浅析python中socketserver模块使用
虽然说用python编写简单的网络程序很方便,但是复杂一点的网络程序还是用现成的框架比较好,这样就可以专心事物逻辑,而不是套接字的各种细节。Socketserver模块简化了编写网络服务程序,同时socketserver模块也是python标准库中很多服务器框架的基础。
socketserver模块类介绍
SocketServer内部使用 IO多路复用 以及 “多线程” 和 “多进程” ,从而实现并发处理多个客户端请求的Socket服务端。即:每个客户端请求连接到服务器时,Socket服务端都会在服务器是创建一个“线程”或者“进 程” 专门负责处理当前客户端的所有请求。
socketserver模块可以简化网络服务器的编写,python把网络服务抽象成两个主要的类,一个是server类,用于处理连接相关的网络操作,另一个是RequestHandler类,用于处理数据相关的操作。并且提供两个Mixln类,用于扩展server,实现多进程或者多线程。
Server类
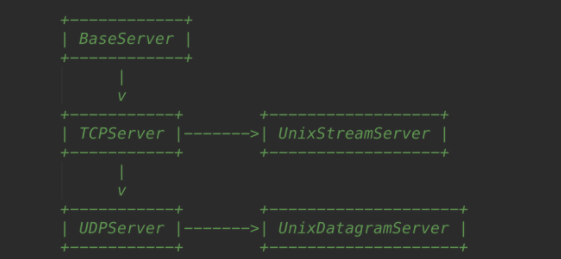
它包含了五种server类,分别是 Baseserver(不直接对外服务);TCPServer(使用TCP协议) ;UDPServer(使用UDP协议),UinixStreamServer 和UnixDatagramServer(后面两个仅仅在unix环境下游泳,一般不常用)
他们五个的关系如下:
BaseServer的源码:
class BaseServer:
"""Base class for server classes.
Methods for the caller:
- __init__(server_address, RequestHandlerClass)
- serve_forever(poll_interval=0.5)
- shutdown()
- handle_request() # if you do not use serve_forever()
- fileno() -> int # for select()
Methods that may be overridden:
- server_bind()
- server_activate()
- get_request() -> request, client_address
- handle_timeout()
- verify_request(request, client_address)
- server_close()
- process_request(request, client_address)
- shutdown_request(request)
- close_request(request)
- service_actions()
- handle_error()
Methods for derived classes:
- finish_request(request, client_address)
Class variables that may be overridden by derived classes or
instances:
- timeout
- address_family
- socket_type
- allow_reuse_address
Instance variables:
- RequestHandlerClass
- socket
"""
timeout = None
def __init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass):
"""Constructor. May be extended, do not override."""
self.server_address = server_address
self.RequestHandlerClass = RequestHandlerClass
self.__is_shut_down = threading.Event()
self.__shutdown_request = False
def server_activate(self):
"""Called by constructor to activate the server.
May be overridden.
"""
pass
def serve_forever(self, poll_interval=0.5):
"""Handle one request at a time until shutdown.
Polls for shutdown every poll_interval seconds. Ignores
self.timeout. If you need to do periodic tasks, do them in
another thread.
"""
self.__is_shut_down.clear()
try:
while not self.__shutdown_request:
# XXX: Consider using another file descriptor or
# connecting to the socket to wake this up instead of
# polling. Polling reduces our responsiveness to a
# shutdown request and wastes cpu at all other times.
r, w, e = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [],
poll_interval)
if self in r:
self._handle_request_noblock()
self.service_actions()
finally:
self.__shutdown_request = False
self.__is_shut_down.set()
def shutdown(self):
"""Stops the serve_forever loop.
Blocks until the loop has finished. This must be called while
serve_forever() is running in another thread, or it will
deadlock.
"""
self.__shutdown_request = True
self.__is_shut_down.wait()
def service_actions(self):
"""Called by the serve_forever() loop.
May be overridden by a subclass / Mixin to implement any code that
needs to be run during the loop.
"""
pass
# The distinction between handling, getting, processing and
# finishing a request is fairly arbitrary. Remember:
#
# - handle_request() is the top-level call. It calls
# select, get_request(), verify_request() and process_request()
# - get_request() is different for stream or datagram sockets
# - process_request() is the place that may fork a new process
# or create a new thread to finish the request
# - finish_request() instantiates the request handler class;
# this constructor will handle the request all by itself
def handle_request(self):
"""Handle one request, possibly blocking.
Respects self.timeout.
"""
# Support people who used socket.settimeout() to escape
# handle_request before self.timeout was available.
timeout = self.socket.gettimeout()
if timeout is None:
timeout = self.timeout
elif self.timeout is not None:
timeout = min(timeout, self.timeout)
fd_sets = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [], timeout)
if not fd_sets[]:
self.handle_timeout()
return
self._handle_request_noblock()
def _handle_request_noblock(self):
"""Handle one request, without blocking.
