【Linux】saltstack 安装及简单使用
准备三台server,一台为master(10.96.20.113),另两台为minion(10.96.20.117,10.96.20.118)
主机名(master、minion1、minion2)、IP配置好(10.96.20.113、10.96.20.117、10.96.20.118)
master-side和minion-side:
[root@master ~]# uname -rm
2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64 x86_64
[root@master ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.5(Santiago)
[root@master ~]# yum -y install python-requests PyYAML python-crypto python-jinja2 #(先使用CentOS6-Base-163.repo或其它yum源安装好这几个包,再用epel源安装salt-master,因为epel源中缺少这几包导致安装会报如下错)
……
Error: Package:salt-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch (epel)
Requires: python-crypto
Error: Package:salt-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch (epel)
Requires: PyYAML
Error: Package:salt-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch (epel)
Requires: python-requests
Error: Package:salt-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch (epel)
Requires: python-jinja2
Youcould try using --skip-broken to work around the problem
Youcould try running: rpm -Va --nofiles --nodigest
master-side:
[root@master ~]# wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/fedora/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@master ~]# rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
warning: epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm:Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID 0608b895: NOKEY
Preparing... ###########################################[100%]
1:epel-release ########################################### [100%]
[root@master ~]# yum -y install salt-master
Running Transaction
Installing : openpgm-5.1.118-3.el6.x86_64 1/6
Installing : zeromq3-3.2.5-1.el6.x86_64 2/6
Installing : python-zmq-14.3.1-1.el6.x86_64 3/6
Installing : python-msgpack-0.4.6-1.el6.x86_64 4/6
Installing : salt-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch 5/6
Installing : salt-master-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch 6/6
……
minion-side:
[root@minion1 ~]# wget http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/fedora/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@minion1 ~]# rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[root@minion1 ~]# yum -y install salt-minion
master-side:
[root@master ~]# vim /etc/salt/master #(master-side默认配置文件/etc/salt/master,可在启动时通过-c或--config-dir指定配置文件存放路径,默认会加载/etc/salt/master.d/*.conf文件,配置文件格式为YAML)
配置文件如下:
##### Primary configuration settings #####
##########################################
#default_include: master.d/*.conf
#interface: 0.0.0.0 #(bind监听的地址)
#ipv6: False
#publish_port: 4505 #(PUB,4505master向minion发送命令的port,而ret_port: 4506,用于接收minion返回的结果)
#user: root #(运行salt-master的用户)
#max_open_files: 100000 #(#ulimit -n;#vim/etc/security/limits.conf)
#worker_threads: 5
#ret_port: 4506
#pidfile: /var/run/salt-master.pid
#root_dir: /
#pki_dir: /etc/salt/pki/master
#cachedir: /var/cache/salt/master
#verify_env: True
#keep_jobs: 24 #(minion端执行命令的结果会返回到master端本地的cachedir指定路径下,默认缓存24h,会占用大量磁盘空间)
#timeout: 5 #(master向minion发送指令,在5s内minion向master返回结果,这时master的salt退出;若在5s内minion没返回结果,master上会执行find_job查找minion端proc的jid,以知道minion执行当前命令的情况,若minion正在执行master会继续等待5s再用find_job了解执行情况;若在第一次find_job时minion端proc就没当前执行的jid,master会直接退出;若minion规模庞大或网络状况不好建议增大该值)
#loop_interval: 60
#output: nested #(这几项是输出设置)
#show_timeout: True
#color: True
# strip_colors: False
#sock_dir: /var/run/salt/master
#job_cache: True #(master是否缓存执行结果,如果规模庞大超5000台server,False关闭,建议使用其它方式来存储jobs)
#minion_data_cache: True
#event_return: mysql
#event_return_queue: 0
# event_return_whitelist:
# -salt/master/a_tag
# -salt/master/another_tag
# event_return_blacklist:
# -salt/master/not_this_tag
# -salt/master/or_this_one
#max_event_size: 1048576
##### Security settings #####
##########################################
#open_mode: False #(公共使用,为安全禁用)
#auto_accept: False #(minion上发来key自动接收,测试环境可用,生产环境禁用)
# autosign_timeout: 120
#autosign_file: /etc/salt/autosign.conf
#autoreject_file: /etc/salt/autoreject.conf
#permissive_pki_access: False
#client_acl: #(访问控制,哪些用户执行指定的命令)
# larry:
# - test.ping
# - network.*
#client_acl_blacklist: #(访问控制,黑名单,指定用户不能执行设定的命令)
# users:
# - root
# - '^(?!sudo_).*$' # all non sudo users
# modules:
# - cmd
#sudo_acl: False
#external_auth: #(外部认证)
# pam:
# fred:
# - test.*
#token_expire: 43200
#file_recv: False #(是否允许minion传文件到master上)
#file_recv_max_size: 100
# sign_pub_messages: False
##### State System settings #####
##########################################
#state_top: top.sls #(管理的入口文件)
##### File Server settings #####
##########################################
#file_roots: #(指定file server目录)
# base:
# - /srv/salt
#hash_type: md5
#file_buffer_size: 1048576
#fileserver_backend: #(可将配置文件放在git上,与master同步)
# -git
# -roots
##### Pillar settings #####
##########################################
#pillar_roots: #(指定pillar目录)
# base:
# - /srv/pillar
#ext_pillar_first: False
#pillar_gitfs_ssl_verify: True
#pillar_opts: False
#pillar_safe_render_error: True
#pillar_source_merging_strategy: smart
##### Peer Publish settings #####
##########################################
#peer: #(指定的minion可控制另一minion)
