μC/OS-III---I笔记8---事件标志
当任务需要同步时可以使用信号量。A任务给B任务发送消息后B任务才能继续运行。如果需要A任务给任务B传递数据的时候就可以采用消息队列。但对于繁杂任务的同步,比如多个时间发生以后执行一个事件,或者是C任务需要任务A和任务B都完成对应的处理任务后才能执行C任务的处理工作,这是用信号量就是等待多个内核对象,有没有一种更好的办法呢,操作系统的大神就创造出了时间标志来进行这类功能的实现。事件标志组的数据结构是最简单的,只需要将多值信号量的Ctr变量换个名字(Flags)就好了。
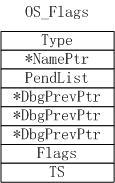
对于不同的处理器Flags的位数可能会有不同,时间标志组中的Flags的每一位都对应一个事件,对于其发生与否的标志在创建时进行了说明。
1,对于事件标志组的创建函数,同样前提是定义一个事件标志组变量,第一个参数是时间标志组的变量地址,第二个参数是时间标志租的Name了,第三个则是初始化的Flags值。样在创建了事件标志组的同时也初始化了其的等待队列。
************************************************************************************************************************
* CREATE AN EVENT FLAG
*
* Description: This function is called to create an event flag group.
*
* Arguments : p_grp is a pointer to the event flag group to create
*
* p_name is the name of the event flag group
*
* flags contains the initial value to store in the event flag group (typically 0).
*
* p_err is a pointer to an error code which will be returned to your application:
*
* OS_ERR_NONE if the call was successful.
* OS_ERR_CREATE_ISR if you attempted to create an Event Flag from an ISR.
* OS_ERR_ILLEGAL_CREATE_RUN_TIME if you are trying to create the Event Flag after you
* called OSSafetyCriticalStart().
* OS_ERR_NAME if 'p_name' is a NULL pointer
* OS_ERR_OBJ_CREATED if the event flag group has already been created
* OS_ERR_OBJ_PTR_NULL if 'p_grp' is a NULL pointer
*
* Returns : none
************************************************************************************************************************
*/ void OSFlagCreate (OS_FLAG_GRP *p_grp,
CPU_CHAR *p_name,
OS_FLAGS flags,
OS_ERR *p_err)
{
CPU_SR_ALLOC(); #ifdef OS_SAFETY_CRITICAL
if (p_err == (OS_ERR *)0) {
OS_SAFETY_CRITICAL_EXCEPTION();
return;
}
#endif #ifdef OS_SAFETY_CRITICAL_IEC61508
if (OSSafetyCriticalStartFlag == DEF_TRUE) {
*p_err = OS_ERR_ILLEGAL_CREATE_RUN_TIME;
return;
}
#endif #if OS_CFG_CALLED_FROM_ISR_CHK_EN > 0u
if (OSIntNestingCtr > (OS_NESTING_CTR)0) { /* See if called from ISR ... */
*p_err = OS_ERR_CREATE_ISR; /* ... can't CREATE from an ISR */
return;
}
#endif #if OS_CFG_ARG_CHK_EN > 0u
if (p_grp == (OS_FLAG_GRP *)0) { /* Validate 'p_grp' */
*p_err = OS_ERR_OBJ_PTR_NULL;
return;
}
#endif OS_CRITICAL_ENTER();
p_grp->Type = OS_OBJ_TYPE_FLAG; /* Set to event flag group type */
p_grp->NamePtr = p_name;
p_grp->Flags = flags; /* Set to desired initial value */
p_grp->TS = (CPU_TS)0;
//等待队列初始化
OS_PendListInit(&p_grp->PendList); #if OS_CFG_DBG_EN > 0u
OS_FlagDbgListAdd(p_grp);
#endif
//事件标志组内核对象计数加1
OSFlagQty++; OS_CRITICAL_EXIT_NO_SCHED();
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
}
OSFlagCreate
2.等待事件标志组:
等待时间标志组的具体操作从函数的签名可以看出,主要是有一下几个条件,第一对应标志组内Flags的哪几位代表请求的时间,第二每一位是置位标志着事件发生了还是复位表明事件已经发生了,第三就是前面提到的是多个时间全部发生(ALL)还是任何一个事件(ANY)发生就标志事件标志组满足条件,最后还要选择满足条件后是否要进行取反(CONSUME)操作。
************************************************************************************************************************
* WAIT ON AN EVENT FLAG GROUP
*
* Description: This function is called to wait for a combination of bits to be set in an event flag group. Your
* application can wait for ANY bit to be set or ALL bits to be set.
