1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)
There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists from all over the world. One may rent a bike at any station and return it to any other stations in the city.
The Public Bike Management Center (PBMC) keeps monitoring the real-time capacity of all the stations. A station is said to be in perfect condition if it is exactly half-full. If a station is full or empty, PBMC will collect or send bikes to adjust the condition of that station to perfect. And more, all the stations on the way will be adjusted as well.
When a problem station is reported, PBMC will always choose the shortest path to reach that station. If there are more than one shortest path, the one that requires the least number of bikes sent from PBMC will be chosen.
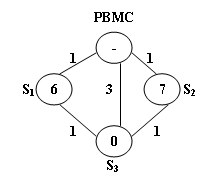
The above figure illustrates an example. The stations are represented by vertices and the roads correspond to the edges. The number on an edge is the time taken to reach one end station from another. The number written inside a vertex S is the current number of bikes stored at S. Given that the maximum capacity of each station is 10. To solve the problem at S3, we have 2 different shortest paths:
PBMC -> S1 -> S3. In this case, 4 bikes must be sent from PBMC, because we can collect 1 bike from S1 and then take 5 bikes to S3, so that both stations will be in perfect conditions.
PBMC -> S2 -> S3. This path requires the same time as path 1, but only 3 bikes sent from PBMC and hence is the one that will be chosen.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains 4 numbers: Cmax (≤), always an even number, is the maximum capacity of each station; N (≤), the total number of stations; Sp, the index of the problem station (the stations are numbered from 1 to N, and PBMC is represented by the vertex 0); and M, the number of roads. The second line contains N non-negative numbers Ci (,) where each Ci is the current number of bikes at Si respectively. Then M lines follow, each contains 3 numbers: Si, Sj, and Tij which describe the time Tij taken to move betwen stations Si and Sj. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print your results in one line. First output the number of bikes that PBMC must send. Then after one space, output the path in the format: 0. Finally after another space, output the number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC after the condition of Sp is adjusted to perfect.
Note that if such a path is not unique, output the one that requires minimum number of bikes that we must take back to PBMC. The judge's data guarantee that such a path is unique.
Sample Input:
10 3 3 5
6 7 0
0 1 1
0 2 1
0 3 3
1 3 1
2 3 1
Sample Output:
3 0->2->3 0题目分析:用Dijkstra算法求解后不对 看了柳神的博客才知道要使用dijkstra与dfs结合的方式
因为minneed和minback在求解过程中不满足最优子结构 换言之 无法在求解过程中就知道那条路是最优的,因此,将最短路径求出后在利用dfs进行遍历判断最优解
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#define INIFITY 65535
using namespace std;
int g[][];
int dist[];
int collected[];
int weight[];
int minNeed = INIFITY;
int minBack = INIFITY;
vector<int> pre[], path, tempath;
int C, N, D, M;
void dfs(int v){
tempath.push_back(v);
if (v == ) {
int need = ;
int back = ;
for (int i = tempath.size()-; i>=; i--){
int id = tempath[i];
if (weight[id] > )
back += weight[id];
else if (back>(-weight[id]))
back += weight[id];
else{
need+= ( - weight[id]) - back;
back = ;
}
}
if (need < minNeed){
minNeed = need;
minBack = back;
path = tempath;
}
else if (need == minNeed && back < minBack){
minBack=back;
path = tempath;
}
tempath.pop_back();
return;
}
for (int i = ; i<pre[v].size(); i++)
dfs(pre[v][i]);
tempath.pop_back();
}
int main()
{
fill(g[], g[] + * , INIFITY);
fill(dist, dist + , INIFITY);
cin >> C >> N >> D >> M;
for (int i = ; i <=N; i++)
{
int w;
cin >> w;
weight[i] = w - C / ;
}
for (int i = ; i < M; i++){
int v1, v2, length;
cin >> v1 >> v2 >> length;
g[v1][v2]=g[v2][v1]= length;
}
//Dijkstra
dist[] = ;
for (int i = ; i <= N; i++){
int Min = INIFITY;
int Minp = -;
for (int v = ; v <= N; v++){
if (!collected[v]&&dist[v] < Min){
Min = dist[v];
Minp = v;
}
}
collected[Minp] = ;
for (int u = ; u <= N; u++){
if(!collected[u]&&g[Minp][u]!=INIFITY)
if (dist[Minp] + g[Minp][u] < dist[u]){
dist[u] = dist[Minp] + g[Minp][u];
pre[u].clear();
pre[u].push_back(Minp);
}
else if (dist[u] == dist[Minp] + g[Minp][u])
pre[u].push_back(Minp);
}
}
dfs(D);
cout << minNeed << "";
for (int i = path.size() - ; i >= ; i--)
cout << "->" << path[i];
cout << " " << minBack;
return ;
}
1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)的更多相关文章
- PAT 甲级 1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(dijstra+dfs,dfs记录路径,做了两天)
1018 Public Bike Management (30 分) There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) 思路分析 + 满分代码
题目 There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) PAT甲级真题 dijkstra + dfs
前言: 本题是我在浏览了柳神的代码后,记下的一次半转载式笔记,不经感叹柳神的强大orz,这里给出柳神的题解地址:https://blog.csdn.net/liuchuo/article/detail ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30分) (迪杰斯特拉+dfs)
思路就是dijkstra找出最短路,dfs比较每一个最短路. dijkstra可以找出每个点的前一个点, 所以dfs搜索比较的时候怎么处理携带和带走的数量就是关键,考虑到这个携带和带走和路径顺序有关, ...