# foo.example.com:
# - test.*
# - pkg.*
##### Logging settings #####
##########################################
#log_file: /var/log/salt/master
#key_logfile: /var/log/salt/key
#log_level: warning #(有garbage、trace、debug、info、warning、error、critical)
上述master全部配置文件
[root@master ~]# service salt-master start
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
[root@master ~]# ps aux | grep salt
root 2876 0.0 0.8 143712 4076 pts/3 S+ Aug23 0:00 vim /etc/salt/master
root 3029 0.0 4.4 292768 21604 ? S 00:22 0:00 /usr/bin/python2.6/usr/bin/salt-master -d
root 3030 0.3 6.8 390944 33184 ? Sl 00:22 0:09 /usr/bin/python2.6/usr/bin/salt-master -d
……
[root@master ~]# netstat -tnulp | egrep '4505|4506'
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:4505 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3031/python2.6
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:4506 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3053/python2.6
minion-side:
[root@minion1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
minion的配置文件如下:
##### Primary configuration settings #####
##########################################
#default_include: minion.d/*.conf
master: 10.96.20.113 #(指定master主机,默认为salt,若按默认salt此处不改,要在本地/etc/hosts中添加解析记录)
#ipv6: False
# retry_dns: 30 #(若上面指定的master处是域名,此处指定多长时间刷新)
#master_port: 4506 #(要与master主机上的ret_port保持一致,指定认证和执行结果发送到master的哪个port)
#user: root #(指定运行salt-minion的用户,由于安装包、启动服务等操作都需要root权限,为规范minion端要使用root)
#root_dir: /
#pki_dir: /etc/salt/pki/minion
#id: #(指定本minion的标识,salt内部使用id作为标识,此处不设置则默认是主机名,若此处id变了,master会认为是不同的主机)
#grains:
# roles:
# - webserver
# - memcache
# deployment: datacenter4
# cabinet: 13
# cab_u: 14-15
#cachedir: /var/cache/salt/minion
#cache_jobs: False #(minion端不缓存执行结果,会发送到master上)
#backup_mode: minion #(若更改文件对源文件进行备份,方便回滚操作;在文件操作时,如file.managed或file.recurse,如果文件发生变更,指定备份目标,备份在cachedir/file_backups/下,以原始文件名+时间戳命名)
##### Minion module management #####
##########################################
#providers: #(指定模块对应的providers,RHEL系列pkg对应的providers是yumpkg5)
# pkg: yumpkg5
##### State Management Settings #####
###########################################
#renderer: yaml_jinja #(指定配置管理系统中的渲染器,解析配置文件使用的模式)
##### File Directory Settings #####
##########################################
#file_client: remote #(指定file_client默认去哪里寻找文件,remote或local)
##### Logging settings #####
##########################################
#log_file: /var/log/salt/minion
#key_logfile: /var/log/salt/key
#log_level: warning
###### Keepalive settings ######
############################################
#tcp_keepalive: True #(minion是否与master保持keepalive检查,zeromq3以下版本有bug导致连接异常后minion无法重连master,建议升级到zeromq3以上版本)
全部配置文件完
[root@minion1 ~]# service salt-minion start
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
[root@minion1 ~]# ps aux | grep salt
root 2683 0.0 1.8 143256 4128 pts/4 S+ 00:23 0:00 vim /etc/salt/minion
root 2785 0.0 11.3 446960 25912 ? S 00:47 0:00 /usr/bin/python2.6/usr/bin/salt-minion -d
root 3149 0.0 0.3 103264 828 pts/3 S+ 01:10 0:00 grep salt
[root@minion2 ~]# service salt-minion start
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
[root@minion2 ~]# ps aux | grep salt
root 59600 0.0 11.2 444852 25724? S 00:49 0:00 /usr/bin/python2.6 /usr/bin/salt-minion -d
root 59932 0.0 0.3 103252 828 pts/1 S+ 01:10 0:00 grep salt
master-side:
[root@master ~]# salt<TAB>
salt salt-cp salt-key salt-master salt-run salt-unity
[root@master ~]# salt-key -h
Usage: salt-key [options]
Options:
--version showprogram's version number and exit
--versions-report showprogram's dependencies version number and exit
……
Actions:
-l ARG, --list=ARG List the public keys. The args"pre", "un", and
"unaccepted"will list unaccepted/unsigned keys. "acc"
or "accepted"will list accepted/signed keys. "rej" or
"rejected"will list rejected keys. "den" or "denied"
will list denied keys.Finally, "all" will list all
keys.
-L, --list-all List all public keys. (Deprecated: use"--list all")
-a ACCEPT,--accept=ACCEPT
Accept the specifiedpublic key (use --include-all to
match rejected keys inaddition to pending keys).
Globs are supported.
-A, --accept-all Accept all pending keys
-r REJECT,--reject=REJECT
Reject the specifiedpublic key (use --include-all to
match accepted keys inaddition to pending keys).
Globs are supported.
-R, --reject-all Reject all pending keys
--include-all Includenon-pending keys when accepting/rejecting
-p PRINT, --print=PRINT
Print the specifiedpublic key
-P, --print-all Print allpublic keys
-d DELETE,--delete=DELETE
Delete the specifiedkey. Globs are supported.
-D, --delete-all Delete all keys
……
[root@master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
Rejected Keys:
[root@master ~]# salt-key -a minion1 -y #(接受指定minion的key,或使用#salt-key-A -y接受所有minion的key;-d删除指定minion的key,-D删除所有minion的key;-r,-R)
The following keys are going to beaccepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
minion1
Key for minion minion1 accepted.
[root@master ~]#salt-key -a minion2 -y
The following keys are going to beaccepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
minion2
Key for minion minion2 accepted.
