hdu3713 Double Maze
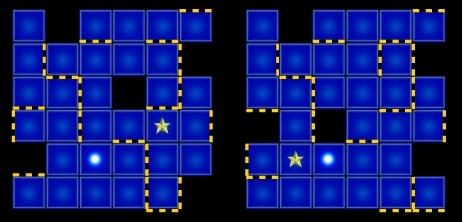
A maze is made up of 6*6 cells. A cell can be either a hole or a square. Moreover, a cell may be surrounded by barriers. There is ONLY one start cell (with a ball) and ONLY one end cell (with a star) in a single maze.These two cells are both squares. It is possible that the start cell and the end cell are the same one. The goal of a single maze is to move the ball from the start cell to the end cell. There are four commands in total,'L', 'D', 'R' and 'U' corresponding to moving the ball left, down, right and up one cell, respectively. The barriers may make the commands take no effect, i.e., the ball does NOT move if there is a barrier on the way.
When the ball gets to a hole or outside of the maze, it fails. A double maze is made up of two single mazes. The commands control two balls simultaneously, and the movements of two balls are according to the rules described above independently. Both balls will continue to move simultaneously if at least one of the balls has not got to the end cell.
So, a ball may move out of the end cell since the other ball has not been to the target. A double maze passes when both balls get to their end cells, or fails if either of the two mazes fails. The goal of double maze is to get the shortest sequence of commands to pass. If there are multiple solutions, get the lexical minimum one.
To simplify the input, a cell is encoded to an integer as follows. The lowest 4 bits signal the existence of the barriers around a cell. The fifth bit indicates whether a cell is a hole or not. The sixth and seventh bits are set for the start cell and end cell. Details are listed in the following table with bits counted from lowest bit. For a barrier, both of the two adjacent cells will have the corresponding barrier bit set. Note that the first two mazes in the sample input is the encoding of two mazes in the figure above, make sure you understand the encoding right.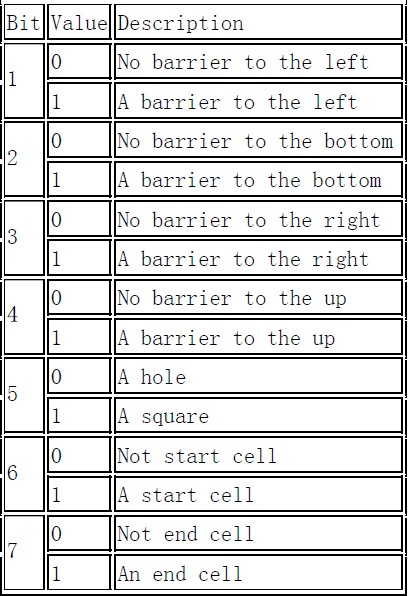
16 0 18 16 18 24
20 19 24 16 28 1
18 28 17 0 22 17
25 20 17 18 88 20
2 16 48 28 17 16
24 16 16 20 23 1
16 0 18 16 18 24
20 19 24 20 29 1
18 28 17 16 22 17
8 20 1 18 24 20
19 80 48 24 16 0
24 16 16 16 22 19
18 16 18 16 18 80
24 18 24 16 24 18
18 24 0 0 18 24
24 18 0 0 24 18
18 24 18 16 18 24
56 18 24 18 24 18
RURDRLLLURDULURRRRRDDU
题意:给出两个迷宫,每个迷宫各有起点和终点,有的格子能走有的不行,格子与格子之间还可能有护栏。同时控制两个迷宫每次朝同一个方向移动,问最快使得两个迷宫同时到达终点的步数,有多个最优解输出字典序最小的一个。
思路:把两个图合成一个图,建边,用bfs,总共也就6的4次方个点。以dlru的顺序查找,找到的保证字典序最小。用一个数组记录其前驱点,找到答案后倒着输出就好。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std; #define two(x) (1<<x)
#define inf 200000000
int T;
char c[4]={'D','L','R','U'};
int d[2][37][4],st[2],en[2],f[37][37];
bool can[2][37];
int fa1[37][37],fa2[37][37],dir[37][37],ans[2000]; void init(int cur)
{
memset(d[cur],0,sizeof(d[cur]));
memset(can[cur],1,sizeof(can[cur]));
int x;
for (int i=1;i<=6;++i)
for (int j=1;j<=6;++j)
{
int t=(i-1)*6+j;
scanf("%d",&x);
if (x & two(1)) d[cur][t][0]=t;
else if (i<6) d[cur][t][0]=t+6;
if (x & two(0)) d[cur][t][1]=t;
else if (j>1) d[cur][t][1]=t-1;
if (x & two(2)) d[cur][t][2]=t;
else if (j<6) d[cur][t][2]=t+1;
if (x & two(3)) d[cur][t][3]=t;
else if (i>1) d[cur][t][3]=t-6;
if ((x & two(4))==0) can[cur][t]=false;
if (x & two(5)) st[cur]=t;
if (x & two(6)) en[cur]=t;
}
} void bfs()
{
queue<int> q1,q2;
bool p[37][37];