*
* Arguments : p_grp is a pointer to the desired event flag group.
*
* flags Is a bit pattern indicating which bit(s) (i.e. flags) you wish to wait for.
* The bits you want are specified by setting the corresponding bits in 'flags'.
* e.g. if your application wants to wait for bits 0 and 1 then 'flags' would contain 0x03.
*
* timeout is an optional timeout (in clock ticks) that your task will wait for the
* desired bit combination. If you specify 0, however, your task will wait
* forever at the specified event flag group or, until a message arrives.
*
* opt specifies whether you want ALL bits to be set or ANY of the bits to be set.
* You can specify the 'ONE' of the following arguments:
*
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL You will wait for ALL bits in 'flags' to be clear (0)
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY You will wait for ANY bit in 'flags' to be clear (0)
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL You will wait for ALL bits in 'flags' to be set (1)
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY You will wait for ANY bit in 'flags' to be set (1)
*
* You can 'ADD' OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME if you want the event flag to be 'consumed' by
* the call. Example, to wait for any flag in a group AND then clear
* the flags that are present, set 'wait_opt' to:
*
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY + OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME
*
* You can also 'ADD' the type of pend with 'ONE' of the two option:
*
* OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING Task will NOT block if flags are not available
* OS_OPT_PEND_BLOCKING Task will block if flags are not available
*
* p_ts is a pointer to a variable that will receive the timestamp of when the event flag group was
* posted, aborted or the event flag group deleted. If you pass a NULL pointer (i.e. (CPU_TS *)0)
* then you will not get the timestamp. In other words, passing a NULL pointer is valid and
* indicates that you don't need the timestamp.
*
* p_err is a pointer to an error code and can be:
*
* OS_ERR_NONE The desired bits have been set within the specified 'timeout'
* OS_ERR_OBJ_PTR_NULL If 'p_grp' is a NULL pointer.
* OS_ERR_OBJ_TYPE You are not pointing to an event flag group
* OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID You didn't specify a proper 'opt' argument.
* OS_ERR_PEND_ABORT The wait on the flag was aborted.
* OS_ERR_PEND_ISR If you tried to PEND from an ISR
* OS_ERR_PEND_WOULD_BLOCK If you specified non-blocking but the flags were not
* available.
* OS_ERR_SCHED_LOCKED If you called this function when the scheduler is locked
* OS_ERR_TIMEOUT The bit(s) have not been set in the specified 'timeout'.
*
* Returns : The flags in the event flag group that made the task ready or, 0 if a timeout or an error
* occurred.
************************************************************************************************************************
*/ OS_FLAGS OSFlagPend (OS_FLAG_GRP *p_grp,
OS_FLAGS flags,
OS_TICK timeout,
OS_OPT opt,
CPU_TS *p_ts,
OS_ERR *p_err)
{
CPU_BOOLEAN consume;
OS_FLAGS flags_rdy;
OS_OPT mode;
OS_PEND_DATA pend_data;
CPU_SR_ALLOC(); #ifdef OS_SAFETY_CRITICAL
if (p_err == (OS_ERR *)0) {
OS_SAFETY_CRITICAL_EXCEPTION();
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
#endif #if OS_CFG_CALLED_FROM_ISR_CHK_EN > 0u
if (OSIntNestingCtr > (OS_NESTING_CTR)0) { /* See if called from ISR ... */
*p_err = OS_ERR_PEND_ISR; /* ... can't PEND from an ISR */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
#endif #if OS_CFG_ARG_CHK_EN > 0u
if (p_grp == (OS_FLAG_GRP *)0) { /* Validate 'p_grp' */
*p_err = OS_ERR_OBJ_PTR_NULL;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
switch (opt) { /* Validate 'opt' */
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY | OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME | OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING:
break; default:
*p_err = OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID;
return ((OS_OBJ_QTY)0);
}
#endif #if OS_CFG_OBJ_TYPE_CHK_EN > 0u
if (p_grp->Type != OS_OBJ_TYPE_FLAG) { /* Validate that we are pointing at an event flag */
*p_err = OS_ERR_OBJ_TYPE;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
#endif
//取反标志位检查
if ((opt & OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CONSUME) != (OS_OPT)0) { /* See if we need to consume the flags */
consume = DEF_TRUE;
} else {
consume = DEF_FALSE;
} if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = (CPU_TS)0; /* Initialize the returned timestamp */
}
//取出模式标志位
mode = opt & OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_MASK;
CPU_CRITICAL_ENTER();
switch (mode) {
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL: /* See if all required flags are set */
// 取出事件标志组的特定位
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(p_grp->Flags & flags); /* Extract only the bits we want */
//满足设定满足条件?
