【转】JDBC学习笔记(2)——Statement和ResultSet
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ysw-go/
Statement执行更新操作
Statement:Statement 是 Java 执行数据库操作的一个重要方法,用于在已经建立数据库连接的基础上,向数据库发送要执行的SQL语句。Statement对象,用于执行不带参数的简单SQL语句。
通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录,需要注意下面的几点:

- * 1.Statement:用于执行SQL语句的对象
- * 1).通过COnnection的createStatement()方法来获取
- * 2).通过excuteUpdate(sql)可以执行SQL语句
- * 3).传入的SQL可以是insert,update或者delete,但是不能是select
- * 2.Connection、Statement都是应用程序和数据库服务器的连接 资源,使用后一定要关闭
- * 需要在finally中关闭Connection和Statement对象
- * 异常可以不处理,但是连接一定要关闭
- * 3.关闭的顺序:先关闭后获取的,即先关闭Statement,后关闭Connection

具体的代码实现:

- 1 public void testStatement() throws Exception{
- 2 //1.获取数据库连接
- 3 // Connection conn=getConnection();
- 4 Connection conn=null;
- 5 //4.执行插入
- 6 //1).获取操作SQL语句的Statement对象:调用Connection的createStatement()方法来获取
- 7 //注意Statement这里是java.sql包中的,而不是java.mysql.jdbc中的
- 8 // Statement statement=conn.createStatement();
- 9 Statement statement=null;
- 10 try {
- 11 //3.准备插入的SQL语句
- 12 conn=getConnection();
- 13 String sql=null;
- 14 //sql的插入操作
- 15 // sql="insert into customers(NAME,email,birth) values('xyz','xyz@atguigu.com','1988-7-1')";
- 16 //删除操作
- 17 // sql="delete from customers where id =1";
- 18 //修改操作
- 19 sql="update customers set name='Tom' where id =2";
- 20 statement = conn.createStatement();
- 21 //2).调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql),执行SQL语句进行插入
- 22 statement.execute(sql);
- 23 //5.关闭Statement对象
- 24 } catch (Exception e) {
- 25 e.printStackTrace();
- 26 } finally {
- 27 try {
- 28 if (statement != null) {
- 29 statement.close();
- 30 }
- 31 } catch (Exception e) {
- 32 e.printStackTrace();
- 33 } finally {
- 34
- 35 // 2.关闭连接
- 36 if (conn != null) {
- 37
- 38 conn.close();
- 39 }
- 40 }
- 41 }
- 42 }

【提示】:代码中的getConnction方法是在笔记一中定义的,可以看到我们可以对数据库中的记录进行插入(insert),更新(update),删除(delete)操作,使用Connection对象的createStatement( )方法创建一个statement对象,并且调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql),执行SQL语句进行插入;
我们的getConnection方法和关闭statement以及conn的操作稍显复杂,我们可以定义一个工具类,里面包含一些通用的方法,实现我们的插入、删除、更新数据的操作
具体代码:

- 1 public class JDBCTools {
- 2 // 关闭conn和statement的操作
- 3 public static void release(Statement statement, Connection conn) {
- 4 if (statement != null) {
- 5 try {
- 6 statement.close();
- 7
- 8 } catch (Exception e2) {
- 9 // TODO: handle exception
- 10 }
- 11 }
- 12 if (conn != null) {
- 13 try {
- 14 conn.close();
- 15 } catch (SQLException e) {
- 16 e.printStackTrace();
- 17 }
- 18 }
- 19 }
- 20
- 21 /**
- 22 * 1。获取连接的方法 通过读取配置文件从数据库服务器获取一个连接
- 23 *
- 24 * @author Administrator
- 25 *
- 26 */
- 27 public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
- 28 String driverClass = null;
- 29 String jdbcUrl = null;
- 30 String user = null;
- 31 String password = null;
- 32 // 读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
- 33 InputStream in = JDBCTools.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(
- 34 "jdbc.properties");
- 35 Properties properties = new Properties();
- 36 properties.load(in);
- 37 driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
- 38 jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
- 39 user = properties.getProperty("user");
- 40 password = properties.getProperty("password");
- 41 // 通过反射创建Driver对象
- 42 Driver driver = (Driver) Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
- 43 Properties info = new Properties();
- 44 info.put("user", user);
- 45 info.put("password", password);
- 46 Connection connection = driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
- 47 return connection;
- 48 }
- 49 }

