青岛 2016ICPC 区域现场赛题目
- 1000ms
- 262144K
The Pocket Cube, also known as the Mini Cube or the Ice Cube, is the 2×2×22 \times 2 \times 22×2×2 equivalence of a Rubik’s Cube. The cube consists of 888 pieces, all corners.
Each piece is labeled by a three dimensional coordinate (h,k,l)(h, k, l)(h,k,l) where hhh, kkk, l∈0,1l \in {0, 1}l∈0,1. Each of the six faces owns four small faces filled with a positive integer.
For each step, you can choose a certain face and turn the face ninety degrees clockwise or counterclockwise.
You should judge that if one can restore the pocket cube in one step. We say a pocket cube has been restored if each face owns four same integers.
Input
The first line of input contains one integer N(N≤30)N(N \le 30)N(N≤30) which is the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line describes the top face of the pocket cube, which is the common 2×22 \times 22×2 face of pieceslabelled by (0,0,1)(0, 0, 1)(0,0,1), (0,1,1)(0, 1, 1)(0,1,1), (1,0,1)(1, 0, 1)(1,0,1), (1,1,1)(1, 1, 1)(1,1,1). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The second line describes the front face, the common face of (1,0,1)(1,0,1)(1,0,1), (1,1,1)(1,1,1)(1,1,1), (1,0,0)(1,0,0)(1,0,0), (1,1,0)(1,1,0)(1,1,0). Four integers aregiven corresponding to the above pieces.
The third line describes the bottom face, the common face of (1,0,0)(1, 0, 0)(1,0,0), (1,1,0)(1, 1, 0)(1,1,0), (0,0,0)(0, 0, 0)(0,0,0), (0,1,0)(0, 1, 0)(0,1,0). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The fourth line describes the back face, the common face of (0,0,0)(0,0,0)(0,0,0), (0,1,0)(0,1,0)(0,1,0), (0,0,1)(0,0,1)(0,0,1), (0,1,1)(0,1,1)(0,1,1). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The fifth line describes the left face, the common face of (0,0,0)(0, 0, 0)(0,0,0), (0,0,1)(0, 0, 1)(0,0,1), (1,0,0)(1, 0, 0)(1,0,0), (1,0,1)(1, 0, 1)(1,0,1). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The six line describes the right face, the common face of (0,1,1)(0, 1, 1)(0,1,1), (0,1,0)(0, 1, 0)(0,1,0), (1,1,1)(1, 1, 1)(1,1,1), (1,1,0)(1, 1, 0)(1,1,0). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
In other words, each test case contains 242424 integers aaa, bbb, ccc to xxx. You can flat the surface to get the surface development as follows.
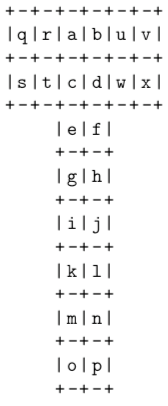
Output
For each test case, output YES if can be restored in one step, otherwise output NO.