if (flags_rdy == flags) { /* Must match ALL the bits that we want */
//是,是否取反
if (consume == DEF_TRUE) { /* See if we need to consume the flags */
//是
p_grp->Flags &= ~flags_rdy; /* Clear ONLY the flags that we wanted */
}
//设定任务控制块的标志变量
OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsRdy = flags_rdy; /* Save flags that were ready */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = p_grp->TS;
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT(); /* Yes, condition met, return to caller */
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
return (flags_rdy);
}
//不满足
else { /* Block task until events occur or timeout */
if ((opt & OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING) != (OS_OPT)0) {
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_PEND_WOULD_BLOCK; /* Specified non-blocking so task would block */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
} else { /* Specified blocking so check is scheduler is locked */
if (OSSchedLockNestingCtr > (OS_NESTING_CTR)0) { /* See if called with scheduler locked ... */
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_SCHED_LOCKED; /* ... can't PEND when locked */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
}
/* Lock the scheduler/re-enable interrupts */
OS_CRITICAL_ENTER_CPU_EXIT();
//事件标志组阻塞任务
OS_FlagBlock(&pend_data,
p_grp,
flags,
opt,
timeout);
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT_NO_SCHED();
}
break;
//任何位满足模式
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY:
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(p_grp->Flags & flags); /* Extract only the bits we want */
//有任何一个位满足
if (flags_rdy != (OS_FLAGS)0) { /* See if any flag set */
if (consume == DEF_TRUE) { /* See if we need to consume the flags */
p_grp->Flags &= ~flags_rdy; /* Clear ONLY the flags that we got */
}
OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsRdy = flags_rdy; /* Save flags that were ready */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = p_grp->TS;
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT(); /* Yes, condition met, return to caller */
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
return (flags_rdy);
} else { /* Block task until events occur or timeout */
if ((opt & OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING) != (OS_OPT)0) {
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_PEND_WOULD_BLOCK; /* Specified non-blocking so task would block */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
} else { /* Specified blocking so check is scheduler is locked */
if (OSSchedLockNestingCtr > (OS_NESTING_CTR)0) { /* See if called with scheduler locked ... */
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_SCHED_LOCKED; /* ... can't PEND when locked */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
}
/* Lock the scheduler/re-enable interrupts */
OS_CRITICAL_ENTER_CPU_EXIT();
OS_FlagBlock(&pend_data,
p_grp,
flags,
opt,
timeout);
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT_NO_SCHED();
}
break;
//为复位标志事件发生模式,其他同上
#if OS_CFG_FLAG_MODE_CLR_EN > 0u
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL: /* See if all required flags are cleared */
//注意这里的区别
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(~p_grp->Flags & flags); /* Extract only the bits we want */
if (flags_rdy == flags) { /* Must match ALL the bits that we want */
if (consume == DEF_TRUE) { /* See if we need to consume the flags */
//这里也有不同
p_grp->Flags |= flags_rdy; /* Set ONLY the flags that we wanted */
}
OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsRdy = flags_rdy; /* Save flags that were ready */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = p_grp->TS;
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT(); /* Yes, condition met, return to caller */
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
return (flags_rdy);
} else { /* Block task until events occur or timeout */
if ((opt & OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING) != (OS_OPT)0) {
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_PEND_WOULD_BLOCK; /* Specified non-blocking so task would block */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
} else { /* Specified blocking so check is scheduler is locked */
if (OSSchedLockNestingCtr > (OS_NESTING_CTR)0) { /* See if called with scheduler locked ... */
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_SCHED_LOCKED; /* ... can't PEND when locked */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
} OS_CRITICAL_ENTER_CPU_EXIT(); /* Lock the scheduler/re-enable interrupts */
OS_FlagBlock(&pend_data,
p_grp,
flags,
opt,
timeout);
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT_NO_SCHED();
}
break; case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY:
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(~p_grp->Flags & flags); /* Extract only the bits we want */