memset(p,1,sizeof(p));
q1.push(st[0]);
q2.push(st[1]);
p[st[0]][st[1]]=false;
while (!q1.empty())
{
int x=q1.front(),y=q2.front();
q1.pop();q2.pop();
for (int i=0;i<=3;++i)
{
int tx=d[0][x][i],ty=d[1][y][i];
if (tx && ty && can[0][tx] && can[1][ty])
if (p[tx][ty])
{
q1.push(tx);
q2.push(ty);
p[tx][ty]=false;
fa1[tx][ty]=x;
fa2[tx][ty]=y;
dir[tx][ty]=i;
}
}
}
} void solve()
{
memset(dir,-1,sizeof(dir));
dir[st[0]][st[1]]=5;
bfs();
int x=en[0],y=en[1];
if (dir[x][y]==-1)
{
printf("-1\n");
return;
}
int tot=0,tx,ty;
while (!(x==st[0] && y==st[1]))
{
ans[++tot]=dir[x][y];
tx=fa1[x][y];
ty=fa2[x][y];
x=tx;y=ty;
}
for (int i=tot;i>0;--i)
printf("%c",c[ans[i]]);
printf("\n");
} int main()
{
scanf("%d",&T);
init(1);
for (int i=2;i<=T;++i)
{
init(1 & i);
solve();
}
return 0;
}
hdu3713 Double Maze的更多相关文章
- hdu - 2216 Game III && xtu 1187 Double Maze (两个点的普通bfs)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2216 zjt和sara在同一个地图里,zjt要去寻找sara,zjt每移动一步sara就要往相反方向移动,如果他 ...
- UVA 10531 Maze Statistics 迷宫统计 迷宫插头DP 四联通 概率
题意: 有一个N*M的图,每个格子有独立概率p变成障碍物.你要从迷宫左上角走到迷宫右下角.求每个格子成为一个有解迷宫中的障碍物的概率.N <= 5,M <= 6 分析: 这真是一道好题,网 ...
- HDU 3853:LOOPS(概率DP)
http://acm.split.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3853 LOOPS Problem Description Akemi Homura is a M ...
- HDU 4035:Maze(概率DP)
http://acm.split.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4035 Maze Special Judge Problem Description When w ...
- HDU-4035 Maze
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4035 树上的概率dp. Maze Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others ...
- hdu 4035 Maze(期待更多经典的树DP)
Maze Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65768/65768 K (Java/Others) Total Submi ...
- Maze HDU - 4035(期望dp)
When wake up, lxhgww find himself in a huge maze. The maze consisted by N rooms and tunnels connecti ...
- hdu4035 Maze
题目链接 hdu4035 Maze 题解 f[u]表示在节点u通关的所需的边数期望 转移方程分叶子节点和非叶子点讨论 发现都可以化成f[x]=af[1]+bf[dad]+c的形式 然后推一下系数 还是 ...
- Meandering Through the Maze of MFC Message and Command Routing MFC消息路由机制分析
Meandering Through the Maze of MFC Message and Command Routing Paul DiLascia Paul DiLascia is a free ...
随机推荐
- STF,docker学习资料整理
- TensorFlow conv2d实现卷积
tf.nn.conv2d是TensorFlow里面实现卷积的函数,参考文档对它的介绍并不是很详细,实际上这是搭建卷积神经网络比较核心的一个方法,非常重要 tf.nn.conv2d(input, fil ...
- iOS动画学习-视觉效果
CALayer不仅仅是iOS动画学习-CALayer中介绍的那些内容,他还有一些其他属性,比如shadowColor,borderWidth,borderColor等等,这些属性我们只需要简单点设置就 ...
- python有三种导入模块的方法(转)
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/allenblogs/archive/2011/11/15/2055149.html python有三种导入模块的方法 其一, import mod ...
- apache2修改用户和组
grep nobody /etc/{passwd,group} groupadd nobody #有nobody用户的情况 usermod -G nobody nobody #没有nobody用户的情 ...
- HDU6043 KazaQ's Socks
Problem Description KazaQ wears socks everyday. At the beginning, he has n pairs of socks numbered f ...
- word2vec原理(三) 基于Negative Sampling的模型
word2vec原理(一) CBOW与Skip-Gram模型基础 word2vec原理(二) 基于Hierarchical Softmax的模型 word2vec原理(三) 基于Negative Sa ...
- mysql5.7.18的安装与主从复制
CentOS6.7安装mysql5.7.18 1. 解压到/usr/local目录 # tar -zxvf mysql-5.7.18-linux-glibc2.5-i686.tar.gz -C /u ...
- 使用Node.js调用阿里云短信的发送以及接收
为了使用Node.js调用阿里云短信服务,我自己写了个npm包, 目前实现了: 使用Node.js调用阿里云短信服务,发送短信: 使用Node.js调用阿里云短信服务以及MNS服务,接收用户上行短信 ...
- 2016 "Bird Cup" ICPC7th@ahstu--“波导杯”安徽科技学院第七届程序设计大赛
"波导杯"安徽科技学院第七届程序设计大赛 原文章网页 Contest - 2016 "Bird Cup" ICPC7th@ahstu Start time: ...