[root@master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
[root@master ~]# tree /etc/salt/pki
/etc/salt/pki
└── master
├──master.pem
├──master.pub
├── minions
│ ├── minion1
│ └── minion2
├──minions_autosign
├──minions_denied
├──minions_pre
└──minions_rejected
minion-side:
[root@minion1 ~]# tree /etc/salt/pki
/etc/salt/pki
└── minion
├──minion_master.pub
├──minion.pem
└──minion.pub
[root@master ~]# salt -h
Usage: salt [options]'<target>' <function> [arguments]
[root@master ~]# salt'*' test.ping #(检测所有的minion是否存活)
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt 'minion1' test.ping
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'echo "hello world"'
minion1:
hello world
minion2:
hello world
[root@master ~]# salt '*' grains.items //可以检测服务器的cpu,内存,os,hostname等很详细的信息
……
[root@master ~]# salt '*' grains.get cpuarch //检测cpu的位数
minion2:
x86_64
minion1:
x86_64
[root@master ~]# salt '*' grains.get os
minion1:
RedHat
minion2:
RedHat
[root@master ~]# salt '*' grains.get kernel
minion2:
Linux
minion1:
Linux
[root@master ~]# salt '*' grains.get ip_interfaces #(可使用get查询到grains.items中所有的信息)
minion2:
----------
eth0:
- 10.96.20.118
- fe80::20c:29ff:fe73:b31a
eth1:
lo:
- 127.0.0.1
- ::1
minion1:
----------
eth0:
- 10.96.20.117
- fe80::20c:29ff:fe15:e6bb
eth1:
lo:
- 127.0.0.1
- ::1
[root@master ~]# salt '*' grains.get hwaddr_interfaces
minion2:
----------
eth0:
00:0c:29:73:b3:1a
eth1:
00:0c:29:73:b3:24
lo:
00:00:00:00:00:00
minion1:
----------
eth0:
00:0c:29:15:e6:bb
eth1:
00:0c:29:15:e6:c5
lo:
00:00:00:00:00:00
[root@master ~]#salt '*' grains.get hwaddr_interfaces:eth0
minion1:
00:0c:29:15:e6:bb
minion2:
00:0c:29:73:b3:1a
[root@master ~]# salt '*' grains.get zmqversion
minion1:
3.2.5
minion2:
3.2.5
pillar的使用:
master-side:
[root@master ~]# mkdir -p /srv/pillar
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.items
minion2:
----------
minion1:
----------
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'*':
- packages
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/packages.sls
{% if grains['os'] =='RedHat' %}
apache: httpd
git: git
xxoo: fuck
{% elif grains['os'] =='Debian' %}
apache: apache2
git: git-core
{% endif %}
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.get apache #(在未刷新时是查不到的)
minion1:
minion2:
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar #(只有刷新后才能查到)
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.get apache
minion2:
httpd
minion1:
httpd
[root@master ~]#salt '*' pillar.get xxoo
minion2:
fuck
minion1:
fuck
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.get git
minion2:
git
minion1:
git
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'*':
-packages
-system
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/system.sls
nofile: 102400
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.get nofile
minion1:
102400
minion2:
102400
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.items --如果脚本编写的有问题,执行这句话会提示问题的所在位置
minion2:
----------
apache:
httpd
git:
git
nofile:
102400
xxoo:
fuck
minion1:
----------
apache:
httpd
git:
git
nofile:
102400
xxoo:
fuck
举例(target支持的matcher):
globing:
[root@master ~]# salt '*' test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]#salt 'minion*' test.ping #(匹配id中含有minion字串的minions)
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt 'minion[1-2]' test.ping #(匹配minion1到minon2的minions)
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt 'minion[1,2]' test.ping #(匹配minion1和minion2)
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
RE:
[root@master ~]# salt -E '.*' test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# salt -E 'minion(1|2)' test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'minion(1|2)':
- match: pcre
-packages
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.get apache
minion1:
httpd
minion2:
httpd
list:
[root@master ~]# salt -L 'minion1,minion2' test.ping
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
grains:
[root@master ~]#salt -G 'os:RedHat' test.ping
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'os:RedHat':
- match: grain
-packages
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
pillar:
[root@master ~]# salt -I 'apache:httpd' test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'minion(1|2)':
-match: pcre
-packages
- role
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/role.sls.
role: web
[root@master ~]# salt '*'saltutil.refresh_pillar
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.get role
minion1:
web
minion2:
web
[root@master ~]# salt -I 'role:web'test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
node groups:
[root@master ~]# mkdir /etc/salt/master.d
[root@master ~]# vim /etc/salt/master.d/nodegroups.conf
nodegroups:
web-cluster: 'minion*'
db-cluster: 'minion*'
[root@master ~]# salt -N 'web-cluster' test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# salt -N 'db-cluster' test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'web-cluster':
- match: nodegroup
-packages
-role
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
compound:
[root@master ~]# salt -C 'minion* and G@os:RedHat' test.ping
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'G@os:RedHat and minion*':
- match: compound
-packages
-role
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
举例(分发文件):
[root@master ~]# salt '*' test.ping
minion2:
True
minion1:
True.