if (flags_rdy != (OS_FLAGS)0) { /* See if any flag cleared */
if (consume == DEF_TRUE) { /* See if we need to consume the flags */
p_grp->Flags |= flags_rdy; /* Set ONLY the flags that we got */
}
OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsRdy = flags_rdy; /* Save flags that were ready */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = p_grp->TS;
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT(); /* Yes, condition met, return to caller */
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
return (flags_rdy);
} else { /* Block task until events occur or timeout */
if ((opt & OS_OPT_PEND_NON_BLOCKING) != (OS_OPT)0) {
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_PEND_WOULD_BLOCK; /* Specified non-blocking so task would block */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
} else { /* Specified blocking so check is scheduler is locked */
if (OSSchedLockNestingCtr > (OS_NESTING_CTR)0) { /* See if called with scheduler locked ... */
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_SCHED_LOCKED; /* ... can't PEND when locked */
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
} OS_CRITICAL_ENTER_CPU_EXIT(); /* Lock the scheduler/re-enable interrupts */
OS_FlagBlock(&pend_data,
p_grp,
flags,
opt,
timeout);
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT_NO_SCHED();
}
break;
#endif default:
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
} OSSched(); /* Find next HPT ready to run */
//任务重新恢复执行入口处,后面判断事件满足的原因
CPU_CRITICAL_ENTER();
switch (OSTCBCurPtr->PendStatus) {
case OS_STATUS_PEND_OK: /* We got the vent flags */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = OSTCBCurPtr->TS;
}
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
break; case OS_STATUS_PEND_ABORT: /* Indicate that we aborted */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = OSTCBCurPtr->TS;
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_PEND_ABORT;
break; case OS_STATUS_PEND_TIMEOUT: /* Indicate that we didn't get semaphore within timeout */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = (CPU_TS )0;
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_TIMEOUT;
break; case OS_STATUS_PEND_DEL: /* Indicate that object pended on has been deleted */
if (p_ts != (CPU_TS *)0) {
*p_ts = OSTCBCurPtr->TS;
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_OBJ_DEL;
break; default:
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_STATUS_INVALID;
break;
}
if (*p_err != OS_ERR_NONE) {
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
//任务在POST时已经将事件标志组放入任务控制块的FlagsRdy里了
flags_rdy = OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsRdy;
//进行相应位取反
if (consume == DEF_TRUE) { /* See if we need to consume the flags */
switch (mode) {
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY: /* Clear ONLY the flags we got */
p_grp->Flags &= ~flags_rdy;
break; #if OS_CFG_FLAG_MODE_CLR_EN > 0u
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL:
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY: /* Set ONLY the flags we got */
p_grp->Flags |= flags_rdy;
break;
#endif
default:
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
}
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE; /* Event(s) must have occurred */
return (flags_rdy);
}
OSFlagPend ()
这是事件标志组特有的阻塞函数,其实原理还是一样就是多了一部分向任务控制块写入的操作。
************************************************************************************************************************
* SUSPEND TASK UNTIL EVENT FLAG(s) RECEIVED OR TIMEOUT OCCURS
*
* Description: This function is internal to uC/OS-III and is used to put a task to sleep until the desired
* event flag bit(s) are set.
*
* Arguments : p_pend_data is a pointer to an object used to link the task being blocked to the list of task(s)
* ----------- pending on the desired event flag group.
*
* p_grp is a pointer to the desired event flag group.
* -----
*
* flags Is a bit pattern indicating which bit(s) (i.e. flags) you wish to check.
* The bits you want are specified by setting the corresponding bits in
* 'flags'. e.g. if your application wants to wait for bits 0 and 1 then
* 'flags' would contain 0x03.
*
* opt specifies whether you want ALL bits to be set/cleared or ANY of the bits
* to be set/cleared.
* You can specify the following argument:
*
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL You will check ALL bits in 'mask' to be clear (0)
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY You will check ANY bit in 'mask' to be clear (0)
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL You will check ALL bits in 'mask' to be set (1)
* OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY You will check ANY bit in 'mask' to be set (1)
*
* timeout is the desired amount of time that the task will wait for the event flag
* bit(s) to be set.
*
* Returns : none
*
* Note(s) : This function is INTERNAL to uC/OS-III and your application should not call it.
