Linux内核实现透视---工作队列
作为Linux中断低半部的另一种实现机制的基础,工作队列的出现更多的是为了解决软中断和Tasklet对于用户进程的时间片的不良影响问题的。工作队列本身是可以使用内核线程来替代的,但是使用线程来实现复杂程度和内存资源的消耗是不利因素,所以Linux内核就实现了这一机制。通过内核线程(worker)作为工作队列的执行者,单个工作采用 struct work_struct来进行描述,而一系列的工作采用struct workqueue_struct来描述,最后为了更好的管理worker又抽象出了 工作线程池由 struct worker_pool描述,最后再由线程池和工作队列关联器 用struct pool_workqueue来描述来 管理工作队列和线程池的关系。接下来逐一了解各个数据结构的定义和关系。
工作(work)
struct work_struct {
//低比特位部分是work的标志位,剩余比特位通常用于存放上一次运行的worker_pool ID或pool_workqueue的指针。存放的内容有WORK_STRUCT_PWQ标志位来决定
atomic_long_t data;
//用于把work挂到其他队列上。
struct list_head entry;
//工作任务的处理函数
work_func_t func;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
}
工作队列(workqueue_struct)
struct workqueue_struct {
struct list_head pwqs; /* WR: all pwqs of this wq */
struct list_head list; /* PL: list of all workqueues */
struct mutex mutex; /* protects this wq */
int work_color; /* WQ: current work color */
int flush_color; /* WQ: current flush color */
atomic_t nr_pwqs_to_flush; /* flush in progress */
struct wq_flusher *first_flusher; /* WQ: first flusher */
struct list_head flusher_queue; /* WQ: flush waiters */
struct list_head flusher_overflow; /* WQ: flush overflow list */
//所有rescue状态下的pool_workqueue数据结构链表
struct list_head maydays; /* MD: pwqs requesting rescue */
//rescue内核线程,内存紧张时创建新的工作线程可能会失败,
//如果创建workqueue是设置了WQ_MEM_RECLAIM,那么rescuer线程会接管这种情况。
struct worker *rescuer; /* I: rescue worker */
int nr_drainers; /* WQ: drain in progress */
int saved_max_active; /* WQ: saved pwq max_active */
struct workqueue_attrs *unbound_attrs; /* WQ: only for unbound wqs */
struct pool_workqueue *dfl_pwq; /* WQ: only for unbound wqs */
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
struct wq_device *wq_dev; /* I: for sysfs interface */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
char name[WQ_NAME_LEN]; /* I: workqueue name */
/* hot fields used during command issue, aligned to cacheline */
unsigned int flags ____cacheline_aligned; /* WQ: WQ_* flags */
struct pool_workqueue __percpu *cpu_pwqs; /* I: per-cpu pwqs */
struct pool_workqueue __rcu *numa_pwq_tbl[]; /* FR: unbound pwqs indexed by node */
};
工作者(struct worker)
struct worker {
/* on idle list while idle, on busy hash table while busy */
union {
struct list_head entry; /* L: while idle */
struct hlist_node hentry; /* L: while busy */
};
struct work_struct *current_work; /* L: work being processed */
work_func_t current_func; /* L: current_work's fn */
struct pool_workqueue *current_pwq; /* L: current_work's pwq */
bool desc_valid; /* ->desc is valid */
struct list_head scheduled; /* L: scheduled works */
/* 64 bytes boundary on 64bit, 32 on 32bit */
struct task_struct *task; /* I: worker task */
struct worker_pool *pool; /* I: the associated pool */
/* L: for rescuers */
struct list_head node; /* A: anchored at pool->workers */
/* A: runs through worker->node */
unsigned long last_active; /* L: last active timestamp */
unsigned int flags; /* X: flags */
int id; /* I: worker id */
/*
* Opaque string set with work_set_desc(). Printed out with task
* dump for debugging - WARN, BUG, panic or sysrq.
*/
char desc[WORKER_DESC_LEN];
/* used only by rescuers to point to the target workqueue */
struct workqueue_struct *rescue_wq; /* I: the workqueue to rescue */
};
工作线程池(struct worker_pool)
struct worker_pool {
spinlock_t lock; /* the pool lock */
int cpu; /* I: the associated cpu */
int node; /* I: the associated node ID */
int id; /* I: pool ID */
unsigned int flags; /* X: flags */
struct list_head worklist; /* L: list of pending works */
int nr_workers; /* L: total number of workers */
/* nr_idle includes the ones off idle_list for rebinding */
int nr_idle; /* L: currently idle ones */
struct list_head idle_list; /* X: list of idle workers */
struct timer_list idle_timer; /* L: worker idle timeout */
struct timer_list mayday_timer; /* L: SOS timer for workers */
/* a workers is either on busy_hash or idle_list, or the manager */
DECLARE_HASHTABLE(busy_hash, BUSY_WORKER_HASH_ORDER);
/* L: hash of busy workers */
/* see manage_workers() for details on the two manager mutexes */
struct mutex attach_mutex; /* attach/detach exclusion */
struct list_head workers; /* A: attached workers */
struct completion *detach_completion; /* all workers detached */
struct ida worker_ida; /* worker IDs for task name */
struct workqueue_attrs *attrs; /* I: worker attributes */
struct hlist_node hash_node; /* PL: unbound_pool_hash node */
int refcnt; /* PL: refcnt for unbound pools */
/*
* The current concurrency level. As it's likely to be accessed
* from other CPUs during try_to_wake_up(), put it in a separate
* cacheline.