样例输入
- 4
- 1 1 1 1
- 2 2 2 2
- 3 3 3 3
- 4 4 4 4
- 5 5 5 5
- 6 6 6 6
- 6 6 6 6
- 1 1 1 1
- 2 2 2 2
- 3 3 3 3
- 5 5 5 5
- 4 4 4 4
- 1 4 1 4
- 2 1 2 1
- 3 2 3 2
- 4 3 4 3
- 5 5 5 5
- 6 6 6 6
- 1 3 1 3
- 2 4 2 4
- 3 1 3 1
- 4 2 4 2
- 5 5 5 5
- 6 6 6 6
样例输出
- YES
- YES
- YES
- NO
- #include<bits/stdc++.h>
- using namespace std;
- int a[][];
- int main()
- {
- int n;
- scanf("%d",&n);
- while(n--)
- {
- for(int i=; i<=; i++)
- {
- for(int j=; j<=; j++)
- {
- scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
- }
- }
- int summ=;
- int sum=;
- for(int i=; i<=; i++)
- {
- if(a[i][]==a[i][] && a[i][]==a[i][] && a[i][]==a[i][])
- {
- summ++;
- }
- }
- if((a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][]) && (a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][]))
- {
- sum=;
- }
- if((a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][]) && (a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][]))
- {
- sum=;
- }
- if((a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][]) && (a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][] && a[][]==a[][]))
- {
- sum=;
- }
- if(summ==)
- {
- printf("YES\n");
- }
- else if(sum==)
- {
- printf("NO\n");
- }
- else if(sum==)
- {
- if(a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][])
- printf("YES\n");
- else if(a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][])
- printf("YES\n");
- else
- printf("NO\n");
- }
- else if(sum==)
- {
- if(a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][])
- printf("YES\n");
- else if(a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][])
- printf("YES\n");
- else
- printf("NO\n");
- }
- else if(sum==)
- {
- if(a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][])
- printf("YES\n");
- else if(a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][]&&
- a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][] &&a[][]==a[][])
- printf("YES\n");
- else
- printf("NO\n");
- }
- else
- {
- printf("NO\n");
- }
- }
- return ;
- }
- 1000ms
- 262144K
Let’s talking about something of eating a pocky. Here is a Decorer Pocky, with colorful decorative stripes in the coating, of length LLL.
While the length of remaining pocky is longer than ddd, we perform the following procedure. We break the pocky at any point on it in an equal possibility and this will divide the remaining pocky into two parts. Take the left part and eat it. When it is not longer than ddd, we do not repeat this procedure.
Now we want to know the expected number of times we should repeat the procedure above. Round it to 666 decimal places behind the decimal point.
Input
The first line of input contains an integer NNN which is the number of test cases. Each of the NNN lines contains two float-numbers LLL and ddd respectively with at most 555 decimal places behind the decimal point where 1≤d,L≤1501 \le d, L \le 1501≤d,L≤150.
Output
For each test case, output the expected number of times rounded to 666 decimal places behind the decimal point in a line.
样例输入
- 6
- 1.0 1.0
- 2.0 1.0
- 4.0 1.0
- 8.0 1.0
- 16.0 1.0
- 7.00 3.00
样例输出
- 0.000000
- 1.693147
- 2.386294
- 3.079442
- 3.772589
- 1.847298
- 思路:微分。
代码:
- #include<bits/stdc++.h>
- using namespace std;
- int n;
- double l,d;
- int main()
- {
- scanf("%d",&n);
- while(n--)
- {
- scanf("%lf%lf",&l,&d);
- if(l<=d)
- {
- printf("0.000000\n");
- }
- else
- {
- printf("%.6f\n",+log(l/d));
- }
- }
- return ;
- }
青岛 2016ICPC 区域现场赛题目的更多相关文章
- HDU 5920 Ugly Problem 高精度减法大模拟 ---2016CCPC长春区域现场赛
题目链接 题意:给定一个很大的数,把他们分为数个回文数的和,分的个数不超过50个,输出个数并输出每个数,special judge. 题解:现场赛的时候很快想出来了思路,把这个数从中间分为两部分,当位 ...
- HDU 4802 && HDU 4803 贪心,高精 && HDU 4804 轮廓线dp && HDU 4805 计算几何 && HDU 4811 (13南京区域赛现场赛 题目重演A,B,C,D,J)
A.GPA(HDU4802): 给你一些字符串对应的权重,求加权平均,如果是N,P不计入统计 GPA Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory ...
- HDU 4811 Ball -2013 ICPC南京区域现场赛
题目链接 题意:三种颜色的球,现给定三种球的数目,每次取其中一个放到桌子上,排成一条线,每次放的位置任意,问得到的最大得分. 把一个球放在末尾得到的分数是它以前球的颜色种数 把一个球放在中间得到的分数 ...
- 2013ACM/ICPC亚洲区南京站现场赛——题目重现
GPA http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4802 签到题,输入两个表,注意细心点就行了. #include<cstdio> #inclu ...
- 2013ACM/ICPC亚洲区南京站现场赛---Poor Warehouse Keeper(贪心)
题目链接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4803 Problem Description Jenny is a warehouse keeper. ...