************************************************************************************************************************
*/ void OS_FlagBlock (OS_PEND_DATA *p_pend_data,
OS_FLAG_GRP *p_grp,
OS_FLAGS flags,
OS_OPT opt,
OS_TICK timeout)
{
//事件标志组的特别操作
OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsPend = flags; /* Save the flags that we need to wait for */
OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsOpt = opt; /* Save the type of wait we are doing */
OSTCBCurPtr->FlagsRdy = (OS_FLAGS)0;
//加入内核对象等待队列,并阻塞任务
OS_Pend(p_pend_data,
(OS_PEND_OBJ *)((void *)p_grp),
OS_TASK_PEND_ON_FLAG,
timeout);
}
OS_FlagBlock ()
3.对应到发布事件组,同样是如此,对应那个几个位,怎么操作,最后就是post函数内的共性就是检查等待列表里是否有满足条件的任务这里区分任何一个还是所有位满足,如果满足就将任务加入到就绪列表里。这里需要注意理解的就是函数内关于位操作的一些写法。
************************************************************************************************************************
* POST EVENT FLAG BIT(S)
*
* Description: This function is called to set or clear some bits in an event flag group. The bits to set or clear are
* specified by a 'bit mask'.
*
* Arguments : p_grp is a pointer to the desired event flag group.
*
* flags If 'opt' (see below) is OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET, each bit that is set in 'flags' will
* set the corresponding bit in the event flag group. e.g. to set bits 0, 4
* and 5 you would set 'flags' to:
*
* 0x31 (note, bit 0 is least significant bit)
*
* If 'opt' (see below) is OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR, each bit that is set in 'flags' will
* CLEAR the corresponding bit in the event flag group. e.g. to clear bits 0,
* 4 and 5 you would specify 'flags' as:
*
* 0x31 (note, bit 0 is least significant bit)
*
* opt indicates whether the flags will be:
*
* OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET set
* OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR cleared
*
* you can also 'add' OS_OPT_POST_NO_SCHED to prevent the scheduler from being called.
*
* p_err is a pointer to an error code and can be:
*
* OS_ERR_NONE The call was successful
* OS_ERR_OBJ_PTR_NULL You passed a NULL pointer
* OS_ERR_OBJ_TYPE You are not pointing to an event flag group
* OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID You specified an invalid option
*
* Returns : the new value of the event flags bits that are still set.
*
* Note(s) : 1) The execution time of this function depends on the number of tasks waiting on the event flag group.
************************************************************************************************************************
*/ OS_FLAGS OSFlagPost (OS_FLAG_GRP *p_grp,
OS_FLAGS flags,
OS_OPT opt,
OS_ERR *p_err)
{
OS_FLAGS flags_cur;
CPU_TS ts; #ifdef OS_SAFETY_CRITICAL
if (p_err == (OS_ERR *)0) {
OS_SAFETY_CRITICAL_EXCEPTION();
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
#endif #if OS_CFG_ARG_CHK_EN > 0u
if (p_grp == (OS_FLAG_GRP *)0) { /* Validate 'p_grp' */
*p_err = OS_ERR_OBJ_PTR_NULL;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
switch (opt) { /* Validate 'opt' */
case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET:
case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR:
case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET | OS_OPT_POST_NO_SCHED:
case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR | OS_OPT_POST_NO_SCHED:
break; default:
*p_err = OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
#endif #if OS_CFG_OBJ_TYPE_CHK_EN > 0u
if (p_grp->Type != OS_OBJ_TYPE_FLAG) { /* Make sure we are pointing to an event flag grp */
*p_err = OS_ERR_OBJ_TYPE;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
#endif ts = OS_TS_GET(); /* Get timestamp */
//延迟发布
#if OS_CFG_ISR_POST_DEFERRED_EN > 0u
if (OSIntNestingCtr > (OS_NESTING_CTR)0) { /* See if called from an ISR */
OS_IntQPost((OS_OBJ_TYPE)OS_OBJ_TYPE_FLAG, /* Post to ISR queue */
(void *)p_grp,
(void *)0,
(OS_MSG_SIZE)0,
(OS_FLAGS )flags,
(OS_OPT )opt,
(CPU_TS )ts,
(OS_ERR *)p_err);
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
#endif
//立即发布
flags_cur = OS_FlagPost(p_grp,
flags,
opt,
ts,
p_err); return (flags_cur);
}
OSFlagPost()
************************************************************************************************************************
* POST EVENT FLAG BIT(S)
*
* Description: This function is called to set or clear some bits in an event flag group. The bits to set or clear are
* specified by a 'bit mask'.