*/
atomic_t nr_running ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/*
* Destruction of pool is sched-RCU protected to allow dereferences
* from get_work_pool().
*/
struct rcu_head rcu;
} ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
线程池和工作队列关联(struct pool_workqueue)
struct pool_workqueue {
struct worker_pool *pool; /* I: the associated pool */
struct workqueue_struct *wq; /* I: the owning workqueue */
int work_color; /* L: current color */
int flush_color; /* L: flushing color */
int refcnt; /* L: reference count */
int nr_in_flight[WORK_NR_COLORS];
/* L: nr of in_flight works */
int nr_active; /* L: nr of active works */
int max_active; /* L: max active works */
struct list_head delayed_works; /* L: delayed works */
struct list_head pwqs_node; /* WR: node on wq->pwqs */
struct list_head mayday_node; /* MD: node on wq->maydays */
/*
* Release of unbound pwq is punted to system_wq. See put_pwq()
* and pwq_unbound_release_workfn() for details. pool_workqueue
* itself is also sched-RCU protected so that the first pwq can be
* determined without grabbing wq->mutex.
*/
struct work_struct unbound_release_work;
struct rcu_head rcu;
} __aligned(1 << WORK_STRUCT_FLAG_BITS);
有时间了画一个简单的图来表示他们的关系。
图片(有时间了来填坑)
前面了解了大致的数据结构关系后下来再来看工作队列的处理过程,因为数据结构的管理都是由内核完成的而驱动开发正真关系的的执行过程的细节。先从内核初始化线程和工作队列开始一步步深入。
工作队列的初始化
在系统启动过程中通过init_workqueues()初始化了工作线程,并创建的一部分内核工作队列。创建的规则是每一个CPU核心创建两个线程一个高优先级(内核最高)一个低优先级(中间优先)的线程这些线程和CPU是绑定的,只处理指定CPU上的pool_workqueue。除此之外内核还创建了两个个和CPU无关的线程可以用来处理所有的工作。这里需要注意的是工作线程的创建也是根据激活在线的CPU的个数创建的而不是总的CPU的个数,所以在CPU激活的接口中会有回调接口用于创建内核工作线程,对应的在CPU休眠时就有对应的销毁回调。来看源码:
static int __init init_workqueues(void)
{
//NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS = 2 对应一个高优先级-20(最高)和一个低优先级0(中间)
int std_nice[NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS] = { 0, HIGHPRI_NICE_LEVEL };
int i, cpu; WARN_ON(__alignof__(struct pool_workqueue) < __alignof__(long long)); pwq_cache = KMEM_CACHE(pool_workqueue, SLAB_PANIC);
//这里就是绑定在CPU激活和休眠的时候创建和销毁工作线程的接口
cpu_notifier(workqueue_cpu_up_callback, CPU_PRI_WORKQUEUE_UP);
hotcpu_notifier(workqueue_cpu_down_callback, CPU_PRI_WORKQUEUE_DOWN); wq_numa_init(); /* initialize CPU pools */
//遍历每个CPU
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
struct worker_pool *pool; i = 0;
//这里会拿到CPU per 类型的工作线程池结构体地址(实际上是数组而CPU编号为index)到pool
for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) {
/*
调用init_worker_pool 初始化工作线程程池,绑定CPU,设置优先级等
*/
BUG_ON(init_worker_pool(pool));
pool->cpu = cpu;
cpumask_copy(pool->attrs->cpumask, cpumask_of(cpu));
pool->attrs->nice = std_nice[i++];
pool->node = cpu_to_node(cpu); /* alloc pool ID */
mutex_lock(&wq_pool_mutex);
BUG_ON(worker_pool_assign_id(pool));
mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_mutex);
}
} /* create the initial worker */
//遍历激活的cpu
for_each_online_cpu(cpu) {
struct worker_pool *pool;
//同上面一样遍历cpu per pool
for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) {
//创建线程在线程池中并启动工作线程、修改线程池标志
pool->flags &= ~POOL_DISASSOCIATED;
BUG_ON(create_and_start_worker(pool) < 0);
}
}
//创建不绑定的线程属性并绑定
/* create default unbound and ordered wq attrs */
for (i = 0; i < NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS; i++) {
struct workqueue_attrs *attrs; BUG_ON(!(attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(GFP_KERNEL)));
attrs->nice = std_nice[i];
unbound_std_wq_attrs[i] = attrs; /*
* An ordered wq should have only one pwq as ordering is
* guaranteed by max_active which is enforced by pwqs.
* Turn off NUMA so that dfl_pwq is used for all nodes.