[root@master ~]# salt -v '*' pkg.install httpd
Executing job with jid 20160826024016671210
-------------------------------------------
minion2:
----------
minion1:
----------
[root@master ~]# mkdir -p/srv/salt/apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/
[root@master ~]# echo '# jason' >>/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@master ~]# cp/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /srv/salt/apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/
[root@master ~]# salt '*' cp.get_file salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf #(或用方法二,#salt-cp)
minion1:
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
minion2:
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@master ~]# salt-cp '*' /srv/salt/apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf #(两种方式任选一)
{'minion1': {'/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf':True},
'minion2': {'/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf':True}}
[root@master ~]# salt '*' service.start httpd
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]#salt -v '*' service.status httpd
Executing job with jid 20160826031234533015
-------------------------------------------
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]#salt-run jobs.list_jobs
……
[root@master ~]# salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20160826024930368134
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@minion1 ~]# tail -2 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf #(在minion端检测)
#</VirtualHost>
# jason
[root@minion1 ~]# netstat -tnlp | grep :80
tcp 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 5424/httpd
举例(理解YAML):
[root@master ~]# vim parse_yaml.py
----------------script start----------------
#!/usr/bin/env python
#
import yaml
import sys
fd=open(sys.argv[1])
print yaml.load(fd)
----------------script end-----------------
[root@master ~]# chmod 755 parse_yaml.py
[root@master ~]# vim test.yaml
- name: jason
- gender: man
[root@master ~]# ./parse_yaml.py test.yaml
[{'name': 'jason'}, {'gender': 'man'}]
举例(通过配置安装httpd,层层深入理解salt的配置管理;注意*.sls配置文件中各级之间的空格要是2的倍数,例如一级顶格,二级2个空格,3级4个空格,否则提示state.py in render_state sls之类的错误):
[root@master ~]#vim /srv/salt/top.sls
base:
'*':
-apache
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/apache/init.sls
include:
- apache.deploy
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/apache/deploy.sls
apache:
pkg.installed:
- name: httpd
file.managed:
- name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- source:salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
service.running:
- name: httpd
- enable: True
[root@master ~]# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /srv/salt/apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/
[root@master ~]# salt '*' state.highstate
……
Summary
------------
Succeeded: 3 (changed=1)
Failed: 0
------------
Total states run: 3
[root@master ~]# salt '*' service.status httpd
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
注:deploy.sls也可以写为:
apache:
pkg.installed: []
-name: httpd
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
file.managed:
-source: salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
httpd:
service.running:
-enable: True
举例(上例仅简单实现了部署与分发配置文件,如果配置文件分发在软件包安装之前的话则最后服务启动后的配置将受影响;增加需求:配置文件分发执行前软件包必须已安装,避免先同步配置文件再安装软件会覆盖掉已分发的文件;增加监控,若软件包更新或配置文件发生变化,这两点要能被监控到,监控到发生变化了要重启服务):
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/apache/deploy.sls
apache:
pkg.installed:
-name: httpd
file.managed:
-name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-source: salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- require:
- pkg: apache
service.running:
-name: httpd
-enable: True
- watch:
- pkg: apache
- file: apache
[root@master ~]# echo '# chinese' >>/srv/salt/apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@master ~]# salt '*' state.sls apache
……
Summary
------------
Succeeded: 3 (changed=2)
Failed: 0
------------
Total states run: 3
注:deploy.sls也可写成以下两种方式:
apache:
pkg:
-installed
-name: httpd
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
file:
-managed
-source: salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-require:
- pkg: apache
httpd:
service:
-running
-enable: True
-watch:
- pkg: apache
- file: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
------------------------------------------------
或者是
------------------------------------------------
apache:
pkg.installed:
-name: httpd
- require_in: file
- watch_in:
- service: apache
file.managed:
-name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-source: salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- watch_in:
- service: apache
service.running:
-name: httpd
-enable: True
举例(增加需求,利用jinja渲染,改各minion的httpd.conf中port为8080):
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Listen ` port `
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/apache/deploy.sls
apache:
pkg:
-installed
-name: httpd
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
file:
-managed
-source: salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-require:
- pkg: apache
- template: jinja
- context:
port: 8080
httpd:
service:
-running
-enable: True
-watch:
- pkg: apache
- file: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@master ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'netstat -tnulp | grep httpd'
minion2:
tcp 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 75368/httpd
minion1:
tcp 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 7936/httpd
[root@master ~]# salt '*' state.highstate
……
[root@master ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'netstat -tnulp | grep httpd'
minion2:
tcp 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 75837/httpd
minion1:
tcp 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 8352/httpd
举例(增加需求,各minion的httpd port号不一致;业务数据应独立存放,/srv/salt/apache/deploy.sls中仅存放业务处理逻辑,/srv/pillar/apache/pillar_deploy.sls中存放数据):
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Listen ` port `
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/apache/deploy.sls
apache:
pkg:
-installed
-name: httpd
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
file:
-managed
-source: salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-require:
- pkg: apache
- template: jinja
- defaults:
port: {{ salt['pillar.get']('apache:port',80)}}
httpd:
service:
-running
-enable: True
-watch:
- pkg: apache
- file: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls #(top.sls文件中定义的内容,只要能匹配到minion都会先后执行所有操作,而不是像iptables那样先匹配到就不匹配之后的内容)
base:
'*':
- apache
[root@master ~]# mkdir /srv/pillar/apache
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/apache/init.sls
include:
- apache.pillar_deploy
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/apache/pillar_deploy.sls
apache:
{% if grains.id=='minion1' %}
port: 8081
{% elif grains.id=='minion2' %}
port: 8082
{% else %}
port: 80
{% endif %}
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.getapache:port
minion2:
8082
minion1:
8081
[root@master ~]# salt '*' state.highstate #(若直接执行此命令则不需要执行刷新pillar操作,此命令会先刷新再执行)
[root@master ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'netstat -tnulp | grep httpd'
minion2:
tcp 0 0 :::8082 :::* LISTEN 76024/httpd
minion1:
tcp 0 0 :::8081 :::* LISTEN 8564/httpd
注:deploy.sls,也可以将业务逻辑和数据放在一起:
apache:
pkg:
-installed
-name: httpd
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
file:
-managed
-source: salt://apache/files/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-require:
- pkg: apache
- template: jinja
- context:
{% if grains['id']=='minion1' %}
port: 8081
{% elif grains['id']=='minion2' %}
port: 8082
{% else %}
port: 80
{% endif %}
httpd:
service:
-running
-enable: True
-watch:
- pkg: apache
- file: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
举例(模块带参数执行):
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/top.sls
base:
'*':
-apache
'minion(1|2)*':
-match: pcre
-system
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/system/init.sls
include:
-system.system
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/salt/system/system.sls
hello:
cmd.run:
-name: echo "hello world"
[root@master ~]# salt '*' state.highstate
举例(schedule):
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/top.sls
base:
'*':
- schedule
[root@master ~]# vim /srv/pillar/schedule.sls
schedule:
hello:
function: cmd.run
args:
- date >> /tmp/test.log
seconds: 30
[root@master ~]# salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
minion1:
True
minion2:
True
[root@master ~]# salt '*' pillar.get schedule
……
[root@minion1 ~]# cat /tmp/test.log #(在minion端查看)
Mon Aug 29 02:34:41 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:35:11 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:35:41 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:36:11 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:36:41 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:37:11 PDT 2016
[root@minion2 ~]# cat /tmp/test.log
Mon Aug 29 02:34:08 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:34:38 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:35:08 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:35:38 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:36:08 PDT 2016
Mon Aug 29 02:36:38 PDT 2016
举例(salt-ssh):
[root@master ~]# yum -y install salt-ssh
[root@master ~]# vim /etc/salt/roster
minion1:
host: 10.96.20.117
user: root
passwd: chai
minion2:
host: 10.96.20.118
user: root
passwd: chai
[root@master ~]# service salt-master stop
Stopping salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
[root@master ~]# salt-ssh '*' test.ping #(有如下报错,解决办法:严格检查禁用或者先用ssh连接minion)
minion1:
----------
retcode:
254
stderr:
stdout:
The host key needs to be accepted, to auto accept run salt-ssh with the-i flag:
The authenticity of host '10.96.20.117 (10.96.20.117)' can't beestablished.