*
* Arguments : p_grp is a pointer to the desired event flag group.
*
* flags If 'opt' (see below) is OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET, each bit that is set in 'flags' will
* set the corresponding bit in the event flag group. e.g. to set bits 0, 4
* and 5 you would set 'flags' to:
*
* 0x31 (note, bit 0 is least significant bit)
*
* If 'opt' (see below) is OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR, each bit that is set in 'flags' will
* CLEAR the corresponding bit in the event flag group. e.g. to clear bits 0,
* 4 and 5 you would specify 'flags' as:
*
* 0x31 (note, bit 0 is least significant bit)
*
* opt indicates whether the flags will be:
*
* OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET set
* OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR cleared
*
* you can also 'add' OS_OPT_POST_NO_SCHED to prevent the scheduler from being called.
*
* ts is the timestamp of the post
*
* p_err is a pointer to an error code and can be:
*
* OS_ERR_NONE The call was successful
* OS_ERR_OBJ_PTR_NULL You passed a NULL pointer
* OS_ERR_OBJ_TYPE You are not pointing to an event flag group
* OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID You specified an invalid option
*
* Returns : the new value of the event flags bits that are still set.
*
* Note(s) : 1) The execution time of this function depends on the number of tasks waiting on the event flag group.
************************************************************************************************************************
*/ OS_FLAGS OS_FlagPost (OS_FLAG_GRP *p_grp,
OS_FLAGS flags,
OS_OPT opt,
CPU_TS ts,
OS_ERR *p_err)
{
OS_FLAGS flags_cur;
OS_FLAGS flags_rdy;
OS_OPT mode;
OS_PEND_DATA *p_pend_data;
OS_PEND_DATA *p_pend_data_next;
OS_PEND_LIST *p_pend_list;
OS_TCB *p_tcb;
CPU_SR_ALLOC(); CPU_CRITICAL_ENTER();
switch (opt) {
case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET:
case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_SET | OS_OPT_POST_NO_SCHED:
p_grp->Flags |= flags; /* Set the flags specified in the group */
break; case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR:
case OS_OPT_POST_FLAG_CLR | OS_OPT_POST_NO_SCHED:
p_grp->Flags &= ~flags; /* Clear the flags specified in the group */
break; default:
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT(); /* INVALID option */
*p_err = OS_ERR_OPT_INVALID;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
//记录发布时间
p_grp->TS = ts;
//取出等待队列
p_pend_list = &p_grp->PendList;
if (p_pend_list->NbrEntries == 0u) { /* Any task waiting on event flag group? */
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT(); /* No */
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
return (p_grp->Flags);
} OS_CRITICAL_ENTER_CPU_EXIT();
p_pend_data = p_pend_list->HeadPtr;
p_tcb = p_pend_data->TCBPtr;
//依次查找等待队列,找出满足条件的任务
while (p_tcb != (OS_TCB *)0) { /* Go through all tasks waiting on event flag(s) */
p_pend_data_next = p_pend_data->NextPtr;
mode = p_tcb->FlagsOpt & OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_MASK;
switch (mode) {
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ALL: /* See if all req. flags are set for current node */
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(p_grp->Flags & p_tcb->FlagsPend);
if (flags_rdy == p_tcb->FlagsPend) {
//将任务就绪 ,同时从等待队列删除,下同
OS_FlagTaskRdy(p_tcb, /* Make task RTR, event(s) Rx'd */
flags_rdy,
ts);
}
break; case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_SET_ANY: /* See if any flag set */