*/
BUG_ON(!(attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(GFP_KERNEL)));
attrs->nice = std_nice[i];
attrs->no_numa = true;
ordered_wq_attrs[i] = attrs;
}
//创建内核工作队列
system_wq = alloc_workqueue("events", 0, 0);
system_highpri_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_highpri", WQ_HIGHPRI, 0);
system_long_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_long", 0, 0);
system_unbound_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_unbound", WQ_UNBOUND,
WQ_UNBOUND_MAX_ACTIVE);
system_freezable_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_freezable",
WQ_FREEZABLE, 0);
system_power_efficient_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_power_efficient",
WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT, 0);
system_freezable_power_efficient_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_freezable_power_efficient",
WQ_FREEZABLE | WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT,
0);
BUG_ON(!system_wq || !system_highpri_wq || !system_long_wq ||
!system_unbound_wq || !system_freezable_wq ||
!system_power_efficient_wq ||
!system_freezable_power_efficient_wq);
return 0;
}
具体来看创建和启动内核工作线程的接口create_and_start_worker():
static int create_and_start_worker(struct worker_pool *pool)
{
struct worker *worker;
worker = create_worker(pool);
if (worker) {
spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock);
start_worker(worker);
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
} return worker ? 0 : -ENOMEM;
} static struct worker *create_worker(struct worker_pool *pool)
{
struct worker *worker = NULL;
int id = -1;
char id_buf[16]; /* ID is needed to determine kthread name */
//从对应的pool中取线程id这体现了内核新的采用工作线程pool来管理工作线程的思想
id = ida_simple_get(&pool->worker_ida, 0, 0, GFP_KERNEL);
if (id < 0)
goto fail; worker = alloc_worker();
if (!worker)
goto fail;
//指定工作线程池和id
worker->pool = pool;
worker->id = id;
//工作线程池中的cpu 指定绑定的cpu如果为-1则是不绑定CPU
if (pool->cpu >= 0)
snprintf(id_buf, sizeof(id_buf), "%d:%d%s", pool->cpu, id,
pool->attrs->nice < 0 ? "H" : "");
else
snprintf(id_buf, sizeof(id_buf), "u%d:%d", pool->id, id);
//关键点:创建工作线程 线程函数为worker_thread ,工作线程还被挂接到pool上
worker->task = kthread_create_on_node(worker_thread, worker, pool->node,
"kworker/%s", id_buf);
if (IS_ERR(worker->task))
goto fail;
//由此可见线程池中的线程的优先级和所属的线程池相同
set_user_nice(worker->task, pool->attrs->nice);
//这个标志阻碍用户接口修改当前线程优先级
/* prevent userland from meddling with cpumask of workqueue workers */
worker->task->flags |= PF_NO_SETAFFINITY;
//链表操作将worker 串入worker_pool
/* successful, attach the worker to the pool */
worker_attach_to_pool(worker, pool); return worker; fail:
if (id >= 0)
ida_simple_remove(&pool->worker_ida, id);
kfree(worker);
return NULL;
}
这里也验证我前面的一个猜测,即一个worker_pool中的的worker线程的优先级都是继承自所属线程池的。启动线程的操作时内核的通用线程操作这里不在看,来重点蓝worker线程接口函数worker_thread。
static int worker_thread(void *__worker)
{
struct worker *worker = __worker;
struct worker_pool *pool = worker->pool; /* tell the scheduler that this is a workqueue worker */
//告诉调度器这是一个worker 可见工作线程的支持是深入内核的
worker->task->flags |= PF_WQ_WORKER;
woke_up:
spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock);
//worker 需要销毁?此时和他关联的线程已经销毁了(猜的找机会验证)
/* am I supposed to die? */
if (unlikely(worker->flags & WORKER_DIE)) {
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&worker->entry));
worker->task->flags &= ~PF_WQ_WORKER; set_task_comm(worker->task, "kworker/dying");
ida_simple_remove(&pool->worker_ida, worker->id);
worker_detach_from_pool(worker, pool);
kfree(worker);
return 0;
}
//清楚空闲标志,并从空闲线程链表上移到运行线程list上
worker_leave_idle(worker);
recheck:
/* no more worker necessary? */
//如果当前worker_pool->worklist中没有待处理的任务,并且当前pool没有正在运行的worker这个接口返回False,这里就会休眠
if (!need_more_worker(pool))
goto sleep;
//may_start_working()检查是否还有空闲状态worker,没有则通过 manage_workers()创建一个
/* do we need to manage? */
if (unlikely(!may_start_working(pool)) && manage_workers(worker))
//返回再次检查
goto recheck; /*
* ->scheduled list can only be filled while a worker is
* preparing to process a work or actually processing it.
* Make sure nobody diddled with it while I was sleeping.
*/
//scheduled 中保存着正在处理的work或即将处理的work(必然)
WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&worker->scheduled)); /*
* Finish PREP stage. We're guaranteed to have at least one idle
* worker or that someone else has already assumed the manager
* role. This is where @worker starts participating in concurrency
* management if applicable and concurrency management is restored
* after being rebound. See rebind_workers() for details.
*/
//维护线程池属性 这里worker_pool->nr_running 计数维护
worker_clr_flags(worker, WORKER_PREP | WORKER_REBOUND);
//遍历线程池上的work,并处理
do {
struct work_struct *work =
list_first_entry(&pool->worklist,
struct work_struct, entry); if (likely(!(*work_data_bits(work) & WORK_STRUCT_LINKED))) {
/* optimization path, not strictly necessary */
//当前worker 处理当前work
process_one_work(worker, work);
if (unlikely(!list_empty(&worker->scheduled)))
//如果当前worker上有待处理的work,先处理它(这是个补丁应该)
process_scheduled_works(worker);
} else {
//如果当前work_struct置位WORK_STRUCT_LINKED表示work后面还串上其它work,
//把这些work迁移到woeker_pool->scheduled中,然后一并再用process_one_work()函数处理。
move_linked_works(work, &worker->scheduled, NULL);
process_scheduled_works(worker);
}
} while (keep_working(pool));
//处理完了
worker_set_flags(worker, WORKER_PREP, false);
//空闲睡眠处理
sleep:
/*
* pool->lock is held and there's no work to process and no need to
* manage, sleep. Workers are woken up only while holding
* pool->lock or from local cpu, so setting the current state
* before releasing pool->lock is enough to prevent losing any
* event.
