attr.mq_maxmsg 不能超过文件 /proc/sys/fs/mqueue/msg_max 中的数值,我的机器上面是10. (2)attr.mq_msgsiz ...
- Linux 系统编程 学习:06-基于socket的网络编程1:有关概念
Linux 系统编程 学习:006-基于socket的网络编程1:有关概念 背景 上一讲 进程间通信:System V IPC(2)中,我们介绍了System IPC中关于信号量的概念,以及如何使用. ...