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(p_grp->Flags & p_tcb->FlagsPend);
if (flags_rdy != (OS_FLAGS)0) {
OS_FlagTaskRdy(p_tcb, /* Make task RTR, event(s) Rx'd */
flags_rdy,
ts);
}
break; #if OS_CFG_FLAG_MODE_CLR_EN > 0u
case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ALL: /* See if all req. flags are set for current node */
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(~p_grp->Flags & p_tcb->FlagsPend);
if (flags_rdy == p_tcb->FlagsPend) {
OS_FlagTaskRdy(p_tcb, /* Make task RTR, event(s) Rx'd */
flags_rdy,
ts);
}
break; case OS_OPT_PEND_FLAG_CLR_ANY: /* See if any flag set */
flags_rdy = (OS_FLAGS)(~p_grp->Flags & p_tcb->FlagsPend);
if (flags_rdy != (OS_FLAGS)0) {
OS_FlagTaskRdy(p_tcb, /* Make task RTR, event(s) Rx'd */
flags_rdy,
ts);
}
break;
#endif
default:
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_FLAG_PEND_OPT;
return ((OS_FLAGS)0);
}
p_pend_data = p_pend_data_next; /* Point to next task waiting for event flag(s) */
if (p_pend_data != (OS_PEND_DATA *)0) {
p_tcb = p_pend_data->TCBPtr;
} else {
p_tcb = (OS_TCB *)0;
}
}
OS_CRITICAL_EXIT_NO_SCHED(); if ((opt & OS_OPT_POST_NO_SCHED) == (OS_OPT)0) {
OSSched();
} CPU_CRITICAL_ENTER();
flags_cur = p_grp->Flags;
CPU_CRITICAL_EXIT();
*p_err = OS_ERR_NONE;
return (flags_cur);
}
OS_FlagPost ()
这是事件标志组特有的任务就绪函数,其实原理还是一样还是多了一部分向任务控制块写入的操作。
************************************************************************************************************************
* MAKE TASK READY-TO-RUN, EVENT(s) OCCURRED
*
* Description: This function is internal to uC/OS-III and is used to make a task ready-to-run because the desired event
* flag bits have been set.
*
* Arguments : p_tcb is a pointer to the OS_TCB of the task to remove
* -----
*
* flags_rdy contains the bit pattern of the event flags that cause the task to become ready-to-run.
*
* ts is a timestamp associated with the post
*
* Returns : none
*
* Note(s) : This function is INTERNAL to uC/OS-III and your application should not call it.
************************************************************************************************************************
*/ void OS_FlagTaskRdy (OS_TCB *p_tcb,
OS_FLAGS flags_rdy,
CPU_TS ts)
{
p_tcb->FlagsRdy = flags_rdy;
p_tcb->PendStatus = OS_STATUS_PEND_OK; /* Clear pend status */
p_tcb->PendOn = OS_TASK_PEND_ON_NOTHING; /* Indicate no longer pending */
p_tcb->TS = ts;
switch (p_tcb->TaskState) {
case OS_TASK_STATE_RDY:
case OS_TASK_STATE_DLY:
case OS_TASK_STATE_DLY_SUSPENDED:
case OS_TASK_STATE_SUSPENDED:
break; case OS_TASK_STATE_PEND:
case OS_TASK_STATE_PEND_TIMEOUT:
OS_TaskRdy(p_tcb);
p_tcb->TaskState = OS_TASK_STATE_RDY;
break; case OS_TASK_STATE_PEND_SUSPENDED:
case OS_TASK_STATE_PEND_TIMEOUT_SUSPENDED:
p_tcb->TaskState = OS_TASK_STATE_SUSPENDED;
break; default:
break;
}
OS_PendListRemove(p_tcb);
}
#endif
OS_FlagTaskRdy ()
时间标志组 最重要的是将位和任务联系起来,同时继续了信号量的等待任务管理。
μC/OS-III---I笔记8---事件标志的更多相关文章
- 【uTenux实验】事件标志
事件标志是一个用来实现同步的对象,由多个位组成,用作指示对应事件存在的标志.事件标志由用来指示对应事件存在的位模式(bitpattern)和一个等待事件标志的任务队列组成. uTenux提供了一组AP ...
- Android笔记:触摸事件的分析与总结----TouchEvent处理机制
原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任.http://glblong.blog.51cto.com/3058613/1559320 ...
- 16.3-uC/OS-III同步 (事件标志组实验)
事件标志组,顾名思义,就是若干个事件标志的组合,代表若干个事件是否发生,通常用于集合两个或两个以上事件的状态 . 1.如果想要使用事件标志组,就必须事先使能事件标志组.消息队列的使能位于“os_cfg ...
- 16.2-uC/OS-III同步 (事件标志组)
事件标志组 1.当任务要与多个事件同步时可以使用事件标志.若其中的任意一个事件发生时任务被就绪, 叫做逻辑或(OR).若所有的事件都发生时任务被就绪,叫做逻辑与( AND). 2.用户可以创建任意个事 ...