*/
worker_enter_idle(worker);
__set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock);
schedule();
goto woke_up;
}
然后就是具体的处理过程其实上面的process_scheduled_works()接口最后实际也是调用的process_one_work()接口进行处理的所以这里来看一下具体的处理过程:
static void process_scheduled_works(struct worker *worker)
{
while (!list_empty(&worker->scheduled)) {
struct work_struct *work = list_first_entry(&worker->scheduled,
struct work_struct, entry);
process_one_work(worker, work);
}
} static void process_one_work(struct worker *worker, struct work_struct *work)
__releases(&pool->lock)
__acquires(&pool->lock)
{
struct pool_workqueue *pwq = get_work_pwq(work);
struct worker_pool *pool = worker->pool;
//判断当前的workqueue是否是CPU_INTENSIVE,会对其所在工作线程进行特殊设置。
bool cpu_intensive = pwq->wq->flags & WQ_CPU_INTENSIVE;
int work_color;
struct worker *collision;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
/*
* It is permissible to free the struct work_struct from
* inside the function that is called from it, this we need to
* take into account for lockdep too. To avoid bogus "held
* lock freed" warnings as well as problems when looking into
* work->lockdep_map, make a copy and use that here.
*/
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map; lockdep_copy_map(&lockdep_map, &work->lockdep_map);
#endif
/* ensure we're on the correct CPU */
WARN_ON_ONCE(!(pool->flags & POOL_DISASSOCIATED) &&
raw_smp_processor_id() != pool->cpu); /*
* A single work shouldn't be executed concurrently by
* multiple workers on a single cpu. Check whether anyone is
* already processing the work. If so, defer the work to the
* currently executing one.
*/
//查询当前work是否在worker_pool->busy_hash表中正在运行,
//如果在就移到当前work正在执行的worker->scheduled并退出当前处理。
collision = find_worker_executing_work(pool, work);
if (unlikely(collision)) {
move_linked_works(work, &collision->scheduled, NULL);
return;
} /* claim and dequeue */
debug_work_deactivate(work);
hash_add(pool->busy_hash, &worker->hentry, (unsigned long)work);
worker->current_work = work;
worker->current_func = work->func;
worker->current_pwq = pwq;
work_color = get_work_color(work); list_del_init(&work->entry); /*
* CPU intensive works don't participate in concurrency management.
* They're the scheduler's responsibility. This takes @worker out
* of concurrency management and the next code block will chain
* execution of the pending work items.
*/
if (unlikely(cpu_intensive))
//设置当前工作线程flags,调度器就知道内核线程属性了,
//但实际上调度器暂时并没有做特殊处理。
worker_set_flags(worker, WORKER_CPU_INTENSIVE); /*
* Wake up another worker if necessary. The condition is always
* false for normal per-cpu workers since nr_running would always
* be >= 1 at this point. This is used to chain execution of the
* pending work items for WORKER_NOT_RUNNING workers such as the
* UNBOUND and CPU_INTENSIVE ones.
*/
//判断是否需要唤醒更多工作线程,wake_up_worker()去唤
//醒worker_pool中第一个idle线程。对于bound型worker_pool此时一般nr_running>=1,所以条件不成立。
if (need_more_worker(pool))
wake_up_worker(pool); /*
* Record the last pool and clear PENDING which should be the last
* update to @work. Also, do this inside @pool->lock so that
* PENDING and queued state changes happen together while IRQ is
* disabled.
*/
//清除struct worker中data成员pending标志位,
//里面使用了smp_wmb保证了pending之前的写操作完成之后才清除pending。
set_work_pool_and_clear_pending(work, pool->id); spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); lock_map_acquire_read(&pwq->wq->lockdep_map);
lock_map_acquire(&lockdep_map);
trace_workqueue_execute_start(work);
//真正执行work的回调函数
worker->current_func(work);
/*
* While we must be careful to not use "work" after this, the trace
* point will only record its address.
*/
trace_workqueue_execute_end(work);
lock_map_release(&lockdep_map);
lock_map_release(&pwq->wq->lockdep_map); if (unlikely(in_atomic() || lockdep_depth(current) > 0)) {
pr_err("BUG: workqueue leaked lock or atomic: %s/0x%08x/%d\n"
" last function: %pf\n",
current->comm, preempt_count(), task_pid_nr(current),
worker->current_func);
debug_show_held_locks(current);
dump_stack();
} /*
* The following prevents a kworker from hogging CPU on !PREEMPT
* kernels, where a requeueing work item waiting for something to
* happen could deadlock with stop_machine as such work item could
* indefinitely requeue itself while all other CPUs are trapped in
* stop_machine. At the same time, report a quiescent RCU state so
* the same condition doesn't freeze RCU.