我们更新数据的操作可以写成这样:这里update就是这个通用的方法;

- 1 public void update(String sql){
- 2 Connection conn=null;
- 3 Statement statement=null;
- 4 try {
- 5 //用到了我们写的一个工具类JDBCTools
- 6 conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
- 7 statement=conn.createStatement();
- 8 statement.execute(sql);
- 9 } catch (Exception e) {
- 10 // TODO: handle exception
- 11 }finally{
- 12 JDBCTools.release(statement, conn);
- 13 }
- 14 }

传入不同的sql,执行相应的操作;
通过ResultSet执行查询操作
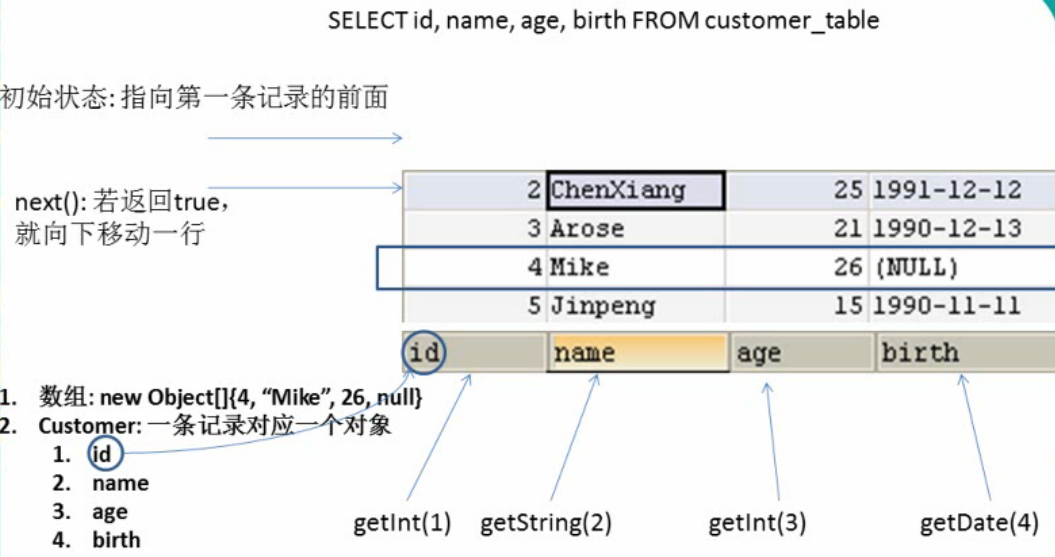
ResultSet:

- /**
- * ResultSet:结果集,封装了使用JDBC进行查询的结果
- * 1.调用Statement对象的excuteQuery(sql)方法可以得到结果集
- * 2.ResultSet返回的实际上就是一张数据表,有一个指针
- * 指向数据表的第一样的前面,可以调用next()方法检测下一行是否有效,若有效则返回true
- * ,并且指针下移,相当于迭代器对象的hasNext()和next()的结合体
- * 3.当指针对位到确定的一行时,可以通过调用getXxx(index)或者getXxx(columnName)
- * 获取每一列的值,例如:getInt(1),getString("name")
- * 4.ResultSet当然也需要进行关闭
- */

ResultSet的返回结果:

具体的代码实现:

- 1 @Test
- 2 public void testResultSet(){
- 3 //获取id=2的customers数据表的记录,并打印
- 4 //面向接口的编程
- 5 Connection conn=null;
- 6 Statement statement=null;
- 7 ResultSet rs=null;
- 8 try {
- 9 //1.获取Connection
- 10 conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
- 11 System.out.println(conn);
- 12 //2.获取Statement
- 13 statement=conn.createStatement();
- 14 System.out.println(statement);
- 15 //3.准备SQL
- 16 String sql="select id,name,email,birth from customers";
- 17 //4.执行查询,得到ResultSet
- 18 rs=statement.executeQuery(sql);
- 19 System.out.println(rs);
- 20 //5.处理ResultSet
- 21 while(rs.next()){
- 22 int id=rs.getInt(1);
- 23 String name=rs.getString("name");
- 24 String email=rs.getString(3);
- 25 Date birth=rs.getDate(4);
- 26 System.out.println(id);
- 27 System.out.println(name);
- 28 System.out.println(email);
- 29 System.out.println(birth);
- 30 System.out.println("--------------");
- 31 }
- 32 //6.关闭数据库资源
- 33
- 34 } catch (Exception e) {
- 35 e.printStackTrace();
- 36 }finally{
- 37 JDBCTools.release(rs, statement, conn);
- 38 }
- 39 }

到目前为止的完整代码:

- 1 package com.atguigu.jdbc;
- 2
- 3 import java.io.InputStream;
- 4 import java.sql.*;
- 5 import java.util.Properties;
- 6
- 7 import org.junit.Test;
- 8
- 9 import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
- 10
- 11 //JDBC学习
- 12 public class JDBCTest {
- 13 /**
- 14 * ResultSet:结果集,封装了使用JDBC进行查询的结果
- 15 * 1.调用Statement对象的excuteQuery(sql)方法可以得到结果集
- 16 * 2.ResultSet返回的实际上就是一张数据表,有一个指针
- 17 * 指向数据表的第一样的前面,可以调用next()方法检测下一行是否有效,若有效则返回true
- 18 * ,并且指针下移,相当于迭代器对象的hasNext()和next()的结合体
- 19 * 3.当指针对位到确定的一行时,可以通过调用getXxx(index)或者getXxx(columnName)
- 20 * 获取每一列的值,例如:getInt(1),getString("name")
- 21 * 4.ResultSet当然也需要进行关闭
- 22 */
- 23 @Test
- 24 public void testResultSet(){
- 25 //获取id=2的customers数据表的记录,并打印
- 26 //面向接口的编程
- 27 Connection conn=null;
- 28 Statement statement=null;
- 29 ResultSet rs=null;
- 30 try {
- 31 //1.获取Connection
- 32 conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
- 33 System.out.println(conn);
- 34 //2.获取Statement
- 35 statement=conn.createStatement();
- 36 System.out.println(statement);
- 37 //3.准备SQL
- 38 String sql="select id,name,email,birth from customers";
- 39 //4.执行查询,得到ResultSet
- 40 rs=statement.executeQuery(sql);
- 41 System.out.println(rs);
- 42 //5.处理ResultSet
- 43 while(rs.next()){
- 44 int id=rs.getInt(1);
- 45 String name=rs.getString("name");
- 46 String email=rs.getString(3);
- 47 Date birth=rs.getDate(4);
- 48 System.out.println(id);
- 49 System.out.println(name);
- 50 System.out.println(email);
- 51 System.out.println(birth);
- 52 System.out.println("--------------");
- 53 }
- 54 //6.关闭数据库资源
- 55
- 56 } catch (Exception e) {
- 57 e.printStackTrace();
- 58 }finally{
- 59 JDBCTools.release(rs, statement, conn);
- 60 }
- 61 }
- 62 /**
- 63 * 通用的更新的方法:包括insert,update,delete
- 64 * 版本1.
- 65 */
- 66 /*public void update(String sql){
- 67 Connection conn=null;
- 68 Statement statement=null;
- 69 try {
- 70 //用到了我们写的一个工具类JDBCTools
- 71 conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
- 72 statement=conn.createStatement();
- 73 statement.execute(sql);
- 74 } catch (Exception e) {
- 75 // TODO: handle exception
- 76 }finally{
- 77 JDBCTools.release(statement, conn);
- 78 }
- 79 }*/
- 80 /*
- 81 * 通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录
- 82 * 我这里用的是图形化界面SQLyog
- 83 * SQLyog图形化界面连接mysql数据库,注册码:
- 84 * 这个可用【我用了还是可以】
- 85 Name:BAKA!
- 86 Code:560f17bf57745cf9
- 87 */
- 88 /**
- 89 * 通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录
- 90 * 1.Statement:用于执行SQL语句的对象
- 91 * 1).通过COnnection的createStatement()方法来获取
- 92 * 2).通过excuteUpdate(sql)可以执行SQL语句
- 93 * 3).传入的SQL可以是insert,update或者delete,但是不能是select
- 94 * 2.Connection、Statement都是应用程序和数据库服务器的连接资源,使用
- 95 * 后一定要关闭
- 96 * 需要在finally中关闭Connection和Statement对象
- 97 * 异常可以不处理,但是连接一定要关闭
- 98 * 3.关闭的顺序:先关闭后获取的,即先关闭Statement,后关闭Connection
- 99 * @throws Exception
- 100 */
- 101 @Test
- 102 public void testStatement() throws Exception{
- 103 //1.获取数据库连接
- 104 // Connection conn=getConnection();
- 105 Connection conn=null;
- 106 //4.执行插入
- 107 //1).获取操作SQL语句的Statement对象:调用Connection的createStatement()方法来获取
- 108 //注意Statement这里是java.sql包中的,而不是java.mysql.jdbc中的
- 109 // Statement statement=conn.createStatement();
- 110 Statement statement=null;
- 111 try {
- 112 //3.准备插入的SQL语句
- 113 conn=getConnection();
- 114 String sql=null;
- 115 //sql的插入操作
- 116 // sql="insert into customers(NAME,email,birth) values('xyz','xyz@atguigu.com','1988-7-1')";
- 117 //删除操作
- 118 // sql="delete from customers where id =1";
- 119 //修改操作
- 120 sql="update customers set name='Tom' where id =2";
- 121 statement = conn.createStatement();
- 122 //2).调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql),执行SQL语句进行插入
- 123 statement.execute(sql);
- 124 //5.关闭Statement对象
- 125 } catch (Exception e) {
- 126 e.printStackTrace();
- 127 } finally {
- 128 try {
- 129 if (statement != null) {
- 130 statement.close();
- 131 }
- 132 } catch (Exception e) {
- 133 e.printStackTrace();
- 134 } finally {
- 135
- 136 // 2.关闭连接
- 137 if (conn != null) {
- 138
- 139 conn.close();
- 140 }
- 141 }
- 142 }
- 143 }
- 144
- 145 public Connection testGetConnection2() throws Exception{
- 146 //1.准备连接数据库的四个字符串
- 147 //1).创建Properties对象
- 148 Properties properties=new Properties();
- 149 //2).获取jdbc.properties对应的输入流
- 150 InputStream in=this.getClass().
- 151 getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
- 152 //3).加载2)对应的输入流
- 153 properties.load(in);
- 154 //4).具体决定user,password等四个字符串
- 155 String user=properties.getProperty("user");
- 156 String jdbcUrl=properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
- 157 String password=properties.getProperty("password");
- 158 String driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
- 159 //2.加载数据库驱动程序(对应的Driver实现类中注册驱动的静态代码块)
- 160 Class.forName(driver);
- 161 //3.通过DriverManager的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接
- 162 return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl,user,password);