I assume that select.select has returned that the socket is
readable before this function was called, so there should be
no risk of blocking in get_request().
"""
try:
request, client_address = self.get_request()
except OSError:
return
if self.verify_request(request, client_address):
try:
self.process_request(request, client_address)
except:
self.handle_error(request, client_address)
self.shutdown_request(request)
def handle_timeout(self):
"""Called if no new request arrives within self.timeout.
Overridden by ForkingMixIn.
"""
pass
def verify_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Verify the request. May be overridden.
Return True if we should proceed with this request.
"""
return True
def process_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Call finish_request.
Overridden by ForkingMixIn and ThreadingMixIn.
"""
self.finish_request(request, client_address)
self.shutdown_request(request)
def server_close(self):
"""Called to clean-up the server.
May be overridden.
"""
pass
def finish_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Finish one request by instantiating RequestHandlerClass."""
self.RequestHandlerClass(request, client_address, self)
def shutdown_request(self, request):
"""Called to shutdown and close an individual request."""
self.close_request(request)
def close_request(self, request):
"""Called to clean up an individual request."""
pass
def handle_error(self, request, client_address):
"""Handle an error gracefully. May be overridden.
The default is to print a traceback and continue.
"""
print('-'*)
print('Exception happened during processing of request from', end=' ')
print(client_address)
import traceback
traceback.print_exc() # XXX But this goes to stderr!
print('-'*)
RequestHandler类
所有requestHandler都继承BaseRequestHandler基类。
请求的基类是baserequesthandler,其中一般需要重写的方法就是handle方法,主要就是如何处理接下里的请求,在这个类中,主要有三个方法,分别是setup ,handle ,finish方法,在调用这个类的时候,先调用setup进行一些初始化的工作,然后调用handle方法进行处理请求,然后调用finish方法,做一些关闭连接什么的,在这个里面最主要的参数就是self.request,也就是请求的socket对象,其中可以发送消息sendall或者send,接受消息就是recv
在请求处理的子类中有两个,一个是SreamRequestHandle和DatagramRequestHandle,在这个里面重写了基类的setup方法和finish方法,handle方法没有重写,因为这个是留给用户做处理请求的方法
requestHandler源码:
class BaseServer:
"""Base class for server classes.
Methods for the caller:
- __init__(server_address, RequestHandlerClass)
- serve_forever(poll_interval=0.5)
- shutdown()
- handle_request() # if you do not use serve_forever()
- fileno() -> int # for select()
Methods that may be overridden:
- server_bind()
- server_activate()
- get_request() -> request, client_address
- handle_timeout()
- verify_request(request, client_address)
- server_close()
- process_request(request, client_address)
- shutdown_request(request)
- close_request(request)
- service_actions()
- handle_error()
Methods for derived classes:
- finish_request(request, client_address)
Class variables that may be overridden by derived classes or
instances:
- timeout
- address_family
- socket_type
- allow_reuse_address
Instance variables:
- RequestHandlerClass
- socket
"""
timeout = None
def __init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass):
"""Constructor. May be extended, do not override."""
self.server_address = server_address
self.RequestHandlerClass = RequestHandlerClass
self.__is_shut_down = threading.Event()
self.__shutdown_request = False
def server_activate(self):
"""Called by constructor to activate the server.
May be overridden.
"""
pass
def serve_forever(self, poll_interval=0.5):
"""Handle one request at a time until shutdown.
Polls for shutdown every poll_interval seconds. Ignores
self.timeout. If you need to do periodic tasks, do them in
another thread.
"""
self.__is_shut_down.clear()
try:
while not self.__shutdown_request:
# XXX: Consider using another file descriptor or
# connecting to the socket to wake this up instead of
# polling. Polling reduces our responsiveness to a
# shutdown request and wastes cpu at all other times.
r, w, e = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [],
poll_interval)
if self in r:
self._handle_request_noblock()
self.service_actions()
finally:
self.__shutdown_request = False
self.__is_shut_down.set()
def shutdown(self):
"""Stops the serve_forever loop.
Blocks until the loop has finished. This must be called while
serve_forever() is running in another thread, or it will
deadlock.
"""
self.__shutdown_request = True
self.__is_shut_down.wait()
def service_actions(self):
"""Called by the serve_forever() loop.
May be overridden by a subclass / Mixin to implement any code that
needs to be run during the loop.
"""
pass
# The distinction between handling, getting, processing and
# finishing a request is fairly arbitrary. Remember:
#
# - handle_request() is the top-level call. It calls
# select, get_request(), verify_request() and process_request()
# - get_request() is different for stream or datagram sockets
# - process_request() is the place that may fork a new process
# or create a new thread to finish the request
# - finish_request() instantiates the request handler class;
# this constructor will handle the request all by itself
def handle_request(self):
"""Handle one request, possibly blocking.