*/
cond_resched_rcu_qs(); spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); /* clear cpu intensive status */
if (unlikely(cpu_intensive))
worker_clr_flags(worker, WORKER_CPU_INTENSIVE); /* we're done with it, release */
//work回调函数执行完成后的清理工作
hash_del(&worker->hentry);
worker->current_work = NULL;
worker->current_func = NULL;
worker->current_pwq = NULL;
worker->desc_valid = false;
pwq_dec_nr_in_flight(pwq, work_color);
}
处理过程除了涉及工作队列的数据维护外其余的需要注意的就是清除struct worker中data成员pending标志位的操作了,他可以说明工作队列调度一次执行一次处理就结束了。到这里其实关键的工作队列相关的处理的部分都算已经处理完了。其余剩余的CPU激活和睡眠的回调接口不再去看内容精炼一下,其次是工作队列的创建相关的内容暂时不用就不去看了看用不上就记不住--徒劳。接下来重点看一下如何使用工作队列。
工作队列的使用
工作队列的使用就三部曲,定义一个工作,初始化工作,调度他(其实是将其加入到内核的数据结构中由内核调度执行)。
定义工作
可以使用动态分配的也可以使用静态方式定义,最后再调用__INIT_WORK()来初始化work,其次是衍生的一些其他接口,大多是标志位的不同,其次是delay_work这才是中断低半部常用的接口。
初始化
#define __INIT_WORK(_work, _func, _onstack) \
do { \
__init_work((_work), _onstack); \
(_work)->data = (atomic_long_t) WORK_DATA_INIT(); \
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(_work)->entry); \
(_work)->func = (_func); \
} while (0)
这里在将work封装的相关接口记录一下:
#define TIMER_DEFERRABLE 0x1LU
#define TIMER_IRQSAFE 0x2LU #define __INIT_WORK(_work, _func, _onstack) \
do { \
__init_work((_work), _onstack); \
(_work)->data = (atomic_long_t) WORK_DATA_INIT(); \
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(_work)->entry); \
(_work)->func = (_func); \
} while (0) #define INIT_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 0) #define INIT_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 1) #define __INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, _tflags) \
do { \
INIT_WORK(&(_work)->work, (_func)); \
__setup_timer(&(_work)->timer, delayed_work_timer_fn, \
(unsigned long)(_work), \
(_tflags) | TIMER_IRQSAFE); \
} while (0) #define __INIT_DELAYED_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func, _tflags) \
do { \
INIT_WORK_ONSTACK(&(_work)->work, (_func)); \
__setup_timer_on_stack(&(_work)->timer, \
delayed_work_timer_fn, \
(unsigned long)(_work), \
(_tflags) | TIMER_IRQSAFE); \
} while (0) #define INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, 0) #define INIT_DELAYED_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func, 0) #define INIT_DEFERRABLE_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, TIMER_DEFERRABLE) #define INIT_DEFERRABLE_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK_ONSTACK(_work, _func, TIMER_DEFERRABLE)
调度
work初始化完成后就需要将work加入到工作队列中去了,而默认的工作队列是system_wq 回想初始化过程创建的工作队列。调用的接口是schedule_work()如下的调用过程:
/**
* schedule_work - put work task in global workqueue
* @work: job to be done
*
* Returns %false if @work was already on the kernel-global workqueue and
* %true otherwise.
*
* This puts a job in the kernel-global workqueue if it was not already
* queued and leaves it in the same position on the kernel-global
* workqueue otherwise.
*/
static inline bool schedule_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
return queue_work(system_wq, work);
} /**
* queue_work - queue work on a workqueue
* @wq: workqueue to use
* @work: work to queue
*
* Returns %false if @work was already on a queue, %true otherwise.
*
* We queue the work to the CPU on which it was submitted, but if the CPU dies
* it can be processed by another CPU.
*/
static inline bool queue_work(struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct work_struct *work)
{
return queue_work_on(WORK_CPU_UNBOUND, wq, work);
} /**
* queue_work_on - queue work on specific cpu
* @cpu: CPU number to execute work on
* @wq: workqueue to use
* @work: work to queue
*
* We queue the work to a specific CPU, the caller must ensure it
* can't go away.
*
* Return: %false if @work was already on a queue, %true otherwise.
*/
bool queue_work_on(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct work_struct *work)
{
bool ret = false;
unsigned long flags; local_irq_save(flags); if (!test_and_set_bit(WORK_STRUCT_PENDING_BIT, work_data_bits(work))) {
__queue_work(cpu, wq, work);
ret = true;
} local_irq_restore(flags);
return ret;
}
由这个过程可以知道,这个接口添加的工作队列是不指定具体的CPU执行的,其中的__queue_work()是重要的添加操作过程:
static void __queue_work(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq,
struct work_struct *work)
{
struct pool_workqueue *pwq;
struct worker_pool *last_pool;
struct list_head *worklist;
unsigned int work_flags;
unsigned int req_cpu = cpu;
//是否处于关中断状态
WARN_ON_ONCE(!irqs_disabled()); debug_work_activate(work);
/*
__WQ_DRAINING表示要销毁workqueue,那么挂入workqueue中所有的work都要处理完
毕才能把这个workqueue销毁。在销毁过程中,一般不允许再有新的work加入队列中。
有一种特殊例外是正在清空work时触发了一个queue work操作,这种情况被称为chained work。
*/
/* if draining, only works from the same workqueue are allowed */
if (unlikely(wq->flags & __WQ_DRAINING) &&
WARN_ON_ONCE(!is_chained_work(wq)))
return;
retry:
if (req_cpu == WORK_CPU_UNBOUND)
cpu = raw_smp_processor_id(); /* pwq which will be used unless @work is executing elsewhere */
if (!(wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND))
//对于bound型的workqueue,直接使用本地CPU对应pool_workqueue。
pwq = per_cpu_ptr(wq->cpu_pwqs, cpu);
else
//对于unbound型,调用unbound_pwq_by_node()寻找本地node节点对应的unbound类型的pool_workqueue。
pwq = unbound_pwq_by_node(wq, cpu_to_node(cpu)); /*
* If @work was previously on a different pool, it might still be
* running there, in which case the work needs to be queued on that
* pool to guarantee non-reentrancy.