- FreeRTOS 事件标志组 ——提高篇
假设你已经看过FreeRTOS 事件标志组这篇随笔了. 之前的基础篇,真的就只是简单了解一下,相当于大学实验室的实验,但是,我们实际公司项目中,需要更多地思考,就算我们之前只是学习了基础概念以及基础语 ...
- RTX——第13章 事件标志组
以下内容转载自安富莱电子: http://forum.armfly.com/forum.php 前面的章节我们已经讲解了任务管理和时间管理,从本章节开始讲解任务间的通信和同步机制.首先讲解任务间的通信 ...
- javascript - 工作笔记 (事件四)
在javascript - 工作笔记 (事件绑定二)篇中,我将事件的方法做了简单的包装, JavaScript Code 12345 yx.bind(item, "click&quo ...
- uc/os iii移植到STM32F4---IAR开发环境
也许是先入为主的原因,时钟用不惯Keil环境,大多数的教程都是拿keil写的,尝试将官方的uc/os iii 移植到IAR环境. 1.首先尝试从官网上下载的官方移植的代码,编译通过,但是执行会报堆栈溢 ...
- ucos中信号量 事件标志 消息队列都怎么用
信号量 事件标志和消息队列分别应用于什么场景(反正我学的时候有点闹不清,现在总结一下): 信号量和事件标志用于任务同步.详细来说,这个功能可以替代以前裸机中你打一个标记的功能,比如使用了一个定时器,5 ...
- 基于μC/OS—III的CC1120驱动程序设计
基于μC/OS—III的CC1120驱动程序设计 时间:2014-01-21 来源:电子设计工程 作者:张绍游,张贻雄,石江宏 关键字:CC1120 嵌入式操作系统 STM32F103ZE ...
随机推荐
- Python爬虫:数据分析小能手:JSON库的用法
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人阅读和编写. 给大家推荐一个Python交流的q裙,大家在学习遇到了什么问题都可以进群一起交流,大家 ...
- 关于springboot项目通过jar包启动之后无法读取项目根路径静态资源
在一次项目开发过程中,项目根路径下存放了一张图片,生成二维码的时候调用了该图片作为二维码的logo,在windows环境下二维码可以正常生成,但是部署到生产测试环境之后二维码生成报错,FileNotF ...
- linux 文件目录权限
文件目录权限: 什么是文件权限: 在Linux中,每个文件都有所属的所有者,和所有组,并且规定了文件的所有者,所有组以及其他人对文件的,可读,可写,可执行等权限. 对于目录的权限来说,可读是读取目录文 ...
- history附上时间戳,history命令_Linux history命令:查看和执行历史命令
起因是这样的,一台机器客户反馈连接不上,说没有任何操作.好吧,排查吧. 1.第一步先看网络是否通: 从图中可以看到一开始是一直不通的.然后就通了,问了客户有没操作重启什么的结果说没有任何操作,还让给个 ...
- 文件的上传/下载+在线游览(转化html)--不需要在线插件//自己写的小方法
1 /// <summary> 2 /// 文件上传下载帮助类 3 /// </summary> 4 public static class FileHelper 5 { 6 ...
- 纯手工撸一个vue框架
前言 vue create 真的很方便,但是很多人欠缺的是手动撸一遍.有些人离开脚手架都不会开发了. Vue最简单的结构 步骤 搭建最基本的结构 打开空文件夹,通过 npm init 命令生成pack ...
- Go 如何实现热重启
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/UVZKFmv8p4ghm8ICdz85wQ Go 如何实现热重启 原创 zhijiezhang 腾讯技术工程 2020-09-09
- OpenSSL 常见对称加密算法特性分析
在选择加密算法,面对一大长串的选项时,大家都有这样的疑问,究竟哪种加密方式是最好的呢? 对于加密方式.算法来说,一般安全性与性能呈负相关,越是安全的,对性能要求则更高. 现在主流的加密协议的安全性均能 ...
- 济南学习D1T5__HEAP
死亡 [问题描述] 现在有个位置可以打sif,有个人在排队等着打sif.现在告诉你前个人每个人需要多长的时间打sif,问你第个人什么时候才能打sif.(前个人必须按照顺序来) [输入格式] 第一行两个 ...
- SpringMVC听课笔记(四:映射请求参数 & 请求头)
1.请求参数 @RequestParam 来映射请求参数 http://localhost:8080/springmvc-1/springmvc/testRequestParam?username ...