RSA key fingerprint is 63:f5:2e:dc:96:64:54:72:8e:14:7e:ec:ef:b8:a1:0c.
Are you sure you want to continueconnecting (yes/no)?
minion2:
----------
retcode:
254
stderr:
stdout:
The host key needs to be accepted, to auto accept run salt-ssh with the-i flag:
The authenticity of host '10.96.20.118 (10.96.20.118)' can't beestablished.
RSA key fingerprint is 63:f5:2e:dc:96:64:54:72:8e:14:7e:ec:ef:b8:a1:0c.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
[root@master ~]# touch .ssh/config
[root@master ~]# vim .ssh/config
host 10.96.20.117
StrictHostKeyChecking no
host 10.96.20.118
StrictHostKeyChecking no
[root@master ~]# salt-ssh '*' test.ping
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
[root@master ~]# salt-ssh '*' -r 'df -h'
minion1:
----------
retcode:
0
stderr:
stdout:
root@10.96.20.117's password:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 18G 4.9G 12G 30% /
tmpfs 112M 12K 112M 1% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 291M 91M 185M 33% /boot
/dev/sr0 3.6G 3.6G 0 100% /mnt/cdrom
minion2:
----------
retcode:
0
stderr:
stdout:
root@10.96.20.118's password:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 18G 4.3G 13G 26% /
tmpfs 112M 12K 112M 1% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 291M 58M 219M 21% /boot
/dev/sr0 3.6G 3.6G 0 100% /mnt/cdrom
[root@master ~]# salt-ssh '*' -r 'ip ro li'
minion1:
----------
retcode:
0
stderr:
stdout:
root@10.96.20.117's password:
10.96.20.0/24 dev eth0 protokernel scope link src 10.96.20.117
default via 10.96.20.1 dev eth0
minion2:
----------
retcode:
0
stderr:
stdout:
root@10.96.20.118's password:
10.96.20.0/24 dev eth0 protokernel scope link src 10.96.20.118 metric 1
default via 10.96.20.1 dev eth0 proto static
举例(salt syndic):
masterofmaster:10.96.20.113,主机名master
syndic:10.96.20.114,主机名syndic
minion1:10.96.20.117,主机名minion1
minion2:10.96.20.118,主机名minion2
syndic-side:
[root@syndic ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d
[root@syndic yum.repos.d]# ll
total 20
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1856 Jul 19 00:28CentOS6-Base-163.repo
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 957 Nov 4 2012 epel.repo
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1056 Nov 4 2012epel-testing.repo
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 474 Mar 30 23:00 rhel-source.repo
[root@syndic yum.repos.d]# cd
[root@syndic ~]# yum -y install PyYAML python-requests python-jinja2 #(先用CentOS6-Base-163的yum源安装这几个依赖包)
[root@syndic ~]# yum -y install salt-master salt-syndic #(再用epel的yum源安装salt-master和salt-syndic)
……
Running Transaction
Installing : openpgm-5.1.118-3.el6.x86_64 1/8
Installing : zeromq3-3.2.5-1.el6.x86_64 2/8
Installing : python-zmq-14.3.1-1.el6.x86_64 3/8
Installing : python-crypto-2.0.1-22.el6.x86_64 4/8
Installing: python-msgpack-0.4.6-1.el6.x86_64 5/8
Installing : salt-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch 6/8
Installing : salt-master-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch 7/8
Installing : salt-syndic-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch 8/8
……
[root@syndic ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
##### Syndic settings #####
##########################################
syndic_master:10.96.20.113
#syndic_master_port: 4506
#syndic_pidfile:/var/run/salt-syndic.pid
#syndic_log_file:syndic.log
[root@syndic ~]# service salt-master start
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
[root@syndic ~]# service salt-syndic start
Starting salt-syndic daemon: [ OK ]
masterofmaster-side:
[root@master ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
##### Syndic settings #####
##########################################
order_masters: True
[root@master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
syndic
Rejected Keys:
[root@master ~]# salt-key -D -y
……
Key for minion minion1 deleted.
Key for minion minion2 deleted.
Key for minion syndic deleted.
[root@master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
syndic
Rejected Keys:
[root@master ~]# salt-key -a 'syndic' -y
The following keys are going to beaccepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
syndic
Key for minion syndic accepted.