*/
//通过work_struct的成员data查询该work上一次是在哪个worker_pool中运行的。
last_pool = get_work_pool(work);
//如果上次运行的worker_pool和本次不一致
if (last_pool && last_pool != pwq->pool) {
struct worker *worker; spin_lock(&last_pool->lock);
//判断一个work是否正在last_pool上运行,也即不在当前worker_pool运行,如果是返回这个正在执行的工作线程worker
worker = find_worker_executing_work(last_pool, work); if (worker && worker->current_pwq->wq == wq) {
//利用当前work正在执行的pool_workqueue,利用缓存热度,不进行调度。
pwq = worker->current_pwq;
} else {
/* meh... not running there, queue here */
spin_unlock(&last_pool->lock);
spin_lock(&pwq->pool->lock);
}
} else {
spin_lock(&pwq->pool->lock);
} if (unlikely(!pwq->refcnt)) {
//对unbound类型pool_workqueue释放是异步的,当refcnt减少到0时,
//说明该pool_workqueue已经被释放,那么需要跳转到retry出重新选择pool_workqueue。
if (wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND) {
spin_unlock(&pwq->pool->lock);
cpu_relax();
goto retry;
}
/* oops */
WARN_ONCE(true, "workqueue: per-cpu pwq for %s on cpu%d has 0 refcnt",
wq->name, cpu);
} /* pwq determined, queue */
trace_workqueue_queue_work(req_cpu, pwq, work); if (WARN_ON(!list_empty(&work->entry))) {
spin_unlock(&pwq->pool->lock);
return;
} pwq->nr_in_flight[pwq->work_color]++;
work_flags = work_color_to_flags(pwq->work_color); if (likely(pwq->nr_active < pwq->max_active)) {
//判断当前pool_workqueue的work活跃数量,如果少于最高限值,
//就加入pending状态链表worker_pool->worklist,否则加入delayed_works链表中。
trace_workqueue_activate_work(work);
pwq->nr_active++;
worklist = &pwq->pool->worklist;
} else {
work_flags |= WORK_STRUCT_DELAYED;
worklist = &pwq->delayed_works;
}
//将当前work加入到pool_workqueue->worklist尾部。
insert_work(pwq, work, worklist, work_flags); spin_unlock(&pwq->pool->lock);
}
在关中断的情况下将,work通过insert_work添加到对应的work_queue中。在添加的过程最后会检查当前的线程池中是否有工作的线程即线程池有活动的线程,因为只有线程池中有活动的线程才能回执行worker线程处理函数,进而发现有待处理的work进行执行处理。所以如果没有任何worker在运行则需要唤醒一个线程采用wake_up_worker(pool)接口。这个接口的执行也十分简单就是进入线程池找到第一个空闲的worker然后执行线程唤醒接口wake_up_process(task)唤醒这个线程即可。static void insert_work(struct pool_workqueue *pwq, struct work_struct *work,
struct list_head *head, unsigned int extra_flags)
{
struct worker_pool *pool = pwq->pool; /* we own @work, set data and link */
//把pool_workqueue指针的值和一些flag设置到data成员中,
//方便下次调用queue_work()知道本次使用哪个pool_workqueue()。
set_work_pwq(work, pwq, extra_flags);
将work加入到worker_pool->worklist尾部。
list_add_tail(&work->entry, head);
//增加pool_workqueue->refcnt成员引用计数。
get_pwq(pwq); /*
* Ensure either wq_worker_sleeping() sees the above
* list_add_tail() or we see zero nr_running to avoid workers lying
* around lazily while there are works to be processed.