- 163 }
- 164 /**
- 165 * DriverManager是驱动的管理类
- 166 * 1).可以通过重载的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接,较为方便
- 167 * 2).可以同时管理多个驱动程序:若注册了多个数据库连接
- 168 * ,则调用getConnection()方法时传入的参数不同,即返回不同的数据库连接
- 169 * @throws Exception
- 170 */
- 171 public void testDriverManager() throws Exception{
- 172 //1.准备连接数据库的四个字符串
- 173 //驱动的全类名
- 174 String driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
- 175 //url
- 176 String jdbcUrl="dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/atguigu";
- 177 //user
- 178 String user="root";
- 179 //password
- 180 String password="123456";
- 181 //读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
- 182 InputStream in=getClass().getClassLoader()
- 183 .getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
- 184 Properties properties=new Properties();
- 185 properties.load(in);
- 186 driverClass=properties.getProperty("driver");
- 187 jdbcUrl=properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
- 188 user=properties.getProperty("user");
- 189 //2.加载数据库驱动程序(对应的Driver实现类中注册驱动的静态代码块)
- 190 /*
- 191 *使用Drivermanager的好处:可以加载多个驱动
- 192 DriverManager
- 193 .registerDriver(Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance());
- 194 *
- 195 */
- 196 Class.forName(driverClass);
- 197 password=properties.getProperty("password");
- 198 //3.通过DriverManager的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接
- 199 Connection connection=DriverManager
- 200 .getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, password);
- 201 System.out.println(connection);
- 202 }
- 203
- 204 /**
- 205 * Driver是一个接口,数据库厂商必须提供实现的接口
- 206 * 能从其中获取数据库连接,可以通过Driver的实现类的对象获取连接
- 207 * 1.加入mysql驱动
- 208 * 1).解压mysql-connector-java-5.1.18.zip
- 209 * 2).在当前目录下新建lib目录
- 210 * 3).把mysql-connector-java-5.1.18-bin.jar复制到lib目录
- 211 * 4).右键->build-path->add build path加载到类路径下
- 212 * @throws SQLException
- 213 *
- 214 */
- 215 /*
- 216 * MySQL附带了一个空密码有的root用户。成功后安装了数据库和客户端,需要进行如下设置root密码:
- 217
- 218 D:\software\mysql-5.6.25-winx64\bin> mysqladmin -u root password "123456";
- 219 注:
- 220
- 221 1. 关闭正在运行的MySQL服务。
- 222 2. 打开DOS窗口,转到 D:\software\mysql-5.6.25-winx64\bin 目录。
- 223 3. 输入mysqld --skip-grant-tables 回车。--skip-grant-tables 的意思是启动MySQL服务的时候跳过权限表认证。
- 224 4. 再开一个DOS窗口(因为刚才那个DOS窗口已经不能动了),转到mysql\bin目录。
- 225 5. 输入mysql回车,如果成功,将出现MySQL提示符 >。
- 226 6. 连接权限数据库: use mysql; 。
- 227 6. 改密码:update user set password=password("123456") where user="root";(别忘了最后加分号) 。
- 228 7. 刷新权限(必须步骤):flush privileges;
- 229 8. 退出 quit。
- 230 9. 注销系统,再进入,使用用户名root和刚才设置的新密码 123456 登录。
- 231 现在使MySQL服务器的连接,那么使用下面的命令:
- 232 */
- 233 public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
- 234 //1.创建一个Driver实现类的对象
- 235 Driver driver=new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
- 236 /*
- 237 * JDBC URL的标准由三部分组成
- 238 * jdbc:<子协议>:<子名称>
- 239 * 1).协议:JDBC URL中的协议总是JDBC
- 240 * 2).子协议:子协议用于标识一个数据库驱动程序
- 241 * 3).紫明成:一种标识数据库的方法。子名称可以一句不同的
- 242 * 子协议而变化,用子名称的目的是为了定位数据库提供足够的信息
- 243 * 例如:jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test【这是我的主机上的,你的不一定】
- 244 * 查看端口号:在mysql后面输入show global variables like 'port';别写错了,切记别忘记写英文状态下的分号
- 245 */
- 246 //2.准备连接数据库的基本信息,url,user,password
- 247 String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
- 248 Properties info=new Properties();
- 249 info.put("user", "root");
- 250 info.put("password", "123456");
- 251 //3.调用Driver接口实现类对象的connect(url,info)方法获取数据库的连接
- 252 //此处Connection是一个接口,java.sql包下的接口
- 253 Connection connection=driver.connect(url, info);
- 254 System.out.println(connection);
- 255 }
- 256 /**
- 257 * 编写一个通用的方法,在不修改源程序的情况下,可以获取任何数据库的连接
- 258 * 解决方案:把数据库驱动Driver实现类的全类名、url、user、password
- 259 * 放入一个配置文件中,通过修改配置文件的方法实现和具体的数据库解耦
- 260 * @throws ClassNotFoundException
- 261 * @throws IllegalAccessException
- 262 * @throws InstantiationException
- 263 */
- 264 public Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
- 265 String driverClass=null;
- 266 String jdbcUrl=null;
- 267 String user=null;
- 268 String password=null;
- 269 //读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
- 270 InputStream in=getClass().getClassLoader()
- 271 .getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
- 272 Properties properties=new Properties();
- 273 properties.load(in);
- 274 driverClass=properties.getProperty("driver");
- 275 jdbcUrl=properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
- 276 user=properties.getProperty("user");
- 277 password=properties.getProperty("password");
- 278 //通过反射创建Driver对象
- 279 Driver driver=(Driver) Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
- 280 Properties info=new Properties();
- 281 info.put("user", user);
- 282 info.put("password", password);
- 283 Connection connection=driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
- 284 return connection;
- 285 }
- 286 @Test
- 287 public void testGetConnection() throws Exception{
- 288 System.out.println(getConnection());
- 289 }
- 290 }