[root@master ~]#salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
syndic
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
Rejected Keys:
minion{1,2}-side:
[root@minion1 ~]# service salt-minion stop
Stopping salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
[root@minion1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
master: 10.96.20.114
[root@minion1 ~]# rm -f /etc/salt/minion_id
[root@minion1 ~]# rm -rf /etc/salt/pki
[root@minion1 ~]# hostname
minion1
[root@minion1 ~]# service salt-minion start
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
[root@minion2 ~]# service salt-minion stop
Stopping salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
[root@minion2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
master: 10.96.20.114
[root@minion2 ~]# rm -f /etc/salt/minion_id
[root@minion2 ~]# rm -rf /etc/salt/pki
[root@minion2 ~]# service salt-minion start
Starting salt-minion daemon: [ OK ]
syndic-side:
[root@syndic ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
Rejected Keys:
[root@syndic ~]# salt-key -A -y
The following keys are going to beaccepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
minion1
minion2
Key for minion minion1 accepted.
Key for minion minion2 accepted.
masterofmaster上测试:
[root@master ~]# salt -v '*' test.ping
Executing job with jid 20160829193921851966
-------------------------------------------
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
#salt '*' MODULE.FUNCTION #(*匹配所有的minion,此命令禁用,生产环境复杂,容易出问题)
#salt '*' cmd.run 'PARAMETER' #(cmd.run超级命令,不建议使用)
#salt -v '*' test.ping #(-v可查看jid)
#salt '*' saltutil.running
#salt '*' saltutil.kill_job <jid>
#salt '*' saltutil.sync_grains
#salt '*' saltutil.refresh_pillar
[root@server1 ~]# salt-run manage.status #(经常用,在test.ping后列出当前minion的在线情况,up和down)
down:
up:
-minion1
-minion2
[root@server1 ~]# salt-run manage.down
[root@server1 ~]# salt-run manage.up
- minion1
- minion2
[root@server1 ~]# salt-run manage.versions #(查看版本,用于版本不一致时升级)
Master:
2015.5.10
Up to date:
----------
minion1:
2015.5.10
minion2:
2015.5.10
注:
主机名一定要能解析到master和所有minion(#hostname所得出的主机名,主机名最好为fqdn)
生产环境复杂,不要开启自动认证功能(auto_accept: False);
minion-side在每次启动时会在minion-side的/etc/salt/pki/minon/下生成minion.pem(private key)和minion.pub(public key),并将minion.pub发给master-side,经master-side认证(#salt-key-a MINION_ID)之后会放在master-side的/etc/salt/pki/master/minions/下(此目录下存放所有认证过的minion,以minion_id为文件名);同时minion-side的/etc/salt/pki/minion/下存放master-side的public key(文件名为minion_master.pub);以此双方实现互相认证;
minion-side与master-side的4505port保持长连接,如果断了会自动重连,所以执行操作很快;
file_roots中的base(默认/srv/salt/)定义的是基础环境,在其下按不同部门或业务,对应的创建不同的目录,规划好,例如/srv/salt/init/下放所有server都要执行的操作;
/srv/salt/top.sls(在/etc/salt/master中定义state_top:top.sls,定义在什么环境下,哪些server,该做什么事;The state system uses a "top" file to tell the minionswhat environment to use and what modules to use. The state_top file is definedrelative to the root of the base environment as defined in "File Serversettings" below.);
[root@server1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/init/pkg.sls
pkg.init:
pkg.installed:
- names:
- lrzsz
- tree
- mtr
- nmap
- MySQL-python
- sysstat
- iptraf
- ntp
- e2fsprogs-devel
- keyutils-libs-devel
- krb5-devel
- libselinux-devel
- libsepol-devel
- ncurses-devel
- openssl-devel
- zlib-devel
- OpenIPMI-tools
- ipmitool
- zlib-devel
- mysql
- lockdev
- minicom
- nmap
pkg.group_installed: #不可用
- names:
- Desktop Platform
- Desktop Platform Development
- Server Platform Development
- Development tools
- Compatibility libraries
[root@server1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/top.sls
base:
'*':
-init.pkg
#salt '*' state.sls init.pkg #(或使用#salt '*'state.highstate)
举例(将所有minion-side的执行结果导入到MySQL中):
https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/returners/all/salt.returners.mysql.html
master-side:
[root@server1 ~]# yum -y install MySQL-python
[root@server1 ~]# salt '*' state.sls init.pkg #(让所有minion执行安装上面写的包)
[root@server1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master #(master_job_cache,master上使用此项后就不需在minion-side配置如下mysql的相关信息,指让master-side收到minion-side的返回信息写入mysql中,有此项在执行命令时就不需输入--return mysql)
##### Returner settings ######
############################################
# Which returner(s) will be used for minion'sresult:
return: mysql
mysql.host:'10.96.20.113'
mysql.user: 'salt'
mysql.pass: 'salt'
mysql.db: 'salt'
mysql.port: 3306
master_job_cache: mysql
[root@server1 ~]# servicesalt-master restart
Stopping salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
Starting salt-master daemon: [ OK ]
[root@server1 ~]# cat salt_returners_mysql.sql #(将如下信息导入到mysql中)
---------------------file start-------------------------
CREATE DATABASE `salt`
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8
DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
USE `salt`;
--
-- Table structure for table `jids`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `jids`;
CREATE TABLE `jids` (
`jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`load` mediumtext NOT NULL,
UNIQUE KEY `jid` (`jid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE INDEX jid ON jids(jid) USING BTREE;
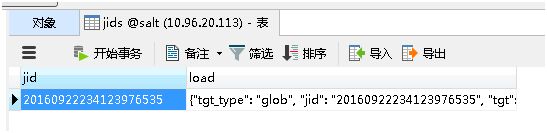
--
-- Table structure for table `salt_returns`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salt_returns`;
CREATE TABLE `salt_returns` (
`fun` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`return` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`id` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`success` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`full_ret` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
KEY`id` (`id`),
KEY`jid` (`jid`),
KEY`fun` (`fun`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
--
-- Table structure for table `salt_events`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salt_events`;
CREATE TABLE `salt_events` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`tag` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`data` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`master_id` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `tag` (`tag`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-----------------------------file end-------------------
[root@server1 ~]# mysql
mysql> create user 'salt'@'%' identified by 'salt';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> grant all on salt.* to'salt'@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
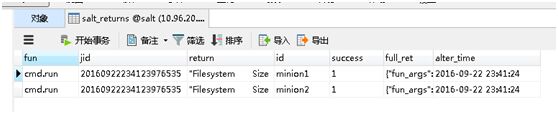
测试:
[root@server1 ~]# salt '*' test.ping
minion2:
True
minion1:
True
举例(源码安装nginx):
[root@server1 ~]# mkdir -p /srv/salt/nginx/files
[root@server1 ~]# cd /srv/salt/nginx
[root@server1 nginx]# vim nginx.sls
include:
- init.pkg
nginx-source-install:
file.managed:
- name: /usr/local/src/nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz
- source: salt://nginx/files/nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
cmd.run:
- name: groupadd -r -g 108 nginx && useradd -r -g 108 -u 108 nginx&& cd /usr/local/src/ && tar xf nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz && cd nginx-1.8.0 && ./configure --prefix=/usr --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi --with-pcre && make && make install
- unless: test -f /usr/sbin/nginx
require:
- file: nginx-source-install
[root@server1 nginx]# cp /usr/local/src/nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz files/
[root@server1 nginx]# cd ..