- 2016 ACM/ICPC亚洲区青岛站现场赛(部分题解)
摘要 本文主要列举并求解了2016 ACM/ICPC亚洲区青岛站现场赛的部分真题,着重介绍了各个题目的解题思路,结合详细的AC代码,意在熟悉青岛赛区的出题策略,以备战2018青岛站现场赛. HDU 5 ...
- 2014ACM/ICPC亚洲区域赛牡丹江现场赛总结
不知道怎样说起-- 感觉还没那个比赛的感觉呢?如今就结束了. 9号.10号的时候学校还评比国奖.励志奖啥的,由于要来比赛,所以那些事情队友的国奖不能答辩.自己的励志奖班里乱搞要投票,自己又不在,真是无 ...
- 2014ACMICPC亚洲区域赛牡丹江现场赛之旅
下午就要坐卧铺赶回北京了.闲来无事.写个总结,给以后的自己看. 因为孔神要保研面试,所以仅仅有我们队里三个人上路. 我们是周五坐的十二点出发的卧铺,一路上不算无聊.恰巧邻床是北航的神犇.于是下午和北航 ...
- 2018ICPC青岛现场赛 重现训练
先贴代码,以及简要题解. 和一个队友下午双排打了一下,队友光速签到,我签的J被嫌弃写得慢以及演员...然后我秒出了E了思路然而难以置信这么简单的思路当时才过了十几个,于是发现D.F不是太好做.最后交了 ...
随机推荐
- 解决在 win10 下 vs2017 中创建 MFC 程序拖放文件接收不到 WM_DROPFILES 消息问题
解决方案 这个问题是由于 win10 的安全机制搞的鬼,即使以管理员权限运行也不行,因为它会把 WM_DROPFILES 消息过滤掉,那怎么办呢?只需在窗口初始化 OnInitDialog() 里添加 ...
- Spark RDD理解
目录 ----RDD简介 ----RDD操作类别 ----RDD分区 ----宽依赖和窄依赖作用 ----RDD分区划分器 ----RDD到调度 返回顶部 RDD简介 RDD是弹性分布式数据集(Res ...
- 树莓派GPIO控制LED彩灯
树莓派使用GPIO接口来控制LED灯,自制五彩炫光的节日彩灯. 1.硬件准备 a. 树莓派(Raspberry Pi)一个 b. 彩色RGB二极管 c. 杜邦线 d. 5V电源引脚 以上所有零件均可在 ...
- 经典傅里叶算法小集合 附完整c代码
前面写过关于傅里叶算法的应用例子. <基于傅里叶变换的音频重采样算法 (附完整c代码)> 当然也就是举个例子,主要是学习傅里叶变换. 这个重采样思路还有点瑕疵, 稍微改一下,就可以支持多通 ...
- NodeJs实现简单的爬虫
1.爬虫:爬虫,是一种按照一定的规则,自动地抓取网页信息的程序或者脚本:利用NodeJS实现一个简单的爬虫案例,爬取Boss直聘网站的web前端相关的招聘信息,以广州地区为例: 2.脚本所用到的nod ...
- Hadoop安装配置
1.集群部署介绍 1.1 Hadoop简介 Hadoop是Apache软件基金会旗下的一个开源分布式计算平台.以Hadoop分布式文件系统(HDFS,Hadoop Distributed Filesy ...
- 20155212 实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践
20155212 实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 实验要求 没有Linux基础的同学建议先学习<Linux基础入门(新版)><Vim编辑器&g ...
- 20155235 2006-2007-2 《Java程序设计》第1周学习总结
20155235 2006-2007-2 <Java程序设计>第1周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第二章 使用的JRE不同,对JAVA的执行有什么影响 第三章 字符串的用法在JAVA和C中有 ...
- 20155305 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》实验二 Java面向对象程序设计
实验二 Java面向对象程序设计 实验内容 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装.继承.多态 初步掌握UML建模 熟悉S.O.L.I.D原则 了解设计模式 实验步骤 单元测试 1. ...
- 20155306 实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践
20155306 实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 实验要求 1.没有Linux基础的同学建议先学习<Linux基础入门(新版)><Vim编辑器 ...