JDBCTools:

- 1 package com.atguigu.jdbc;
- 2
- 3 import java.io.InputStream;
- 4 import java.sql.Connection;
- 5 import java.sql.ResultSet;
- 6 import java.sql.SQLException;
- 7 import java.sql.Statement;
- 8 import java.util.Properties;
- 9
- 10 import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
- 11
- 12 /**
- 13 * 操作JDBC的工具类,其中封装了一些工具方法
- 14 * Version 1
- 15 * @author Administrator
- 16 *
- 17 */
- 18 public class JDBCTools {
- 19 // 关闭conn和statement的操作
- 20 public static void release(ResultSet rs,Statement statement, Connection conn) {
- 21 if(rs!=null){
- 22 try {
- 23 rs.close();
- 24 } catch (Exception e) {
- 25 // TODO: handle exception
- 26 }
- 27 }
- 28 if (statement != null) {
- 29 try {
- 30 statement.close();
- 31
- 32 } catch (Exception e2) {
- 33 // TODO: handle exception
- 34 }
- 35 }
- 36 if (conn != null) {
- 37 try {
- 38 conn.close();
- 39 } catch (SQLException e) {
- 40 e.printStackTrace();
- 41 }
- 42 }
- 43 }
- 44
- 45 /**
- 46 * 1。获取连接的方法 通过读取配置文件从数据库服务器获取一个连接
- 47 *
- 48 * @author Administrator
- 49 *
- 50 */
- 51 public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
- 52 String driverClass = null;
- 53 String jdbcUrl = null;
- 54 String user = null;
- 55 String password = null;
- 56 // 读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
- 57 InputStream in = JDBCTools.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(
- 58 "jdbc.properties");
- 59 Properties properties = new Properties();
- 60 properties.load(in);
- 61 driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
- 62 jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
- 63 user = properties.getProperty("user");
- 64 password = properties.getProperty("password");
- 65 // 通过反射创建Driver对象
- 66 Driver driver = (Driver) Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
- 67 Properties info = new Properties();
- 68 info.put("user", user);
- 69 info.put("password", password);
- 70 Connection connection = driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
- 71 return connection;
- 72 }
- 73 }