[root@server1 salt]# vim init/pkg.sls
pkg.init:
pkg.installed:
- names:
- lrzsz
- tree
- mtr
- nmap
- MySQL-python
- pcre-devel
[root@server1 salt]# vim top.sls
base:
'*':
-init.pkg
- nginx.nginx
[root@server1 salt]# salt '*' state.sls nginx.nginx test=True
[root@server1 salt]# salt '*' state.sls nginx.nginx
举例(安装jdk、tomcat):
test1(192.168.23.129,既有master也有minion);
test2(192.168.23.130,仅minion);
[root@test1 ~]# mkdir -p /srv/salt
[root@test1 ~]# cd /srv/salt
[root@test1 salt]# mkdir -p jdk/filestomcat/files
[root@test1 salt]# tree
.
├── jdk
│ └── files
└── tomcat
└── files
4 directories, 0 files
[root@test1 salt]# tree #(上传文件到/srv/salt/jdk/files/下和/srv/salt/tomcat/files/下)
.
├── jdk
│ └── files
│ └──jdk-8u111-linux-x64.gz
└── tomcat
└── files
└── apache-tomcat-8.5.6.tar.gz
4 directories, 2 files
[root@test1 salt]# vim tomcat/files/java.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/jre/bin
export CLASSPATH=.:$CLASSPATH:$JAVA_HOME/lib:$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA
export TOMCAT_HOME=/usr/local/tomcat
export PATH=$PATH:$TOMCAT_HOME/bin
[root@test1 salt]# vim jdk/install.sls
#------------------file-start-----------------------
jdk-install:
file.managed:
- name: /usr/local/src/jdk-8u111-linux-x64.gz
- source: salt://jdk/files/jdk-8u111-linux-x64.gz
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name: cd /usr/local/src && tar xf jdk-8u111-linux-x64.gz -C /usr/local/ && ln -s /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_111 /usr/local/jdk && chown -Rroot:root /usr/local/jdk
- unless: test -d /usr/local/jdk
- require:
- file: jdk-install
#jdk-config:
# file.managed:
# - name: /etc/profile.d/java.sh
# - text:
# - export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
# - export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/jre/bin
# - export CLASSPATH=.:$CLASSPATH:$JAVA_HOME/lib:$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar
#-------------------------file-end-----------------------------------
[root@test1 salt]# vim tomcat/install.sls
#--------------------------file-start-----------------------------------
include:
-jdk.install
tomcat-install:
file.managed:
- name: /usr/local/src/apache-tomcat-8.5.6.tar.gz
- source: salt://tomcat/files/apache-tomcat-8.5.6.tar.gz
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 755
cmd.run:
- name: cd /usr/local/src && tar xf apache-tomcat-8.5.6.tar.gz -C/usr/local && ln -s /usr/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.6 /usr/local/tomcat&& chown -R root:root /usr/local/tomcat
- unless: test -d /usr/local/tomcat
- require:
- file: tomcat-install
tomcat-config:
file.managed:
- name: /etc/profile.d/java.sh
- source: salt://tomcat/files/java.sh
- user: root
- group: root
- mode: 644
#tomcat-config:
# file.append:
# - name: /etc/profile.d/java.sh
# - text:
# - export TOMCAT_HOME=/usr/local/tomcat
# - export PATH=$PATH:$TOMCAT_HOME/bin
#-------------------------file-end----------------------------
[root@test1 salt]# vim top.sls
base:
'*':
-tomcat.install
[root@test1 salt]# salt '*' test.ping
test2:
True
test1:
True
[root@test1 salt]# salt-run manage.status
down:
up:
-test1
-test2
[root@test1 salt]# java -version
java version "1.5.0"
gij (GNU libgcj) version 4.4.7 20120313(Red Hat 4.4.7-17)
Copyright (C) 2007 Free SoftwareFoundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source forcopying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY orFITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
[root@test1 salt]# rpm -qa | grep gcj
java-1.5.0-gcj-1.5.0.0-29.1.el6.x86_64
libgcj-4.4.7-17.el6.x86_64
[root@test1 salt]# rpm -e --nodeps java-1.5.0-gcj-1.5.0.0-29.1.el6.x86_64
[root@test2 ~]# rpm -e --nodeps java-1.5.0-gcj-1.5.0.0-29.1.el6.x86_64
[root@test2 ~]# java -version
-bash: /usr/bin/java: No such file ordirectory
[root@test1 salt]# salt '*' state.highstate
……
[root@test1 ~]# java -version #(再次开一窗口检测)
java version "1.8.0_111"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build1.8.0_111-b14)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build25.111-b14, mixed mode)
[root@test2 ~]# java -version
java version "1.8.0_111"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build1.8.0_111-b14)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build25.111-b14, mixed mode)
如果服务器没有网的话,还想安装的话,建议从这个网站上吧相应的包下好后,再进行rpm安装
http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/
需要的包及下面的安装如下
rpm -ivh openpgm-5.1.118-3.el6.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh zeromq3-3.2.5-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh python-zmq-14.3.1-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh python-msgpack-0.4.6-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
yum install -y PyYAML m2crypto python-crypto python-msgpack python-requests python-zmq yum-utils python-babel python-msgpack python-markupsafe python-babel python-crypto python-crypto --这个可以直接yum安装
rpm -ivh python-jinja2-2.2.1-2.el6_5.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh salt-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch.rpm
rpm -ivh salt-master-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch.rpm // rpm -ivh salt-minion-2015.5.10-2.el6.noarch.rpm
参考:http://blog.51cto.com/jowin/1844231
【Linux】saltstack 安装及简单使用的更多相关文章
- Redis之在Linux上安装和简单的使用
我只是一个搬运工 Redis之在Linux上安装和简单的使用https://blog.csdn.net/qq_20989105/article/details/76390367 一.安装gcc 1.R ...