- 【PAT甲级】1018 Public Bike Management (30 分)(SPFA,DFS)
题意: 输入四个正整数C,N,S,M(c<=100,n<=500),分别表示每个自行车站的最大容量,车站个数,此次行动的终点站以及接下来的M行输入即通路.接下来输入一行N个正整数表示每个自 ...
- 1018 Public Bike Management (30)(30 分)
时间限制400 ms 内存限制65536 kB 代码长度限制16000 B There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides ...
- 1018. Public Bike Management (30)
时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue There is a public bike service i ...
- PAT Advanced 1018 Public Bike Management (30) [Dijkstra算法 + DFS]
题目 There is a public bike service in Hangzhou City which provides great convenience to the tourists ...
- PAT A 1018. Public Bike Management (30)【最短路径】
https://www.patest.cn/contests/pat-a-practise/1018 先用Dijkstra算出最短路,然后二分答案来验证,顺便求出剩余最小,然后再从终点dfs回去求出路 ...
随机推荐
- 开发RTSP 直播软件 H264 AAC 编码
上一篇对摄像头预览,拍照做了大概的介绍,现在已经可以拿到视频帧了,在加上 RTSP 实现,就是直播的雏形,当然还要加上一些 WEB 管理和手机平台的支援,就是一整套直播软件. 介绍一些基础概念:RTP ...
- 编译putty 源码去掉 Are you sure you want to close this session? 提示
0, 为什么要编译 putty ?在关闭窗口的时候,会弹出一个 Are you sure you want to close this session?要把这个去掉.当然也可以用 OD 之类的来修改. ...
- Redis07——Redis到底能用在什么地方(下)
在前一篇文章中,我们已经介绍过Redis的一些实际应用.如KV缓存.分布式锁.消息队列,由于篇幅原因,并未介绍完全.接下来将继续为各位带来Redis的更多应用. bitmat(位图) 实现 位图的基本 ...
- win10 安装虚拟机提示 主IP地址显示网络信息不可用
问题:在虚拟机详情下面显示 主ip地址:网络信息不可用 解决办法: 先root用户[root@dfhf~]#cd ..[root@dfhf/]#cd /etc/sysconfig/network-sc ...
- TCP/IP协议基本知识
1.TCP/IP协议中主机与主机之间通信的三要素: IP地址(IP address) 子网掩码(subnet mask) IP路由(IP router) 2.IP地址的分类及每一类的范围: A类1-1 ...
- call、apply和bind的学习
相似之处:1.都是用来改变函数的this对象的指向的.2.第一个参数都是this要指向的对象.3.都可以利用后续参数传参. var xw = { name : "小王",gend ...
- 6.前台项目vue环境、创建、目录重构、CSS、JS配置
目录 前台 vue环境 创建项目 重构项目目录 文件修订:目录中非配置文件的多余文件可以移除 App.vue router/index.js Home.vue 全局配置:全局样式.配置文件 globa ...
- .NET 开发工具盘点和现状
在这里我盘点一下.NET的开发工具:Visual Studio.Jetbrains Rider.Mono Develop.SharpDevelop.QuickSharp.Visual Studio C ...
- Map-->HashMap练习(新手)
//导入的包.import java.util.*;//创建的一个类.public class zylx1 { //公共静态的主方法. public static void main(String[] ...
- Java14来了!Switch竟如此简单?Lombok也不需要了?来使用Idea配置Java14的开发环境吧!
Java 14 在 2020.3.17 日发布正式版了,但现在很多公司还在使用 Java 7 或 Java 8,每当看到 Java 又发布新版本心里就慌得一匹.不过此版本并不是 LTS (长期支持版) ...