*/
//保证wake_up_worker()唤醒worker时,在__schedule()->wq_worker_sleeping()时
//这里的list_add_tail()已经完成。同时保证下面__need_more_worker()读取nr_running时链表已经完成。
smp_mb();
//如果当前nr_running为0,表示当前worker可能并没有处于运行状态需要唤醒一个工作线程。
if (__need_more_worker(pool))那么需要wake_up_worker()
wake_up_worker(pool);
}
除了以上的接口还有其他的接口可以控制work的添加
//指定执行处理的CPU
int schedule_work_on(int cpu, struct work_struct *work)
{
return queue_work_on(cpu, system_wq, work);
}
//延迟执行这个work,一般作为中断低半部处理机制使用在中断上下文调用而在进程上下文处理
int schedule_delayed_work(struct delayed_work *dwork,
unsigned long delay)
{
return queue_delayed_work(system_wq, dwork, delay);
}
//指定在那个cpu上延迟处理,上面的结合体
int schedule_delayed_work_on(int cpu,
struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay)
{
return queue_delayed_work_on(cpu, system_wq, dwork, delay);
}
schedule_work()接口最后默认是将工作加了到system_wq,上面的这些接口支持将工作队列加到别的工作队列上进行处理,所以这里在了解一下其他的工作队列如下。
其他工作队列
- schedule_work(),其默认将work放入system_wq上。系统还有其它很多默认workqueue,这些workqueue也都是通过queue_work()将work放入其上。下面介绍一些其它系统全局workqueue的使用。
- system_highpri_wq 和system_wq的区别在于WQ_HIGHPRI,这些work对应的工作线程位于cpu_worker_pool[1]中。工作线程的nice为-20,要比system_wq对应的工作线程优先级要高。
- system_long_wq和system_wq类似,但是一般system_long_wq用于执行时间较长的work,而system_wq放执行较短的work。这两个workqueue没有明显的区别,更多的是靠使用者自觉。
- system_nrt_wq相对于system_wq使用了WQ_NON_REENTRANT。默认情况下工作队列只是确保在同一CPU不可重入,即工作在同一CPU上不会被多个工作线程并发执行,但容许在多个CPU上并发执行。该标志表明在多个CPU上也是不可重入的,工作将在不可重入workqueue上,并确保至多在一个系统范围内的工作线程上执行。
- system_unbound_wq相对于system_wq的区别是被设置为WQ_UNBOUND,没有并发管理,且work最大活跃数不超过WQ_UNBOUND_MAX_ACTIVE,一般为WQ_MAX_ACTIVE=512。
- system_unbound_wq对应的工作线程不会被绑定到特定CPU,所有排队的work会被立即执行,只要资源足够并且不超过最大活跃数。
- system_freezable_wq 相对于system_wq多了WQ_FREEZABLE标志,表示可以冻结workqueue参与系统的暂停操作,该workqueue的工作将被暂停,除非被唤醒,否者没有新的work被执行。
- system_power_efficient_wq相对于system_wq多了WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT标志,将工作队列表示为unbound已达到节省功耗的目的,并且还需要wq_power_efficient打开。否则和system_wq没啥区别。
- system_freezable_power_efficient_wq兼具system_freezable_wq的freezable和system_power_efficient_wq的power efficient两个特性。
在有些时候还可能需要自己创建工作队列来完成自己的work的调度使用,此时会使用创建工作队列的接口相关的内容,这里暂时记录不去深究后续用到了再来完善。
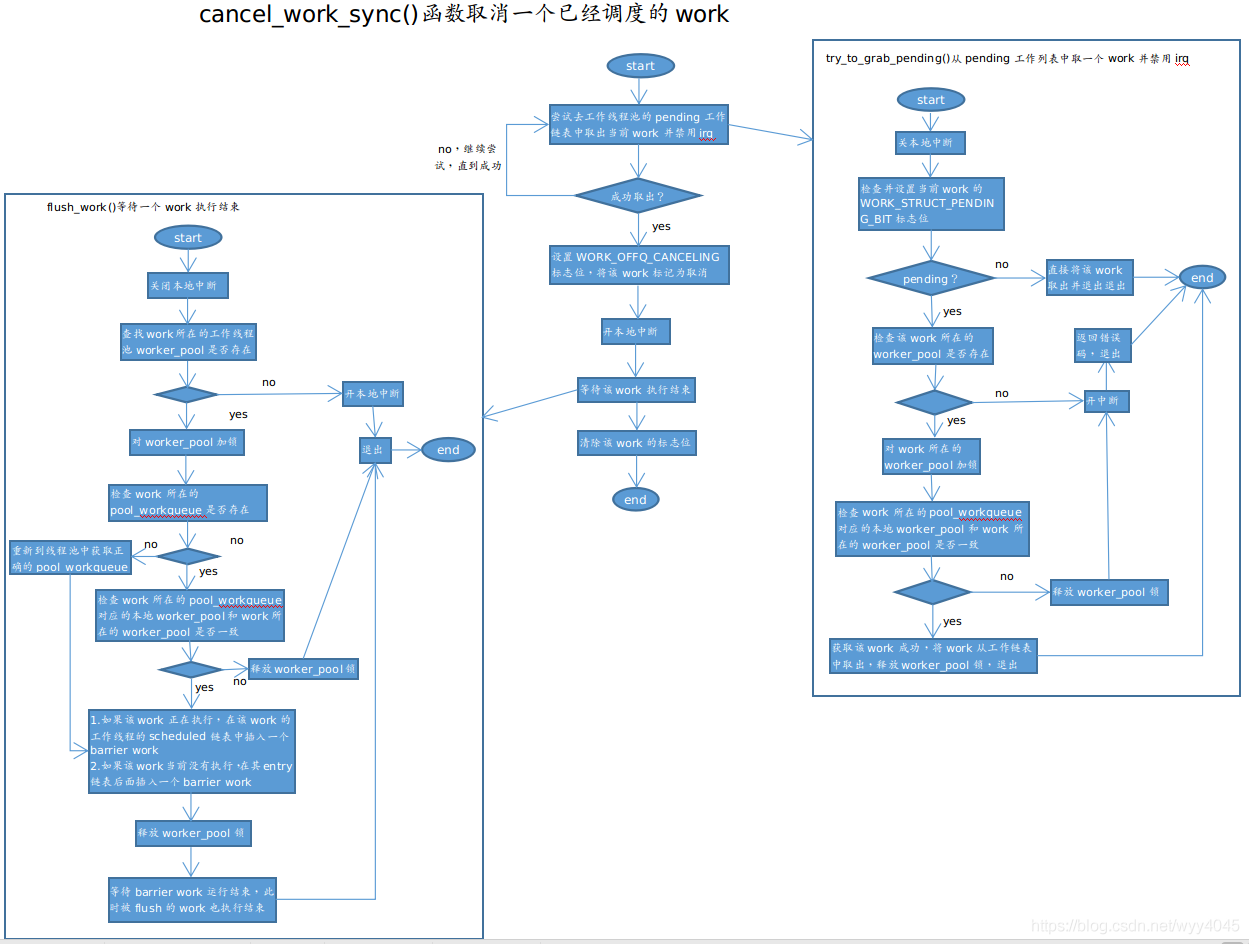
取消一个work
work添加到工作队列后会被执行,但有时也需要取消比如驱动程序在关闭设备节点,出现错误,或者要挂起时,需要取消一个已经被调度的work。cancel_work_sync()函数取消一个已经调度的work,该函数的工作流程图如下。
以上就是Linux内核工作队列的相关流程和处理过车梳理,不是全部但是可以对工作队列的工作特性骨架有一定的了解。
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/wyy4045/article/details/104676525
https://www.cnblogs.com/arnoldlu/p/8659988.html
Linux内核实现透视---工作队列的更多相关文章
- Linux内核学习之工作队列
Author : Toney Email : vip_13031075266@163.com Date : 2020.12.02 Copyright : ...