- Linux libusb 安装及简单使用
Linux libusb 安装及简单使用 一.参考文档: . libusb1 fails do_configure task with “udev support requested but libu ...
- linux下安装phpunit简单方法
现在安装phpunit相当简单,只需要下载phar压缩格式的phpunit文件,给个执行权限,就可以执行了 以下是一段官方安装文档 wget https://phar.phpunit.de/phpun ...
- SaltStack 安装、简单配置和远程执行
1:安装 修改hosts文件,必须保证Master端和Minion端都有完整的FQDN名示例如下: vim /etc/hosts 192.168.31.101 node2 node2.crazylin ...
- linux下安装mysql简单步骤
linux下使用yum安装mysql 1.安装 查看有没有安装过: yum list installed mysql* rpm -qa | grep mysql* 查看有没有安装包: yum list ...
- Linux FTP安装与简单配置
1.检測是否原有启动 ps -ef|grep vsftpd 2.检測是否有安装包 rpm -qa|grep vsftpd 3.假设有输出.查看状态并启动 service vsftp status - ...
- Nginx在linux下安装及简单命令
安装环境:Centos7 创建目录及切换至目录 # mkdir /usr/local/nginx # cd /usr/local/nginx/ 下载nginx包,访问http://nginx.org下 ...
- Linux下Hadoop的简单安装
Hadoop 的安装极为简单,一共只有三步: 安装JDK 安装Hadoop 配置Hadoop 1,安装JDK 下载JDK,ftp传到linux或者linux中下载 切换 ...
- Kali Linux虚拟机安装完整安装过程及简单配置(视频)
点击播放视频 附:视频中出现的两个txt文本,包含了大致的安装与配置过程: 文本1:KaliLinux虚拟机安装和初步配置 Kali Linux虚拟机安装和初步配置 大家好,今天给大家演示一下在VMw ...
随机推荐
- celery定时执行任务 的使用
1 参照博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaonq/p/9303941.html#i1 1 创建celery_pro包 # 可在任意文件下 2 在 celery_pro 下 ...
- gnuplot名词缩写
http://blog.163.com/yucheng_xiao/blog/static/7660019220141017114630822/ with 缩写成 w lt 是 linetype 的缩 ...
- IDEA中flink程序报错找不到类
Idea中运行flink程序,报错找不到类,其中pom文件中一项依赖为: <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId& ...
- OS第六章
OS第七次实验 多进程 添加一个进程体 添加进程B,首先设置i的初值为0x1000,这样来方便程序运行时的时候能区分.其余地方与A一致. 相关变量和宏 Minix中定义了一个数组,叫做tasktab的 ...
- 8. 老板 不加薪,我用了 这篇 加了 3K
在K8S中,容器本身是非持久化的,当容器崩溃后,kubelet将以镜像的初始状态重新启动容器,但是此时之前容器的数据已经丢失,我们该如何保护好容器的数据呢? 在同一Pod中的容器往往需要共享一些数据, ...
- Pygal之掷骰子
python之使用pygal模拟掷骰子创建直方图: 1,文件die.py,源码如下: 1 from random import randint 2 3 class Die(): 4 '''表示一个骰子 ...
- Collection集合重难点梳理,增强for注意事项和三种遍历的应用场景,栈和队列特点,数组和链表特点,ArrayList源码解析, LinkedList-源码解析
重难点梳理 使用到的新单词: 1.collection[kəˈlekʃn] 聚集 2.empty[ˈempti] 空的 3.clear[klɪə(r)] 清除 4.iterator 迭代器 学习目标: ...
- SecureCRT的下载、安装和Putty 的使用 SSH连接工具
SecureCRT是一款支持SSH(SSH1和SSH2)的终端仿真程序,简单地说是Windows下登录UNIX或Linux服务器主机的软件.SecureCRT支持SSH,同时支持Telnet和rlog ...
- oracle 19c dataguard aws ORA-03186报错
环境说明 在亚马逊云AWS上面安装了一套oracle 19c dataguard,linux centos 7.7的操作系统,开始时同步正常,实时应用redolog,一会儿之后就不行了.报错如下: o ...
- umi-request 统一异常处理实践
首发于语雀文档 前言 本人在工作中用到了 umi-request,百度谷歌搜了一遍,感觉都没找到超过 3 篇合适且含代码的文章,因此只能自行实践总结了. umi-request 有点不同 umi-re ...