【转】JDBC学习笔记(2)——Statement和ResultSet的更多相关文章
- JDBC学习笔记(2)——Statement和ResultSet
Statement执行更新操作 Statement:Statement 是 Java 执行数据库操作的一个重要方法,用于在已经建立数据库连接的基础上,向数据库发送要执行的SQL语句.Statement ...
- JDBC 学习笔记(八)—— ResultSet
JDBC 使用 ResultSet 来封装 SQL 的查询结果,可以将 ResultSet 类比为数据库表的查询结果. 它拥有如下两个性质: 可滚动. 可更新. 这两个性质,是在创建 Statemen ...
- JDBC 学习笔记(十)—— 使用 JDBC 搭建一个简易的 ORM 框架
1. 数据映射 当我们获取到 ResultSet 之后,显然这个不是我们想要的数据结构. 数据库中的每一个表,在 Java 代码中,一定会有一个类与之对应,例如: package com.gerrar ...
- JDBC学习笔记二
JDBC学习笔记二 4.execute()方法执行SQL语句 execute几乎可以执行任何SQL语句,当execute执行过SQL语句之后会返回一个布尔类型的值,代表是否返回了ResultSet对象 ...
- JDBC学习笔记一
JDBC学习笔记一 JDBC全称 Java Database Connectivity,即数据库连接,它是一种可以执行SQL语句的Java API. ODBC全称 Open Database Conn ...
- JDBC 学习笔记(十一)—— JDBC 的事务支持
1. 事务 在关系型数据库中,有一个很重要的概念,叫做事务(Transaction).它具有 ACID 四个特性: A(Atomicity):原子性,一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的诸操 ...
- JDBC 学习笔记(六)—— PreparedStatement
1. 引入 PreparedStatement PreparedStatement 通过 Connection.createPreparedStatement(String sql) 方法创建,主要用 ...
- JDBC学习笔记(4)——PreparedStatement的使用
PreparedStatement public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement;可以看到PreparedStatement是Stateme ...
- JDBC学习笔记(3)——复习和练习
复习和练习 复习部分 一.获取数据库连接 1)方式一 // 获取数据库连接 @Test public void testGetConnection() throws Exception { // 1. ...
随机推荐
- 提高C++编译速度-------pimpl 模式& 桥接模式(转)
pimpl 模式(Private Implementation),我们常常听到诸如“不要改动你的公有接口”这样的建议,所以我们一般都会修改私有接口,但是这会导致包含该头文件的所有源文件都要重新编译,这 ...
- 2620: [Usaco2012 Mar]Haybale Restacking
2620: [Usaco2012 Mar]Haybale Restacking Time Limit: 5 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 201 Solved: ...
- SEO-友情链接注意事项
为什么要专门给友链一个区域呢?由此就可以想象到友情链接对一个网站有多重要前期,网站没有权重的时候,跟别人换友链,人家基本是不会换的因为你网站没权重,加了友链他也获取不到权重,对网站没有多少好处一般我们 ...
- Solr field alias
Field alias Any field, function, or transformer can be displayed with a different name in the output ...
- java基础之基础语法详录(一)
[前言] java的语法先从基础语法学,Java语言是由类和对象组成的,其对象和类又是由方法和变量组成,而方法,又包含了语句和表达式. 对象:(几乎)一切都是对象,比如:一只熊猫,他的外观,颜色,他在 ...
- php+apache+mysql的安装
1.LAMP的安装顺序问题,现在是默认安装好了Linux系统,我的版本是Ubuntu 12.04.一般来说比较建议的顺序是Mysql Apache 最后安装PHP,在我实践下来 Apache和Mysq ...
- opencv与VS的配置
1.VS2015下配置Opencv3.2教程:http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/4b52d702b3209afc5c774b3c.html http://blog.cs ...
- Ubuntu 16.04系统下出现E: 无法下载 http://ppa.launchpad.net/fcitx-team/nightly/ubuntu/dists/xenial/main/binary-amd64/Packages 404 Not Found
在安装完成Chrome浏览器后,终端执行以下更新命令 sudo apt-get update 时出现E: 无法下载 http://ppa.launchpad.net/fcitx-team/nightl ...
- CSS中清除浮动的方法
CSS浮动,最早是为了达到文字环绕的效果提出的,也可以用来做布局,但是布局会产生很多问题(高度塌陷,漂浮在普通流上),会使当前标签产生上浮的效果,会影响前后标签,同样的代码在不同的浏览器的兼容性也不一 ...
- Linux云自动化运维第五课
Linux云自动化运维第五课 一.进程定义 进程就是cpu未完成的工作 二.ps命令 ps a ###关于当前环境的所有进程 x ###与当前环境无关的所有进程 f ###显示进程从属关系 e ### ...