Respects self.timeout.
"""
# Support people who used socket.settimeout() to escape
# handle_request before self.timeout was available.
timeout = self.socket.gettimeout()
if timeout is None:
timeout = self.timeout
elif self.timeout is not None:
timeout = min(timeout, self.timeout)
fd_sets = _eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [], timeout)
if not fd_sets[0]:
self.handle_timeout()
return
self._handle_request_noblock()
def _handle_request_noblock(self):
"""Handle one request, without blocking.
I assume that select.select has returned that the socket is
readable before this function was called, so there should be
no risk of blocking in get_request().
"""
try:
request, client_address = self.get_request()
except OSError:
return
if self.verify_request(request, client_address):
try:
self.process_request(request, client_address)
except:
self.handle_error(request, client_address)
self.shutdown_request(request)
def handle_timeout(self):
"""Called if no new request arrives within self.timeout.
Overridden by ForkingMixIn.
"""
pass
def verify_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Verify the request. May be overridden.
Return True if we should proceed with this request.
"""
return True
def process_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Call finish_request.
Overridden by ForkingMixIn and ThreadingMixIn.
"""
self.finish_request(request, client_address)
self.shutdown_request(request)
def server_close(self):
"""Called to clean-up the server.
May be overridden.
"""
pass
def finish_request(self, request, client_address):
"""Finish one request by instantiating RequestHandlerClass."""
self.RequestHandlerClass(request, client_address, self)
def shutdown_request(self, request):
"""Called to shutdown and close an individual request."""
self.close_request(request)
def close_request(self, request):
"""Called to clean up an individual request."""
pass
def handle_error(self, request, client_address):
"""Handle an error gracefully. May be overridden.
The default is to print a traceback and continue.
"""
print('-'*40)
print('Exception happened during processing of request from', end=' ')
print(client_address)
import traceback
traceback.print_exc() # XXX But this goes to stderr!
print('-'*40)
混合类(并发类)
两个混合类,一个是ForkingMixin,主要是用fork的,产生一个新的进程去处理;一个是ThreadingMixin,产生一个新的线程,主要是用来提供异步处理的能力,其余tcpserver和udpserver组合,又产生了新的四个类,从而提供异步处理的能力。
(在使用混合类和服务器类的时候,注意混合类需要写在前面,因为混合类重写了服务器类的方法,从而需要放在第一个位置。)
class socketserver.ForkingTCPServer class socketserver.ForkingUDPServer class socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer class socketserver.ThreadingUDPServer
下面主要举例说一下socketserver服务器端和客户端的代码
scoketserver服务器端
在socketserver模块中,主要就是使用一些服务器类,从而简化socket网络编程的方法,先上一段基本的服务器代码:
import socketserver
ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',)
class Myhandler(socketserver.BaseRequestHandler):
def handle(self):
while True:
data = self.request.recv()
print(data,self.client_address)
if data == 'exit':
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
s =socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer((ip_port),Myhandler)
s.serve_forever()
在上述代码中,首先定义了一个类,也就是处理请求的类,从基类baserequesthandler继承,主要就是重写了其中的handle方法,告知服务器如何来处理客户端的请求。然后建立了一个线程的TCP服务器类,也就是通过多线程来进行应答客户端,然后通过使用一直运行的方法就是serve_forever
scoketserver客户端
import socket
ip_port = ('127.0.0.1',)
sk = socket.socket()
sk.connect(ip_port)
print ("客户端启动:")
while True:
inp = input('>>>')
sk.sendall(bytes(inp,"utf8"))
server_response=sk.recv()
print (str(server_response,"utf8"))
if inp == 'exit':
break
sk.close()
客户端的代码和socket编程的代码基本相同,因为在socketserver模块中,主要是创建socke的服务端,而不涉及到客户端,从而客户端不需要修改代码即可进行运行。
class socketserver.ForkingTCPServer
class socketserver.ForkingUDPServer
class socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer
class socketserver.ThreadingUDPServer
socketserver内部调用程序
- 启动服务端程序
- 执行 TCPServer.init 方法,创建服务端Socket对象并绑定 IP 和 端口
- 执行 BaseServer.init 方法,将自定义的继承自SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler 的类 - MyRequestHandle赋值给 self.RequestHandlerClass
- 执行 BaseServer.server_forever 方法,While 循环一直监听是否有客户端请求到达 ...
当客户端连接到达服务器 - 执行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request 方法,创建一个 “线程” 用来处理请求
- 执行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request_thread 方法
- 执行 BaseServer.finish_request 方法,执行 self.RequestHandlerClass() 即:执行 自定义 MyRequestHandler 的构造方法(自动调用基类BaseRequestHandler的构造方法,在该构造方法中又会调用 MyRequestHandler的handle方法)
浅析python中socketserver模块使用的更多相关文章
- 【转】浅析Python中的struct模块
[转]浅析Python中的struct模块 最近在学习python网络编程这一块,在写简单的socket通信代码时,遇到了struct这个模块的使用,当时不太清楚这到底有和作用,后来查阅了相关资料大概 ...