- Linux内核实现透视---软中断&Tasklet
软中断 首先明确一个概念软中断(不是软件中断int n).总来来说软中断就是内核在启动时为每一个内核创建了一个特殊的进程,这个进程会不停的poll检查是否有软中断需要执行,如果需要执行则调用注册的接口 ...
- Linux内核实现透视---硬中断
Linux的中断处理是驱动中比较重要的一部分内容,要清楚具体的实现才能更好的理解而不是靠记住别人理解后总结的规律,所以今天就打算从从源码来学习一下Linux内核对于中断处理过程,设计中断子系统的初始化 ...
- Linux内核实践之工作队列【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/bullbat/article/details/7410563 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. 工作队列(work queue)是 ...
- Linux内核实践之工作队列
工作队列(work queue)是另外一种将工作推后执行的形式,它和tasklet有所不同.工作队列可以把工作推后,交由一个内核线程去执行,也就是说,这个下半部分可以在进程上下文中执行.这样,通过工作 ...
- Linux内核中的软中断、tasklet和工作队列具体解释
[TOC] 本文基于Linux2.6.32内核版本号. 引言 软中断.tasklet和工作队列并非Linux内核中一直存在的机制,而是由更早版本号的内核中的"下半部"(bottom ...
- [Linux内核]软中断、tasklet、工作队列
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/li-hao/archive/2012/01/12/2321084.html 软中断.tasklet和工作队列并不是Linux内核中一直存在的机制, ...
- 《深入理解Linux内核》软中断/tasklet/工作队列
软中断.tasklet和工作队列并不是Linux内核中一直存在的机制,而是由更早版本的内核中的“下半部”(bottom half)演变而来.下半部的机制实际上包括五种,但2.6版本的内核中,下半部和任 ...
- linux 内核 tasklets 原理以及工作队列
如果某种应用并不需要在多个CPU上并行执行,那么软中断其实是没有必要的.因此诞生了弥补以上两个要求的tasklet.它具有以下特性: a)一种特定类型的tasklet只能运行在一个CPU上,不能并行, ...
随机推荐
- 大数据系列2:Hdfs的读写操作
在前文大数据系列1:一文初识Hdfs中,我们对Hdfs有了简单的认识. 在本文中,我们将会简单的介绍一下Hdfs文件的读写流程,为后续追踪读写流程的源码做准备. Hdfs 架构 首先来个Hdfs的架构 ...
- jemeter断言和性能分析
一.添加断言 1.原因:检查是否有该结果,一般一个请求过去除了400和500的只要通过的都会代表请求成功,比如登录页面及时填写了错误密码,虽然会返回密码错误,但这个请求还是成功的,所以我们要添加断言, ...
- 倍增小结 ST 与 LCA
倍增 倍增我是真滴不会 倍增法(英语:binary lifting),顾名思义就是翻倍. 能够使线性的处理转化为对数级的处理,大大地优化时间复杂度. (ps:上次学倍增LCA,没学会,老老实实为了严格 ...
- LOJ10132
在 Adera 的异时空中有一张地图.这张地图上有 N 个点,有 N-1 条双向边把它们连通起来.起初地图上没有任何异象石,在接下来的 M 个时刻中,每个时刻会发生以下三种类型的事件之一: 地图的某个 ...
- 获取java栈异常
package com.loan.modules.extbiz.in.rabbitmq.util; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.io.StringW ...
- 当 .NET 5 遇上OpenTelemetry,会碰撞出怎样的火花?
OpenTelemetry 介绍 我在之前的几篇文章都介绍了 OpenTelemetry, 你可以在这里找到 OpenTelemetry - 云原生下可观测性的新标准 深入研究 .NET 5 的开放式 ...
- Nacos服务心跳和健康检查源码介绍
服务心跳 Nacos Client会维护一个定时任务通过持续调用服务端的接口更新心跳时间,保证自己处于存活状态,防止服务端将服务剔除,Nacos默认5秒向服务端发送一次,通过请求服务端接口/insta ...
- vscode开发vue,热更新
1.首先用vscode去安装热更新插件 2.vscode安装后默认修改的文件是没有开启自动保存的,需要将自动保存勾选 这样就不用每次修改都去open with live server:
- HDOJ 1028 母函数分析
#include<iostream>#include<cstring>using namespace std;int main(){ int c1[10000],c2[1 ...
- STL中pair容器的用法
1.定义pair容器 1 pair <int, int> p, p1; 2 //定义 [int,int] 型容器 //直接初始化了p的内容 pair<string,int>p( ...