- 深入浅析python中的多进程、多线程、协程
深入浅析python中的多进程.多线程.协程 我们都知道计算机是由硬件和软件组成的.硬件中的CPU是计算机的核心,它承担计算机的所有任务. 操作系统是运行在硬件之上的软件,是计算机的管理者,它负责资源 ...
- 浅析JS中的模块规范(CommonJS,AMD,CMD)////////////////////////zzzzzz
浅析JS中的模块规范(CommonJS,AMD,CMD) 如果你听过js模块化这个东西,那么你就应该听过或CommonJS或AMD甚至是CMD这些规范咯,我也听过,但之前也真的是听听而已. ...
- Python中optionParser模块的使用方法[转]
本文以实例形式较为详尽的讲述了Python中optionParser模块的使用方法,对于深入学习Python有很好的借鉴价值.分享给大家供大家参考之用.具体分析如下: 一般来说,Python中有两个内 ...
- python中threading模块详解(一)
python中threading模块详解(一) 来源 http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-27571599-id-3484048.html threading提供了一个比thr ...
- 【转】关于python中re模块split方法的使用
注:最近在研究文本处理,需要用到正则切割文本,所以收索到了这篇文章,很有用,谢谢原作者. 原址:http://blog.sciencenet.cn/blog-314114-775285.html 关于 ...
- Python中的模块介绍和使用
在Python中有一个概念叫做模块(module),这个和C语言中的头文件以及Java中的包很类似,比如在Python中要调用sqrt函数,必须用import关键字引入math这个模块,下面就来了解一 ...
- python中导入模块的本质, 无法导入手写模块的解决办法
最近身边一些朋友发生在项目当中编写自己模块,导入的时候无法导入的问题. 下面我来分享一下关于python中导入模块的一些基本知识. 1 导入模块时寻找路径 在每一个运行的python程序当中,都维护了 ...
- Python中time模块详解
Python中time模块详解 在平常的代码中,我们常常需要与时间打交道.在Python中,与时间处理有关的模块就包括:time,datetime以及calendar.这篇文章,主要讲解time模块. ...
随机推荐
- springMVC(1)---@RequestMapping详解
@RequestMapping详解 RequestMapping是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上.用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径.这句话,太熟悉了. ...
- js----数组处理之splice(有js原始addClass方法哦)
上次写了一个轮播的方法:http://blog.csdn.net/stronglyh/article/details/46833499 由于别人问我的时候,给了我html.于是乎我就看到了页面中引用了 ...
- Android最佳性能实践(四)——布局优化技巧
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/43376527 在前面几篇文章其中.我们学习了怎样通过合理管理内存,以及高性能编码技 ...
- OR1200中指令Cache的结构
下面内容摘自<步步惊芯--软核处理器内部设计分析>一书 12.3 ICache结构 OR1200中实现ICache的文件有or1200_ic_top.v.or1200_ic_fsm.v.o ...
- cxf,两个声明导致 ObjectFactory 类中发生冲突
说明先,这里不管是client还是server端都是用java语言编写,如有写得不好,望原谅! 问题 http://localhost:8080/WEB-SMVC/cxf/userService?ws ...
- linux应用态下的时间
1.时间值 1.1 日历时间(UTC) 该值是自1 9 7 0年1月1日0 0 : 0 0 : 0 0以来国际标准时间( U T C)所经过的秒数累计值(早期的手册称 U T C为格林尼治标准时间) ...
- spring boot https --restful接口篇
我们写的接口默认都是http形式的,不过我们的接口很容易被人抓包,而且一抓全是明文的挺尴尬的 spring boot配置https生成证书大的方向有3种: 1.利用keytool自己生成证书 2.从免 ...
- Python云端系统开发入门——框架基础
Django框架基础 这是我学习北京理工大学嵩天老师的<Python云端系统开发入门>课程的笔记,在此我特别感谢老师的精彩讲解和对我的引导. 1.Django简介与安装 Django是一个 ...
- 页面重绘(repaint)和回流(reflow)
前言 页面显示到浏览器上的过程: 1.1.生成一个DOM树. 浏览器将获取到的HTML代码解析成1个DOM树,包含了所有标签,包括display:none和动态添加的节点. 1.2.生成样式结构体. ...
- Bmob 移动后端云服务器平台实现登录注册
源码下载:http://download.csdn.net/download/jjhahage/10034519 PS:一般情况下,我们在写android程序的时候,想要实现登录注册功能,可以选择自己 ...
